Are you curious about the number of electronic control units in your car and their vital roles? Understanding the intricacies of your vehicle’s electronic systems is crucial for modern car owners and technicians. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive insights into automotive diagnostics, repair guidance, and expert technical support. Let’s explore the world of ECUs, enhance your diagnostic skills, and ensure your vehicle runs smoothly. Our platform also offers specialized technician training programs and remote support to keep you at the forefront of automotive technology.
Contents
- 1. What is an ECU in a Car and How Many are There?
- Why Do Cars Need So Many ECUs?
- Key Types of ECUs in Modern Vehicles
- 2. How Does an ECU Work? A Deep Dive
- The ECU Control Loop
- Communication Networks
- Real-World Examples
- 3. Common Signs of ECU Failure
- Diagnostic Tools for Identifying ECU Issues
- Case Studies
- 4. Causes and Effects of ECU Malfunctions
- Effects of ECU Failure
- Preventative Measures
- 5. Troubleshooting and Replacing ECUs
- Tools and Equipment Needed
- Best Practices
- 6. How Many ECUs: Impact on Vehicle Diagnostics
- Challenges
- Opportunities
- Training and Resources
- 7. The Future of ECU Technology
- Key Trends
- Implications for Technicians
- Preparing for the Future
- 8. ECU Reprogramming and Software Updates
- What is ECU Reprogramming?
- How is it Done?
- Risks and Considerations
- Best Practices
- 9. ECU Security: Protecting Against Cyber Threats
- Common Threats
- Security Measures
- Best Practices
- 10. FAQs About ECUs in Cars
1. What is an ECU in a Car and How Many are There?
An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is essentially a miniature computer that manages various electronic systems within your vehicle. While a single Engine Control Unit (ECU) might control the engine, a modern car often contains numerous ECUs. These manage everything from engine performance and transmission to anti-lock brakes, airbags, and infotainment systems. The number of ECUs in a car can vary significantly, typically ranging from 30 to 100, depending on the vehicle’s complexity and features.
The presence of multiple ECUs reflects the increasing sophistication of modern vehicles. These ECUs communicate with each other via networks like the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus, enabling coordinated control of various functions. According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) in 2023, the average number of ECUs in vehicles has been increasing by approximately 5% annually, driven by advancements in safety, driver assistance, and connectivity features.
 ECU diagram showing various vehicle systems connected
ECU diagram showing various vehicle systems connected
Why Do Cars Need So Many ECUs?
Modern vehicles are equipped with an array of advanced features that require precise electronic control. Each ECU is dedicated to managing specific functions, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Here’s a breakdown of the key reasons for the proliferation of ECUs:
- Complexity of Modern Systems: Modern cars have become increasingly complex with features like advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), sophisticated infotainment setups, and intricate engine management systems.
- Enhanced Safety Features: ECUs are critical for managing safety systems such as airbags, anti-lock brakes (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and adaptive cruise control.
- Improved Performance and Efficiency: ECUs optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions by continuously monitoring and adjusting various parameters.
- Comfort and Convenience: Features like automatic climate control, power windows, and advanced audio systems are all managed by dedicated ECUs.
Key Types of ECUs in Modern Vehicles
To understand the breadth of ECU functions, it’s helpful to know some of the common types found in modern cars:
| ECU Type | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Control Unit (ECU) | Engine Management | Controls fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions to optimize engine performance and efficiency. |
| Transmission Control Unit (TCU) | Transmission Management | Manages gear shifting and transmission performance for smooth and efficient operation. |
| Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) Control Unit | Braking System | Prevents wheel lockup during braking, enhancing stability and control. |
| Airbag Control Unit (ACU) | Safety System | Deploys airbags in the event of a collision, protecting occupants. |
| Body Control Module (BCM) | Body Electronics | Manages various body functions such as lighting, power windows, and door locks. |
| Infotainment Control Unit | Entertainment and Information | Controls the vehicle’s audio system, navigation, and connectivity features. |
| Power Steering Control Unit | Steering System | Provides power assistance for steering, enhancing maneuverability and driver comfort. |
| Climate Control Unit | Climate Management | Regulates the vehicle’s heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system. |
By understanding the roles of these different ECUs, technicians can more effectively diagnose and repair electronic issues in modern vehicles. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers in-depth training and resources to help technicians master ECU diagnostics and repair.
