The 420 Code Obd2 indicates an issue with your vehicle’s catalytic converter efficiency. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive diagnostic tools, detailed repair guides, and expert technical support to help you resolve this issue effectively, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and emissions control. Explore our technician training and remote support for specialized assistance in diagnosing and fixing your car.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the 420 Code OBD2: What Does It Really Mean?
- 1.1 Symptoms Associated with the P0420 Code
- 1.2 Common Causes of the 420 Code
- 2. Diagnosing the 420 Code OBD2: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 2.1. Verifying the Code and Gathering Information
- 2.2. Visual Inspection
- 2.3. Testing the Oxygen Sensors
- 2.4. Testing the Catalytic Converter
- 2.5. Checking for Exhaust Leaks
- 3. Repairing the 420 Code OBD2: Effective Solutions
- 3.1. Replacing the Catalytic Converter
- 3.2. Replacing Oxygen Sensors
- 3.3. Repairing Exhaust Leaks
- 3.4. Addressing Engine Misfires
- 3.5. Resolving Fuel Injector Issues
- 4. Preventing the 420 Code OBD2: Proactive Measures
- 4.1. Regular Maintenance
- 4.2. Quality Fuel
- 4.3. Monitor Vehicle Performance
- 4.4. Addressing Issues Promptly
- 4.5. Catalytic Converter Protection
- 5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for the 420 Code
- 5.1. Using a Scan Tool with Advanced Features
- 5.2. Performing a Fuel Trim Analysis
- 5.3. Conducting an Oscilloscope Test
- 5.4. Performing a Compression Test
- 5.5. Conducting a Cylinder Leakage Test
- 6. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in the 420 Code
- 6.1. Upstream Oxygen Sensor Function
- 6.2. Downstream Oxygen Sensor Function
- 6.3. How Oxygen Sensors Trigger the P0420 Code
- 6.4. Diagnosing Oxygen Sensor Issues
- 6.5. Replacing Oxygen Sensors
- 7. Addressing Exhaust Leaks and Their Impact on the 420 Code
- 7.1. How Exhaust Leaks Affect Oxygen Sensors
- 7.2. Common Locations for Exhaust Leaks
- 7.3. Diagnosing Exhaust Leaks
- 7.4. Repairing Exhaust Leaks
- 7.5. Verifying the Repair
- 8. Engine Misfires and Their Link to the 420 Code
- 8.1. How Engine Misfires Damage the Catalytic Converter
- 8.2. Common Causes of Engine Misfires
- 8.3. Diagnosing Engine Misfires
- 8.4. Repairing Engine Misfires
- 8.5. Preventing Misfires
- 9. When to Consult a Professional Mechanic for the 420 Code
- 9.1. Complex Diagnostic Issues
- 9.2. Difficult Repairs
- 9.3. Lack of Experience
- 9.4. Emissions Testing Failure
- 9.5. Cost Considerations
- 10. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Resolving the 420 Code
- 10.1. Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 10.2. Comprehensive Repair Guides
- 10.3. Expert Technical Support
- 10.4. Technician Training Programs
- 10.5. Community Forum
- FAQ: Addressing Your Questions About the 420 Code OBD2
1. Understanding the 420 Code OBD2: What Does It Really Mean?
The 420 code OBD2, also known as P0420, signals that your vehicle’s catalytic converter system isn’t performing up to par. According to the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), catalytic converters are crucial for reducing harmful emissions, converting pollutants like hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances. When the P0420 code appears, it means the downstream oxygen sensor (located after the catalytic converter) is detecting similar levels of oxygen as the upstream sensor (before the converter), indicating the converter isn’t efficiently cleaning the exhaust gases. This inefficiency can result in increased emissions and potential damage to your vehicle.
1.1 Symptoms Associated with the P0420 Code
While the P0420 code itself doesn’t directly impact drivability, it often accompanies other symptoms that can affect your vehicle’s performance. Common symptoms include:
- Check Engine Light: The most obvious sign is the illumination of the Check Engine Light on your dashboard.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: An inefficient catalytic converter can lead to decreased fuel economy.
- Possible Rough Idle: In some cases, you might experience a slightly rougher idle than usual.
- Failed Emissions Test: Your vehicle will likely fail an emissions test if the P0420 code is present.
1.2 Common Causes of the 420 Code
Several factors can trigger the P0420 code. Identifying the root cause is essential for an effective repair. Common causes include:
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: The most likely culprit is a worn-out or damaged catalytic converter.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system, especially before the downstream oxygen sensor, can skew readings.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: Malfunctioning upstream or downstream oxygen sensors can provide inaccurate data.
