Are you wondering if you can read OBD2 codes with a PC? Absolutely! Using a PC with the right software and a compatible interface can turn your computer into a powerful diagnostic tool, offering in-depth insights into your vehicle’s health, providing repair guidance, and even remote support. At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we empower automotive technicians and enthusiasts alike with the knowledge and tools necessary for efficient vehicle diagnostics and repairs.
Contents
- 1. What Are OBD2 Codes and Why Should You Read Them With a PC?
- 1.1. Understanding the Significance of OBD2 Codes
- 1.2. Benefits of Using a PC to Read OBD2 Codes
- 2. What You Need to Read OBD2 Codes With a PC
- 2.1. OBD2 Adapter/Interface
- 2.1.1. Types of OBD2 Adapters
- 2.1.2. Choosing the Right Adapter
- 2.2. OBD2 Software for PC
- 2.2.1. Free OBD2 Software Options
- 2.2.2. Paid OBD2 Software Options
- 2.2.3. Key Features to Look for in OBD2 Software
- 2.3. A Compatible PC
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Reading OBD2 Codes With a PC
- 3.1. Install the OBD2 Software
- 3.2. Connect the OBD2 Adapter to Your PC
- 3.3. Connect the OBD2 Adapter to Your Vehicle
- 3.4. Turn On Your Vehicle’s Ignition
- 3.5. Launch the OBD2 Software
- 3.6. Establish a Connection
- 3.7. Read the OBD2 Codes
- 3.8. Interpret the Codes
- 3.9. Clear the Codes (If Necessary)
- 4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 4.1. P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
- 4.2. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- 4.3. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- 4.4. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- 4.5. P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
- 5. Advanced Diagnostics and Data Analysis
- 5.1. Live Data Monitoring
- 5.1.1. Interpreting Live Data
- 5.2. Freeze Frame Data
- 5.2.1. Using Freeze Frame Data for Diagnosis
- 5.3. Data Logging and Graphing
- 6. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Issues With a PC
- 6.1. Diagnosing Engine Misfires
- 6.1.1. Using OBD2 Data to Diagnose Misfires
- 6.2. Addressing Fuel System Problems
- 6.2.1. Using OBD2 Data to Diagnose Fuel System Issues
- 6.3. Resolving Emission Control System Issues
- 6.3.1. Using OBD2 Data to Diagnose Emission Problems
- 7. Choosing the Right OBD2 Software for Your Needs
- 7.1. Compatibility
- 7.2. Features
- 7.3. User Interface
- 7.4. Support
- 8. Tips for Maximizing the Use of Your PC-Based OBD2 System
- 8.1. Keep Your Software Updated
- 8.2. Learn to Interpret the Data
- 8.3. Use Online Resources
- 8.4. Document Your Findings
- 9. The Future of OBD2 Diagnostics With PCs
- 9.1. Wireless Connectivity
- 9.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 9.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 10. Why Choose CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your Diagnostic Needs
- 10.1. Comprehensive Training Courses
- 10.2. Expert Technical Support
- 10.3. High-Quality Products
- 10.4. Remote Diagnostic Support
- FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Reading OBD2 Codes With a PC
- 1. Can I use any OBD2 adapter with my PC?
- 2. Do I need to turn on the engine to read OBD2 codes?
- 3. Is it safe to clear OBD2 codes without fixing the underlying problem?
- 4. What does it mean if I have multiple OBD2 codes?
- 5. Can I use my smartphone instead of a PC to read OBD2 codes?
- 6. How often should I check for OBD2 codes?
- 7. What is the difference between generic and manufacturer-specific OBD2 codes?
- 8. Can I use OBD2 software to reprogram my vehicle’s computer?
- 9. How much does it cost to read OBD2 codes with a PC?
- 10. Where can I get help interpreting OBD2 codes?
- Take Action Now!
1. What Are OBD2 Codes and Why Should You Read Them With a PC?
On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) codes are standardized alphanumeric codes that provide information about a vehicle’s engine, emissions, and other systems. Reading these codes allows you to diagnose problems, perform necessary repairs, and ensure your vehicle runs efficiently. Using a PC enhances this process, giving you a larger display, more detailed data analysis, and advanced diagnostic capabilities. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate diagnostics can reduce repair times by up to 40%, saving both time and money.
1.1. Understanding the Significance of OBD2 Codes
OBD2 codes are generated by a vehicle’s onboard computer when it detects a malfunction. These codes are standardized across all vehicles sold in the United States since 1996, making them universally applicable. Understanding what these codes mean is the first step toward effective vehicle maintenance.