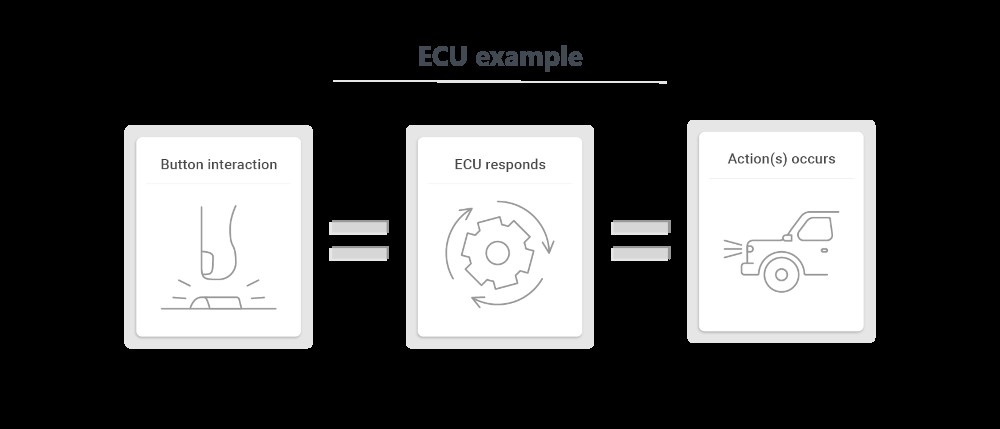
2. How Does an ECU Work? A Deep Dive
ECUs operate by receiving data from sensors, processing that data using pre-programmed algorithms, and then controlling actuators to make adjustments. This closed-loop control system ensures optimal performance and efficiency.
The ECU Control Loop
The ECU control loop involves three main stages:
- Data Acquisition: Sensors throughout the vehicle collect data on various parameters such as engine temperature, air pressure, throttle position, and oxygen levels.
- Data Processing: The ECU processes the sensor data using sophisticated algorithms and lookup tables to determine the appropriate course of action.
- Actuator Control: Based on the processed data, the ECU sends signals to actuators, which are devices that perform physical actions. Examples include fuel injectors, ignition coils, and throttle motors.
For example, consider the process of adjusting fuel injection. When the driver presses the accelerator pedal, the throttle position sensor sends a signal to the ECU. The ECU then calculates the required amount of fuel based on engine speed, air intake, and other factors. Finally, the ECU sends a signal to the fuel injectors to deliver the precise amount of fuel into the engine cylinders.
Communication Networks
ECUs communicate with each other and with diagnostic tools via communication networks such as the CAN bus. The CAN bus allows ECUs to share data and coordinate their actions, enabling advanced features like traction control and stability control.
 CAN bus diagram illustrating ECU communication
CAN bus diagram illustrating ECU communication
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has developed several standards for automotive communication networks, including the CAN bus and the newer CAN FD (Flexible Data-Rate) standard. According to SAE research, CAN FD offers significantly higher data rates than traditional CAN, enabling faster and more reliable communication between ECUs.
Real-World Examples
- Engine Management: The ECU monitors engine temperature, air intake, and exhaust composition to optimize fuel injection and ignition timing.
- Transmission Control: The TCU uses data from wheel speed sensors and throttle position to determine the optimal gear for current driving conditions.
- Anti-lock Braking: The ABS control unit monitors wheel speed during braking and modulates brake pressure to prevent wheel lockup.
- Airbag Deployment: The ACU uses data from crash sensors to determine the severity of a collision and deploy airbags accordingly.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training programs that cover ECU operation, communication protocols, and diagnostic techniques.