- Engine Misfires: Misfires can overload the catalytic converter, leading to premature failure.
- Damaged or Leaking Muffler: A damaged or leaking muffler can disrupt the exhaust flow, affecting the catalytic converter’s efficiency.
- Fuel Injector Issues: Problems with fuel injectors can cause an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture, harming the catalytic converter.
 Check Engine Light Indicating OBD2 Issues
Check Engine Light Indicating OBD2 Issues
2. Diagnosing the 420 Code OBD2: A Step-by-Step Guide
Accurately diagnosing the P0420 code requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you pinpoint the underlying issue:
2.1. Verifying the Code and Gathering Information
- Use an OBD2 Scanner: Connect an OBD2 scanner, such as the tools available at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, to your vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Record the Code: Confirm the presence of the P0420 code and any other related codes.
- Check Freeze Frame Data: Examine the freeze frame data associated with the code. This data captures the engine conditions when the code was triggered, offering valuable clues.
2.2. Visual Inspection
- Exhaust System: Inspect the entire exhaust system for leaks, damage, or corrosion. Pay close attention to joints, welds, and the catalytic converter itself.
- Oxygen Sensors: Visually check the oxygen sensors for any signs of damage or contamination.
- Muffler: Check the muffler for any signs of damage, rust, or leaks.
2.3. Testing the Oxygen Sensors
- Live Data Analysis: Use your OBD2 scanner to monitor the live data from both the upstream and downstream oxygen sensors.
- Compare Readings: Compare the sensor readings. The downstream sensor should show a more stable voltage than the upstream sensor, indicating the catalytic converter is working.
- Sensor Response: Check the response time of the sensors. A slow or erratic response can indicate a faulty sensor.
2.4. Testing the Catalytic Converter
- Temperature Check: Use an infrared thermometer to measure the temperature before and after the catalytic converter.
- Temperature Difference: A properly functioning converter should show a significant temperature increase (around 100°F to 200°F) from the inlet to the outlet.
- Backpressure Test: A backpressure test can help determine if the catalytic converter is clogged. High backpressure indicates a blockage.
2.5. Checking for Exhaust Leaks
- Listen Carefully: With the engine running, listen for any hissing or unusual noises coming from the exhaust system.
- Smoke Test: A smoke test can help locate even small exhaust leaks. Introduce smoke into the exhaust system and watch for leaks.
3. Repairing the 420 Code OBD2: Effective Solutions
Once you’ve identified the root cause of the P0420 code, you can proceed with the necessary repairs. Here are some common solutions:
3.1. Replacing the Catalytic Converter
- Quality Replacement: Install a high-quality, OEM-grade catalytic converter.
- Proper Installation: Ensure the converter is properly installed and sealed to prevent leaks.
Table: Top Catalytic Converter Brands
| Brand | Description | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| MagnaFlow | High-performance converters, known for durability and efficiency. | $200 – $500 |
| Walker | OEM-grade converters, offering reliable performance and compliance. | $150 – $400 |
| Eastern Catalytic | Budget-friendly converters, suitable for older vehicles. | $100 – $300 |
| Flowmaster | Performance-oriented converters, designed for increased flow and power. | $250 – $600 |
| AP Emissions | Affordable converters, providing a balance of quality and price. | $120 – $350 |
3.2. Replacing Oxygen Sensors
- OEM or Equivalent: Use OEM or high-quality aftermarket oxygen sensors.
- Sensor Location: Replace the faulty sensor (upstream or downstream) as needed.
- Proper Installation: Ensure the sensors are properly torqued and connected.
Table: Oxygen Sensor Types and Functions
| Sensor Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Upstream | Measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gas before it enters the catalytic converter, helping the ECU adjust the air-fuel mixture. |
| Downstream | Monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter by measuring the oxygen content in the exhaust gas after it exits the converter. |
| Wideband | Provides a more precise measurement of the air-fuel ratio, allowing for finer adjustments. |
| Titania | Uses a titania dioxide element to measure oxygen levels, commonly found in older vehicles. |
3.3. Repairing Exhaust Leaks
- Locate the Leak: Identify the source of the exhaust leak.
- Welding or Replacement: Repair the leak by welding or replacing the damaged section of the exhaust system.
- Sealing: Use exhaust sealant to ensure a tight seal.