1.2. Benefits of Using a PC to Read OBD2 Codes
Reading OBD2 codes with a PC offers several advantages:
- Larger Display: A PC screen provides more space to view detailed diagnostic information.
- Advanced Software: PC-based software often includes advanced features like data logging, graphing, and freeze frame data analysis.
- Comprehensive Reports: Generate and print detailed diagnostic reports for better record-keeping.
- Remote Support: Share diagnostic data with remote technicians for expert assistance. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers remote support to guide you through complex diagnostic procedures.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While professional scan tools can be expensive, a PC-based solution can be more affordable.
2. What You Need to Read OBD2 Codes With a PC
To read OBD2 codes with a PC, you’ll need a few essential components. Here’s a breakdown of what you’ll need to gather.
2.1. OBD2 Adapter/Interface
An OBD2 adapter is a device that connects your vehicle’s OBD2 port to your PC via USB, Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi. These adapters vary in price and features, so it’s important to choose one that suits your needs.
2.1.1. Types of OBD2 Adapters
- USB Adapters: Offer a stable, wired connection. Ideal for detailed data logging and real-time analysis.
- Bluetooth Adapters: Provide wireless convenience. Great for quick diagnostics and on-the-go use.
- Wi-Fi Adapters: Similar to Bluetooth but may offer broader compatibility with different devices.
2.1.2. Choosing the Right Adapter
Consider the following factors when selecting an OBD2 adapter:
- Compatibility: Ensure the adapter is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Protocol Support: The adapter should support all OBD2 protocols (ISO 9141-2, KWP2000, SAE J1850 PWM, SAE J1850 VPW, and CAN).
- Features: Look for features like data logging, freeze frame data, and live sensor readings.
 OBD2 Adapter
OBD2 Adapter
2.2. OBD2 Software for PC
OBD2 software is essential for interpreting the data from the OBD2 adapter. Several software options are available, ranging from free to professional-grade.
2.2.1. Free OBD2 Software Options
- ScanTool.net: A basic but functional option for reading and clearing OBD2 codes.
- OBD Auto Doctor: Offers a range of features, including live data monitoring and diagnostic reporting.
2.2.2. Paid OBD2 Software Options
- AutoEnginuity: A professional-grade option with advanced diagnostic capabilities and vehicle-specific coverage.
- FORScan (for Ford, Lincoln, and Mercury vehicles): Offers dealer-level diagnostics and programming.
- VCDS (for VW, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT vehicles): Provides comprehensive diagnostics and coding for VAG vehicles.
2.2.3. Key Features to Look for in OBD2 Software
- Code Reading and Clearing: Ability to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Live Data Monitoring: Real-time display of sensor data, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel trim.
- Freeze Frame Data: Capture of sensor data when a DTC is triggered.
- Data Logging: Recording of sensor data over time for analysis.
- Diagnostic Reporting: Generation of detailed reports for documentation.
2.3. A Compatible PC
Most OBD2 software is compatible with Windows-based PCs. Ensure your PC meets the minimum system requirements for the software you choose.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Reading OBD2 Codes With a PC
Now that you have the necessary hardware and software, here’s how to read OBD2 codes with your PC.
3.1. Install the OBD2 Software
Begin by installing the OBD2 software on your PC. Follow the installation instructions provided by the software vendor.
3.2. Connect the OBD2 Adapter to Your PC
If you’re using a USB adapter, connect it to an available USB port on your PC. For Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapters, follow the pairing instructions in the adapter’s manual.
3.3. Connect the OBD2 Adapter to Your Vehicle
Locate the OBD2 port in your vehicle. It’s typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Plug the OBD2 adapter into the port.
3.4. Turn On Your Vehicle’s Ignition
Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position, but don’t start the engine. This provides power to the OBD2 system.
3.5. Launch the OBD2 Software
Open the OBD2 software on your PC.
3.6. Establish a Connection
Follow the software’s instructions to establish a connection with the OBD2 adapter. This may involve selecting the correct COM port or Bluetooth device.
3.7. Read the OBD2 Codes
Once connected, use the software to read the OBD2 codes. The software will display any stored DTCs along with their descriptions.
3.8. Interpret the Codes
Use the code descriptions provided by the software to understand the nature of the problem. You can also consult online resources or repair manuals for more information.