3. Common Signs of ECU Failure
Recognizing the signs of a failing ECU can prevent significant damage. Here are several indicators that an ECU may be malfunctioning:
- Check Engine Light: One of the most common signs is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard. While this light can indicate various issues, it often signals an ECU problem.
- Engine Performance Issues: Problems such as stalling, misfiring, rough idling, and decreased power can indicate ECU failure.
- Starting Problems: Difficulty starting the vehicle or a complete no-start condition can be due to a faulty ECU.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A sudden drop in fuel efficiency can be a sign that the ECU is not properly managing fuel injection and combustion.
- Transmission Problems: Erratic shifting, delayed engagement, or a complete failure to shift can be caused by a malfunctioning transmission control unit (TCU).
- ABS or Airbag Warning Lights: Illumination of the ABS or airbag warning lights can indicate problems with the corresponding control units.
Diagnostic Tools for Identifying ECU Issues
Several diagnostic tools can help identify ECU problems:
- OBD-II Scanners: These tools can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU, providing valuable information about the nature of the problem.
- Multimeters: Multimeters can be used to test the voltage and continuity of ECU circuits, helping to identify electrical faults.
- Oscilloscopes: Oscilloscopes can display waveforms of ECU signals, allowing technicians to analyze the timing and amplitude of electronic signals.
- Specialized Diagnostic Software: Software packages like those offered by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provide advanced diagnostic capabilities, including ECU reprogramming and data analysis.
Case Studies
- Case 1: A vehicle experiences intermittent stalling and a check engine light. An OBD-II scan reveals a code indicating a faulty crankshaft position sensor. After replacing the sensor, the problem persists, suggesting an issue with the ECU’s ability to process sensor data.
- Case 2: A car exhibits poor fuel economy and rough idling. Diagnostic tests reveal that the ECU is not properly adjusting the air-fuel mixture. Further investigation reveals corrosion on the ECU connectors, leading to intermittent signal loss.
4. Causes and Effects of ECU Malfunctions
Understanding the causes and effects of ECU malfunctions is crucial for effective diagnosis and repair. Several factors can lead to ECU failure:
- Electrical Issues: Power surges, short circuits, and voltage spikes can damage the ECU’s internal components.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to extreme temperatures, humidity, and vibration can degrade the ECU over time.
- Water Damage: Water intrusion can corrode the ECU’s circuits and connectors, leading to malfunction.
- Physical Damage: Impact damage from accidents or improper handling can damage the ECU’s internal components.
- Software Corruption: Faulty software updates or corrupted data can cause the ECU to malfunction.
Effects of ECU Failure
The effects of ECU failure can range from minor inconveniences to major safety hazards:
- Reduced Performance: Engine misfires, stalling, and decreased power can significantly impact vehicle performance.
- Safety Issues: Malfunctioning ABS, airbags, or stability control systems can compromise vehicle safety.
- Increased Emissions: Improper engine management can lead to increased emissions and failure to pass emissions tests.
- Vehicle Inoperability: In severe cases, ECU failure can render the vehicle completely inoperable.
Preventative Measures
Taking preventative measures can help extend the life of your ECU:
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure that your vehicle’s electrical systems are regularly inspected and maintained.
- Protect from Moisture: Keep the ECU dry and protected from water intrusion.
- Avoid Power Surges: Use surge protectors when jump-starting your vehicle or connecting diagnostic equipment.
- Proper Installation: Ensure that the ECU is properly installed and secured to prevent vibration damage.
5. Troubleshooting and Replacing ECUs
Troubleshooting and replacing ECUs requires a systematic approach. Here are the key steps involved:
- Gather Information: Collect information about the vehicle’s symptoms, diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and any recent repairs or modifications.
- Perform Visual Inspection: Inspect the ECU and its connectors for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Test ECU Power and Ground: Use a multimeter to verify that the ECU is receiving proper power and ground.
- Check ECU Inputs and Outputs: Use an oscilloscope or scan tool to monitor the ECU’s inputs and outputs, ensuring that they are within specifications.