3.4. Addressing Engine Misfires
- Identify the Cause: Determine the cause of the engine misfire (e.g., faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors).
- Perform Maintenance: Replace spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel injectors as needed.
- Check Compression: Verify proper engine compression to rule out internal engine issues.
3.5. Resolving Fuel Injector Issues
- Cleaning or Replacement: Clean or replace faulty fuel injectors.
- Fuel System Check: Inspect the fuel system for any other issues, such as a clogged fuel filter or a weak fuel pump.
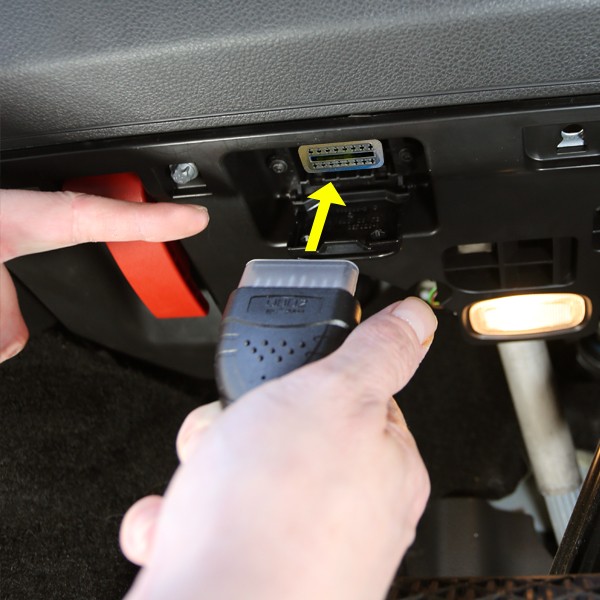 Connecting Diagnostic Tool to Vehicle DLC
Connecting Diagnostic Tool to Vehicle DLC
4. Preventing the 420 Code OBD2: Proactive Measures
Preventing the P0420 code involves regular maintenance and proactive measures to keep your vehicle running smoothly:
4.1. Regular Maintenance
- Scheduled Tune-Ups: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including spark plug replacement, air filter changes, and fuel system cleaning.
- Oil Changes: Regularly change your engine oil to prevent oil-related issues that can affect the catalytic converter.
4.2. Quality Fuel
- Use Recommended Octane: Use the fuel octane level recommended by your vehicle manufacturer.
- Avoid Ethanol: Minimize the use of ethanol-blended fuels, as they can degrade fuel system components over time.
4.3. Monitor Vehicle Performance
- Pay Attention to Symptoms: Be alert to any changes in your vehicle’s performance, such as reduced fuel efficiency, rough idling, or unusual noises.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections of your exhaust system and engine components.
4.4. Addressing Issues Promptly
- Misfire Repair: Address any engine misfires immediately to prevent damage to the catalytic converter.
- Leak Repair: Fix any exhaust leaks as soon as they are detected.
4.5. Catalytic Converter Protection
- Avoid Short Trips: Minimize short trips, as they can prevent the catalytic converter from reaching its optimal operating temperature.
- Proper Warm-Up: Allow your engine to warm up properly before driving aggressively.
5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for the 420 Code
For complex cases, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary to accurately diagnose the P0420 code:
5.1. Using a Scan Tool with Advanced Features
- Data Logging: Use a scan tool with data logging capabilities to record sensor data over a period of time.
- Graphing: Graph the sensor data to visualize patterns and anomalies.
- Bi-Directional Control: Use bi-directional controls to activate and test various engine components.
5.2. Performing a Fuel Trim Analysis
- Monitor Fuel Trims: Analyze the short-term and long-term fuel trims to identify fuel-related issues.
- Lean or Rich Conditions: Determine if the engine is running lean or rich, which can affect the catalytic converter.
5.3. Conducting an Oscilloscope Test
- Oxygen Sensor Waveforms: Use an oscilloscope to analyze the waveforms of the oxygen sensors.
- Sensor Response Time: Measure the response time and amplitude of the waveforms to identify sensor issues.
5.4. Performing a Compression Test
- Cylinder Compression: Check the compression of each cylinder to rule out internal engine issues.
- Compression Variations: Significant variations in compression can indicate problems with valves, rings, or cylinders.
5.5. Conducting a Cylinder Leakage Test
- Leakage Rate: Measure the leakage rate of each cylinder to identify leaks.
- Leakage Location: Determine the location of the leak (e.g., valves, rings, or head gasket).