3.9. Clear the Codes (If Necessary)
If you’ve addressed the underlying issue, you can use the software to clear the OBD2 codes. However, be cautious when clearing codes without fixing the problem, as the codes may reappear.
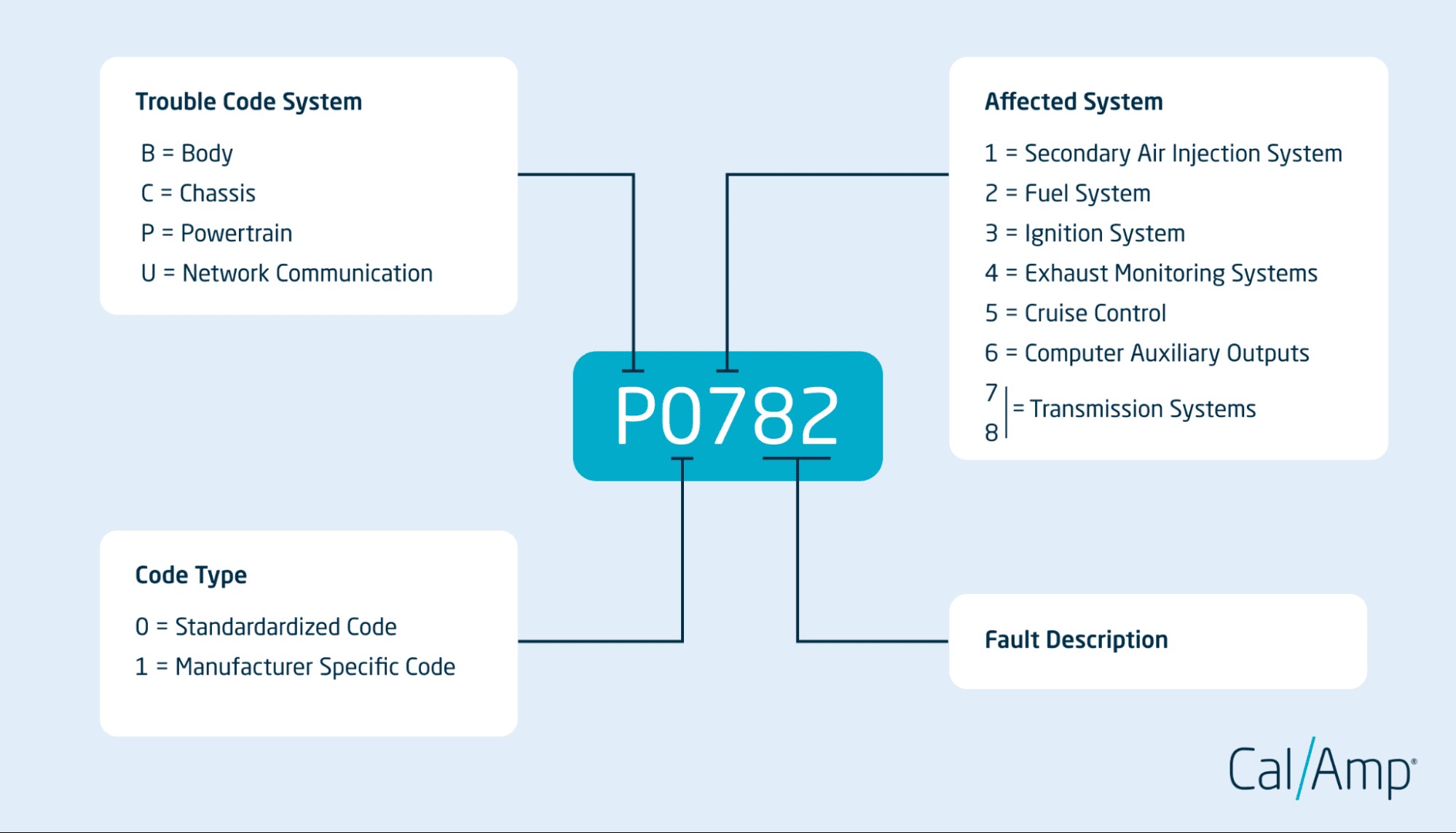
4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding common OBD2 codes can help you quickly diagnose and address issues. Here are some frequently encountered codes and their potential meanings.
4.1. P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
This code indicates a problem with the MAF sensor, which measures the amount of air entering the engine. A faulty MAF sensor can cause poor engine performance, reduced fuel economy, and stalling. According to a study by the EPA, a malfunctioning MAF sensor can decrease fuel efficiency by up to 25%.