- Perform ECU Replacement: If the ECU is determined to be faulty, replace it with a new or remanufactured unit.
- Program or Flash the ECU: In many cases, the new ECU will need to be programmed or flashed with the vehicle’s specific software.
- Verify Operation: After replacing and programming the ECU, verify that all systems are functioning properly.
Tools and Equipment Needed
- OBD-II Scanner: To read and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- Multimeter: To test ECU power, ground, and circuit continuity.
- Oscilloscope: To analyze ECU signals and waveforms.
- ECU Programming Tool: To program or flash new ECUs.
- Wiring Diagrams: To trace ECU circuits and identify wiring problems.
Best Practices
- Follow OEM Procedures: Always follow the vehicle manufacturer’s recommended procedures for ECU troubleshooting and replacement.
- Use Quality Parts: Use only high-quality replacement ECUs and connectors.
- Ensure Proper Grounding: Ensure that the ECU is properly grounded to prevent electrical problems.
- Document All Work: Document all troubleshooting steps, test results, and repairs performed.
6. How Many ECUs: Impact on Vehicle Diagnostics
The increasing number of ECUs in modern vehicles has significantly impacted vehicle diagnostics. Technicians now need a deeper understanding of electronic systems and advanced diagnostic tools to effectively troubleshoot and repair vehicles.
Challenges
- Complexity: Diagnosing problems in a vehicle with dozens of interconnected ECUs can be challenging.
- Data Overload: Analyzing the vast amount of data generated by modern vehicle systems can be overwhelming.
- Training Requirements: Technicians need specialized training to effectively diagnose and repair electronic systems.
- Tool Investment: Advanced diagnostic tools and software can be expensive.
Opportunities
- Improved Accuracy: Advanced diagnostic tools can provide more accurate and detailed information about vehicle problems.
- Faster Repairs: By quickly identifying the root cause of a problem, technicians can perform repairs more efficiently.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Accurate and efficient repairs lead to greater customer satisfaction.
- New Revenue Streams: Specializing in electronic diagnostics can create new revenue streams for repair shops.
Training and Resources
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of training programs and resources to help technicians stay up-to-date with the latest automotive technologies. Our courses cover topics such as:
- ECU Operation and Diagnostics
- CAN Bus Communication
- OBD-II Diagnostics
- ECU Programming and Flashing
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
7. The Future of ECU Technology
The future of ECU technology is rapidly evolving, driven by trends such as autonomous driving, electric vehicles, and connected car services.
Key Trends
- Domain Controllers: Consolidating multiple ECUs into a single, more powerful domain controller.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Updating ECU software wirelessly to improve performance and add new features.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using AI to analyze sensor data and optimize vehicle performance in real-time.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting ECUs from cyberattacks and unauthorized access.
- Integration with Cloud Services: Connecting ECUs to cloud-based services for data analytics and remote diagnostics.
Implications for Technicians
These trends will have significant implications for automotive technicians:
- Increased Specialization: Technicians will need to specialize in specific areas such as electric vehicle technology or ADAS.
- Continuous Learning: Technicians will need to continuously update their skills and knowledge to keep pace with evolving technology.
- Data Analysis Skills: Technicians will need to be able to analyze data from vehicle systems to diagnose problems.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Technicians will need to be aware of cybersecurity threats and how to protect vehicle systems.
Preparing for the Future
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to helping technicians prepare for the future of ECU technology. Our training programs and resources are designed to provide technicians with the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in the rapidly changing automotive industry.
8. ECU Reprogramming and Software Updates
ECU reprogramming and software updates are essential for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and addressing software-related issues. Here’s a closer look at what these processes involve:
What is ECU Reprogramming?
ECU reprogramming, also known as flashing or remapping, involves overwriting the existing software in an ECU with a new version. This can be done to:
- Improve Performance: Optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, or transmission shifting.
- Fix Software Bugs: Correct known software defects or glitches.
- Add New Features: Enable new features or capabilities.