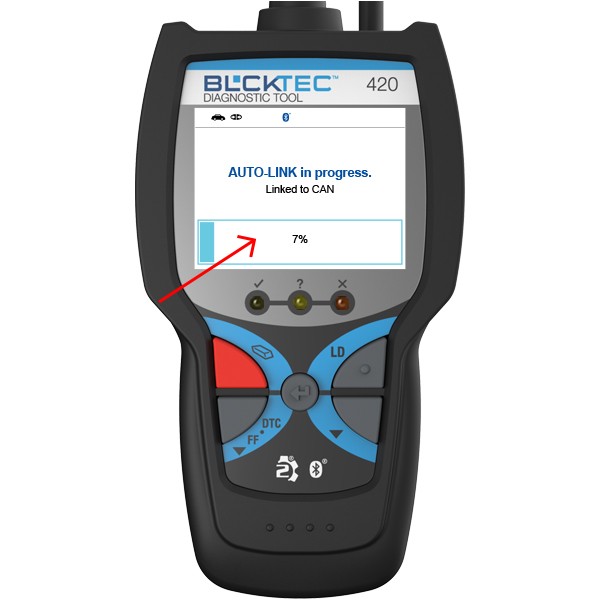 Diagnostic Tool Displaying Trouble Codes
Diagnostic Tool Displaying Trouble Codes
6. The Role of Oxygen Sensors in the 420 Code
Oxygen sensors play a critical role in monitoring the efficiency of the catalytic converter and triggering the P0420 code. Understanding their function and how they relate to the code is essential for accurate diagnosis:
6.1. Upstream Oxygen Sensor Function
- Air-Fuel Mixture: The upstream oxygen sensor measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gas before it enters the catalytic converter.
- ECU Adjustment: This information is used by the Engine Control Unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture, ensuring optimal combustion.
- Sensor Type: Typically, the upstream sensor is a wideband or air-fuel ratio sensor, providing more precise measurements.
6.2. Downstream Oxygen Sensor Function
- Catalytic Converter Efficiency: The downstream oxygen sensor measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gas after it exits the catalytic converter.
- Monitoring Performance: This sensor monitors the performance of the catalytic converter by comparing the oxygen levels before and after the converter.
- Sensor Type: The downstream sensor is typically a narrowband oxygen sensor.
6.3. How Oxygen Sensors Trigger the P0420 Code
- Similar Readings: If the downstream oxygen sensor detects similar oxygen levels to the upstream sensor, it indicates the catalytic converter is not efficiently converting pollutants.
- Code Activation: The ECU interprets this as a failure of the catalytic converter and triggers the P0420 code.
6.4. Diagnosing Oxygen Sensor Issues
- Live Data Analysis: Use a scan tool to monitor the live data from both oxygen sensors.
- Voltage Readings: Check the voltage readings of the sensors. The upstream sensor should fluctuate, while the downstream sensor should be relatively stable.
- Response Time: Verify the response time of the sensors. A slow or erratic response can indicate a faulty sensor.
6.5. Replacing Oxygen Sensors
- OEM or Equivalent: Use OEM or high-quality aftermarket oxygen sensors.
- Sensor Location: Replace the faulty sensor (upstream or downstream) as needed.
- Proper Installation: Ensure the sensors are properly torqued and connected.
7. Addressing Exhaust Leaks and Their Impact on the 420 Code
Exhaust leaks can significantly impact the accuracy of oxygen sensor readings and trigger the P0420 code. Identifying and repairing these leaks is crucial for resolving the issue:
7.1. How Exhaust Leaks Affect Oxygen Sensors
- False Readings: Exhaust leaks introduce additional oxygen into the exhaust system, leading to false readings from the oxygen sensors.
- Air Dilution: Air entering the exhaust system dilutes the exhaust gases, affecting the oxygen sensor’s ability to accurately measure the oxygen content.
- Code Trigger: The skewed oxygen sensor readings can cause the ECU to misinterpret the catalytic converter’s performance and trigger the P0420 code.
7.2. Common Locations for Exhaust Leaks
- Exhaust Manifold Gasket: Leaks can occur at the exhaust manifold gasket, where the manifold connects to the engine.
- Exhaust Pipes: Cracks or holes in the exhaust pipes can cause leaks.
- Welds and Joints: Leaks can develop at welds and joints in the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter Flanges: Leaks can occur at the flanges where the catalytic converter connects to the exhaust pipes.