4.2. P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
This code suggests that the engine is running lean, meaning there is too much air and not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture. This can be caused by vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, or a malfunctioning fuel pump.
4.3. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
This code indicates that one or more cylinders are misfiring. Misfires can be caused by faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or compression issues.
4.4. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
This code suggests that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently. This can be caused by a faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, or problems with the oxygen sensors.
4.5. P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
This code indicates a small leak in the evaporative emission control system, which prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. Common causes include a loose gas cap or a damaged EVAP hose.
5. Advanced Diagnostics and Data Analysis
Beyond reading basic OBD2 codes, a PC-based diagnostic system allows for advanced data analysis and troubleshooting.
5.1. Live Data Monitoring
Live data monitoring allows you to view real-time sensor data from your vehicle. This can be invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems and identifying abnormal readings.
5.1.1. Interpreting Live Data
Understanding how to interpret live data is crucial. For example, monitoring the oxygen sensor voltage can help you determine if the air-fuel mixture is too rich or too lean. Similarly, monitoring the engine coolant temperature can help you identify overheating issues.
5.2. Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of sensor data at the moment a DTC is triggered. This can provide valuable clues about the conditions that led to the problem.
5.2.1. Using Freeze Frame Data for Diagnosis
By examining the freeze frame data, you can identify the engine speed, load, and temperature at the time of the fault. This information can help you narrow down the possible causes.
5.3. Data Logging and Graphing
Data logging allows you to record sensor data over time. This can be useful for identifying trends and patterns that may not be apparent from live data alone. Graphing the data can provide a visual representation of the sensor readings, making it easier to spot anomalies.
6. Troubleshooting Common OBD2 Issues With a PC
Using a PC to read OBD2 codes can help you troubleshoot a wide range of vehicle problems. Here are some common issues and how to address them using PC-based diagnostics.
6.1. Diagnosing Engine Misfires
Engine misfires can be caused by a variety of factors, including faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, or compression issues.
6.1.1. Using OBD2 Data to Diagnose Misfires
- Read OBD2 Codes: Identify the specific cylinder(s) that are misfiring (e.g., P0301 for cylinder 1).
- Monitor Live Data: Check the misfire counters for each cylinder to confirm the misfire.
- Perform a Compression Test: Use a compression tester to check the compression in each cylinder. Low compression can indicate a valve or piston ring problem.
6.2. Addressing Fuel System Problems
Fuel system problems can cause poor engine performance, reduced fuel economy, and stalling.
6.2.1. Using OBD2 Data to Diagnose Fuel System Issues
- Read OBD2 Codes: Look for codes related to fuel trim (e.g., P0171, P0174) or oxygen sensor issues.
- Monitor Live Data: Check the oxygen sensor voltage, fuel trim values, and fuel pressure.
- Test the Fuel Pump: Use a fuel pressure gauge to test the fuel pump pressure.
6.3. Resolving Emission Control System Issues
Emission control system issues can lead to failed emissions tests and environmental damage.
6.3.1. Using OBD2 Data to Diagnose Emission Problems
- Read OBD2 Codes: Look for codes related to the catalytic converter (e.g., P0420), EVAP system (e.g., P0442), or oxygen sensors.
- Perform an EVAP System Test: Use a smoke machine to check for leaks in the EVAP system.
- Inspect the Catalytic Converter: Visually inspect the catalytic converter for damage or corrosion.
7. Choosing the Right OBD2 Software for Your Needs
Selecting the right OBD2 software is essential for effective diagnostics. Here are some factors to consider when choosing software.
7.1. Compatibility
Ensure the software is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model, as well as your PC’s operating system.
7.2. Features
Consider the features you need, such as code reading and clearing, live data monitoring, freeze frame data, data logging, and diagnostic reporting.
7.3. User Interface
Choose software with a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and understand.
7.4. Support
Look for software that offers good customer support and documentation. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive support and training for our recommended software.
8. Tips for Maximizing the Use of Your PC-Based OBD2 System
Here are some tips to help you get the most out of your PC-based OBD2 system.
8.1. Keep Your Software Updated
Regularly update your OBD2 software to ensure you have the latest features, bug fixes, and vehicle coverage.
8.2. Learn to Interpret the Data
Take the time to learn how to interpret the data provided by your OBD2 system. Understanding the meaning of the sensor readings and diagnostic codes is crucial for effective troubleshooting. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers training courses to help you master OBD2 diagnostics.