- Address Emissions Issues: Comply with updated emissions regulations.
How is it Done?
ECU reprogramming is typically done using a specialized tool that connects to the vehicle’s OBD-II port. The tool downloads the new software from the vehicle manufacturer’s website or a third-party provider and uploads it to the ECU.
Risks and Considerations
- Incorrect Software: Using the wrong software version can damage the ECU or cause vehicle malfunctions.
- Interrupted Programming: Interrupting the programming process can corrupt the ECU’s software.
- Warranty Issues: Reprogramming the ECU may void the vehicle’s warranty.
Best Practices
- Use OEM Software: Always use software provided by the vehicle manufacturer or a reputable third-party provider.
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Follow the programming tool’s instructions carefully.
- Ensure Stable Power: Ensure that the vehicle has a stable power supply during the programming process.
- Verify Compatibility: Verify that the software is compatible with the vehicle’s ECU and other systems.
9. ECU Security: Protecting Against Cyber Threats
As vehicles become more connected and reliant on electronic systems, ECU security is becoming increasingly important. Here’s what you need to know about ECU security and how to protect against cyber threats:
Common Threats
- Malware: Malicious software that can infect ECUs and disrupt vehicle operation.
- Hacking: Unauthorized access to ECUs that can allow attackers to control vehicle systems.
- Data Theft: Stealing sensitive data from vehicle systems, such as personal information or vehicle location.
Security Measures
- Firewalls: Protecting ECUs from unauthorized access.
- Encryption: Encrypting data to prevent it from being intercepted or stolen.
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Monitoring vehicle systems for signs of malicious activity.
- Secure Boot: Ensuring that only authorized software can be loaded onto ECUs.
Best Practices
- Keep Software Updated: Install the latest software updates to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Use Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for vehicle systems.
- Be Careful with Third-Party Apps: Be cautious when installing third-party apps that can access vehicle systems.
- Monitor Vehicle Systems: Monitor vehicle systems for signs of suspicious activity.
10. FAQs About ECUs in Cars
Here are some frequently asked questions about ECUs in cars:
Q1: How many ECUs does my car have?
The number of ECUs in a car varies depending on the make, model, and year. Modern cars typically have between 30 and 100 ECUs.
Q2: What is the main function of an ECU?
An ECU controls various electronic systems within the vehicle, such as engine management, transmission control, and safety systems.
Q3: How do I know if my ECU is failing?
Signs of a failing ECU include the check engine light, engine performance issues, starting problems, and poor fuel economy.
Q4: Can I replace my ECU myself?
Replacing an ECU requires specialized tools and knowledge. It is recommended to have it done by a qualified technician.
Q5: How much does it cost to replace an ECU?
The cost of replacing an ECU can range from $300 to over $1,000, depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
Q6: What is ECU reprogramming?
ECU reprogramming involves overwriting the existing software in an ECU with a new version to improve performance or fix software bugs.
Q7: Is it safe to reprogram my ECU?
ECU reprogramming should be done by a qualified technician using OEM software to avoid damaging the ECU or causing vehicle malfunctions.
Q8: How can I protect my ECU from cyber threats?
You can protect your ECU by keeping software updated, using strong passwords, being careful with third-party apps, and monitoring vehicle systems for suspicious activity.
Q9: What training is available for ECU diagnostics and repair?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of training programs and resources for ECU diagnostics and repair.
Q10: Where can I get help with ECU problems?
You can contact a qualified mechanic or consult with the experts at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for assistance with ECU problems.
Understanding the complexities of the electronic control units in your car is essential for maintaining its performance and longevity. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is dedicated to providing the resources, training, and support you need to master automotive diagnostics and repair.
Ready to take your diagnostic skills to the next level? Contact us today for a consultation! Our team at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to provide expert advice and support. Visit our website at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN or call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance. Our office is located at 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States. Reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 to discover how our advanced diagnostic tools and comprehensive training programs can elevate your expertise and optimize your automotive repair processes. Let CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in navigating the future of automotive technology.