- Muffler Connections: Leaks can develop at the connections between the muffler and the exhaust pipes.
7.3. Diagnosing Exhaust Leaks
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the exhaust system for any signs of damage, corrosion, or soot accumulation.
- Auditory Inspection: Listen for any hissing or unusual noises coming from the exhaust system.
- Smoke Test: Use a smoke test to locate even small exhaust leaks. Introduce smoke into the exhaust system and watch for leaks.
7.4. Repairing Exhaust Leaks
- Welding: Weld any cracks or holes in the exhaust pipes.
- Gasket Replacement: Replace any damaged exhaust manifold gaskets.
- Component Replacement: Replace any severely damaged exhaust components.
- Sealing: Use exhaust sealant to ensure a tight seal at joints and connections.
7.5. Verifying the Repair
- Re-Test: After repairing the exhaust leak, re-test the oxygen sensors and catalytic converter to ensure they are functioning properly.
- Clear Codes: Clear the P0420 code and monitor the vehicle for any recurring issues.
8. Engine Misfires and Their Link to the 420 Code
Engine misfires can place excessive stress on the catalytic converter, leading to premature failure and the triggering of the P0420 code. Addressing misfires promptly is essential for maintaining the health of your vehicle’s emissions system:
8.1. How Engine Misfires Damage the Catalytic Converter
- Unburned Fuel: Misfires result in unburned fuel entering the exhaust system.
- Overheating: This unburned fuel can cause the catalytic converter to overheat, damaging its internal components.
- Reduced Efficiency: Over time, repeated misfires can reduce the efficiency of the catalytic converter, leading to the P0420 code.
8.2. Common Causes of Engine Misfires
- Faulty Spark Plugs: Worn or damaged spark plugs can cause misfires.
- Faulty Ignition Coils: Weak or failing ignition coils can prevent the spark plugs from firing properly.
- Faulty Fuel Injectors: Clogged or malfunctioning fuel injectors can disrupt the fuel supply to the cylinders.
- Vacuum Leaks: Vacuum leaks can alter the air-fuel mixture, leading to misfires.
- Low Compression: Low compression in one or more cylinders can prevent proper combustion.
8.3. Diagnosing Engine Misfires
- OBD2 Scanner: Use an OBD2 scanner to identify misfire codes (e.g., P0300, P0301, P0302).
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors for any signs of damage.
- Spark Plug Test: Test the spark plugs to ensure they are firing properly.
- Ignition Coil Test: Test the ignition coils to verify they are providing sufficient spark.
- Fuel Injector Test: Test the fuel injectors to ensure they are delivering the correct amount of fuel.
- Compression Test: Perform a compression test to check the compression of each cylinder.
- Vacuum Leak Test: Check for vacuum leaks using a smoke test or carburetor cleaner.
8.4. Repairing Engine Misfires
- Spark Plug Replacement: Replace faulty spark plugs.
- Ignition Coil Replacement: Replace weak or failing ignition coils.
- Fuel Injector Cleaning or Replacement: Clean or replace clogged or malfunctioning fuel injectors.
- Vacuum Leak Repair: Repair any vacuum leaks.
- Compression Issues: Address any compression issues, such as worn rings or valves.
8.5. Preventing Misfires
- Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including spark plug replacement and fuel system cleaning.
- Quality Parts: Use high-quality replacement parts.
- Proper Fuel: Use the recommended fuel octane level.
9. When to Consult a Professional Mechanic for the 420 Code
While some P0420 code issues can be resolved with DIY repairs, there are situations where consulting a professional mechanic is the best course of action:
9.1. Complex Diagnostic Issues
- Unclear Cause: If you are unable to identify the root cause of the P0420 code after performing basic diagnostic tests.
- Multiple Codes: If the P0420 code is accompanied by numerous other codes, indicating a more complex issue.
- Advanced Testing: If advanced testing techniques, such as oscilloscope testing or fuel trim analysis, are required.
9.2. Difficult Repairs
- Catalytic Converter Replacement: Replacing a catalytic converter can be a challenging task, especially if it requires welding or extensive exhaust system disassembly.
- Engine Misfires: Diagnosing and repairing engine misfires can be complex, particularly if the cause is related to internal engine components.
- Fuel System Issues: Resolving fuel system issues, such as clogged fuel injectors or a weak fuel pump, may require specialized tools and knowledge.
9.3. Lack of Experience
- Limited Knowledge: If you have limited experience working on vehicles, it’s best to consult a professional mechanic.