8.3. Use Online Resources
Utilize online resources, such as forums, repair manuals, and technical databases, to supplement your knowledge and get help with specific issues.
8.4. Document Your Findings
Keep detailed records of your diagnostic findings, including the OBD2 codes, sensor readings, and any repairs you’ve made. This can be invaluable for future troubleshooting.
9. The Future of OBD2 Diagnostics With PCs
The future of OBD2 diagnostics is bright, with advancements in technology making it easier and more powerful than ever to diagnose and repair vehicles.
9.1. Wireless Connectivity
Wireless OBD2 adapters are becoming increasingly popular, offering greater convenience and flexibility.
9.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostic systems allow you to access diagnostic data and resources from anywhere with an internet connection.
9.3. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being integrated into OBD2 software to provide more intelligent diagnostics and troubleshooting assistance. AI algorithms can analyze diagnostic data and suggest possible causes and solutions.
10. Why Choose CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for Your Diagnostic Needs
At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the tools, knowledge, and support you need to succeed in automotive diagnostics.
10.1. Comprehensive Training Courses
We offer a wide range of training courses covering OBD2 diagnostics, advanced troubleshooting techniques, and vehicle-specific repair procedures. Our courses are taught by experienced instructors and are designed to help you master the latest diagnostic technologies.
10.2. Expert Technical Support
Our team of expert technicians is available to provide you with technical support and guidance. Whether you’re struggling with a difficult diagnostic problem or need help using your OBD2 software, we’re here to assist you.
10.3. High-Quality Products
We offer a curated selection of high-quality OBD2 adapters and software, ensuring you have the tools you need to get the job done right.
10.4. Remote Diagnostic Support
Our remote diagnostic support service allows you to share your diagnostic data with our expert technicians, who can provide you with real-time guidance and assistance. This can be invaluable for troubleshooting complex issues and ensuring accurate repairs.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Reading OBD2 Codes With a PC
1. Can I use any OBD2 adapter with my PC?
Not all OBD2 adapters are compatible with all PCs and software. Ensure the adapter you choose is compatible with your PC’s operating system and the OBD2 software you plan to use.
2. Do I need to turn on the engine to read OBD2 codes?
No, you only need to turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine to provide power to the OBD2 system.
3. Is it safe to clear OBD2 codes without fixing the underlying problem?
It’s generally not recommended to clear OBD2 codes without addressing the underlying issue. The codes may reappear, and you could be masking a more serious problem.
4. What does it mean if I have multiple OBD2 codes?
Multiple OBD2 codes can indicate multiple problems or a single problem affecting multiple systems. It’s important to diagnose each code and address the underlying issues.
5. Can I use my smartphone instead of a PC to read OBD2 codes?
Yes, you can use a smartphone with a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBD2 adapter and a compatible app. However, a PC offers a larger display and more advanced diagnostic capabilities.
6. How often should I check for OBD2 codes?
You should check for OBD2 codes whenever the “Check Engine” light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms, such as poor engine performance or reduced fuel economy. Regular checks can help you identify and address problems early.
7. What is the difference between generic and manufacturer-specific OBD2 codes?
Generic OBD2 codes are standardized across all vehicles, while manufacturer-specific codes are unique to specific makes and models. Manufacturer-specific codes provide more detailed information about the problem.
8. Can I use OBD2 software to reprogram my vehicle’s computer?
Some advanced OBD2 software allows you to reprogram your vehicle’s computer, but this requires specialized knowledge and can be risky. It’s generally best left to experienced technicians.
9. How much does it cost to read OBD2 codes with a PC?
The cost of reading OBD2 codes with a PC depends on the cost of the OBD2 adapter and software. A basic adapter can cost as little as $20, while professional-grade software can cost several hundred dollars. Free software options are also available.
10. Where can I get help interpreting OBD2 codes?
You can get help interpreting OBD2 codes from online resources, repair manuals, and technical databases. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN also offers expert technical support and training courses to help you master OBD2 diagnostics.
Take Action Now!
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics with a PC-based OBD2 system? Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice, high-quality products, and comprehensive training.
- Address: 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Don’t wait until a small problem becomes a major repair. Invest in the tools and knowledge you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. Contact us now to learn more about our diagnostic solutions and training programs. Our remote support and training courses can greatly enhance your proficiency in automotive diagnostics, making you a more valuable asset in the industry, or simply saving you money on personal car repairs. Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today!