- Safety Concerns: Working on exhaust systems and fuel systems can pose safety risks if not done properly.
9.4. Emissions Testing Failure
- Repeated Failures: If your vehicle repeatedly fails emissions testing due to the P0420 code, a professional mechanic can help identify and resolve the underlying issue.
- Compliance: Ensuring your vehicle meets emissions standards is crucial for legal compliance.
9.5. Cost Considerations
- DIY vs. Professional: Evaluate the cost of DIY repairs versus professional service.
- Potential Damage: Consider the potential cost of damaging components if repairs are not done correctly.
Table: Cost Comparison of DIY vs. Professional Repair
| Repair | DIY Cost (USD) | Professional Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Sensor Replacement | $50 – $150 | $150 – $300 |
| Exhaust Leak Repair | $20 – $100 | $100 – $400 |
| Catalytic Converter Replacement | $150 – $500 | $400 – $1200 |
| Engine Misfire Repair | $30 – $200 | $100 – $500 |
10. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Resolving the 420 Code
At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of diagnosing and repairing the P0420 code. We offer a range of tools, resources, and support to help you resolve this issue efficiently and effectively:
10.1. Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- OBD2 Scanners: High-quality OBD2 scanners with advanced features such as live data analysis, freeze frame data, and bi-directional controls.
- Professional-Grade Equipment: Access to professional-grade diagnostic equipment used by certified technicians.
10.2. Comprehensive Repair Guides
- Step-by-Step Instructions: Detailed repair guides with step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and repairing the P0420 code.
- Technical Diagrams: Technical diagrams and schematics to help you understand the components and systems involved.
10.3. Expert Technical Support
- Remote Assistance: Remote technical support from experienced technicians who can guide you through the diagnostic and repair process.
- Troubleshooting: Assistance with troubleshooting complex issues and identifying the root cause of the P0420 code.
10.4. Technician Training Programs
- Certification Courses: Certification courses to enhance your diagnostic and repair skills.
- Hands-On Training: Hands-on training sessions to provide practical experience working on vehicles.
10.5. Community Forum
- Peer Support: Access to a community forum where you can connect with other technicians and enthusiasts to share knowledge and experiences.
- Expert Advice: Opportunities to receive advice from experienced professionals in the automotive industry.
Don’t let the 420 code keep you on the sidelines! Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States, and let our team provide you with the expert tools, guidance, and support you need to diagnose and repair your vehicle like a pro.
FAQ: Addressing Your Questions About the 420 Code OBD2
1. What does the 420 code OBD2 mean?
The 420 code OBD2, also known as P0420, indicates that your vehicle’s catalytic converter system efficiency is below the required threshold. This means the converter isn’t effectively reducing harmful emissions.
2. What are the common symptoms associated with the 420 code?
Common symptoms include the Check Engine Light illuminating, reduced fuel efficiency, a possible rough idle, and failure to pass an emissions test.
3. What are the main causes of the 420 code OBD2?
The primary causes are a faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors, engine misfires, and fuel injector issues.
4. How can I diagnose the 420 code myself?
You can diagnose the code by using an OBD2 scanner, visually inspecting the exhaust system, testing the oxygen sensors, and checking for exhaust leaks.
5. Can I drive my car with the 420 code?
While you can drive with the 420 code, it’s not recommended. The underlying issue can lead to reduced fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and potential damage to the vehicle.
6. How do oxygen sensors relate to the 420 code?
Oxygen sensors monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter. If the downstream sensor detects similar oxygen levels to the upstream sensor, it indicates the converter isn’t working properly, triggering the 420 code.
7. How do exhaust leaks affect the 420 code?
Exhaust leaks introduce additional oxygen into the exhaust system, leading to false readings from the oxygen sensors and potentially triggering the 420 code.
8. Can engine misfires cause the 420 code?
Yes, engine misfires can damage the catalytic converter by introducing unburned fuel into the exhaust system, leading to overheating and reduced efficiency.
9. When should I replace the catalytic converter to fix the 420 code?
You should replace the catalytic converter if it is faulty, damaged, or clogged, and other potential causes, such as exhaust leaks and oxygen sensor issues, have been ruled out.
10. Does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offer any assistance in diagnosing and repairing the 420 code?
Yes, CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers advanced diagnostic tools, comprehensive repair guides, expert technical support, technician training programs, and a community forum to help you resolve the 420 code effectively. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States, for personalized assistance.