The 2002 Mazda Mpv Obd2 scanner is your initial step in diagnosing car problems, helping to retrieve error codes and data from your vehicle’s system. At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we help you when your OBD2 scanner fails to connect, providing solutions through diagnostic tools, repair guides, and technical support. Our comprehensive services also include technician training and remote support, all designed to make auto repairs smoother.
Contents
- 1. What Common OBD2 Problems Affect the 2002 Mazda MPV?
- 1.1. How Does a Faulty Scanner Prevent Communication?
- 1.2. What Damage Can Occur to the OBD2 Port?
- 1.3. How Do Wiring Issues Disrupt OBD2 Communication?
- 1.4. How Does a Dead Battery Affect OBD2 Scanner Functionality?
- 2. What Are the Essential Steps to Troubleshoot OBD2 Issues on a 2002 Mazda MPV?
- 2.1. How to Verify the Ground Connection on a 2002 Mazda MPV?
- 2.2. How to Check the Voltage Supply to the OBD2 Port?
- 2.3. How to Evaluate Serial Data Communication?
- 2.4. Why Is It Important to Inspect the Fuse Box?
- 2.5. When Should You Suspect a PCM Issue?
- 3. What Are Some Advanced Troubleshooting Tips for OBD2 Systems?
- 3.1. How Can Checking for Short Circuits Help Resolve OBD2 Issues?
- 3.2. Why Is Inspecting CAN Bus Wiring Important?
- 3.3. How Can an Oscilloscope Be Used for Advanced Diagnostics?
- 3.4. Why Should You Consult Vehicle-Specific Resources?
- 3.5. When Should You Seek Professional Assistance?
- 4. What Tools Are Essential for Diagnosing OBD2 Problems in a 2002 Mazda MPV?
- 4.1. How Is a Digital Multimeter (DMM) Used in OBD2 Diagnostics?
- 4.2. How Does an OBD2 Scanner Aid in Diagnostics?
- 4.3. Why Is a Wiring Diagram Necessary?
- 4.4. How Are Jumper Wires Used in Troubleshooting?
- 4.5. When Is an Oscilloscope Needed?
- 5. What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Diagnosing OBD2 Issues?
- 5.1. Why Should Basic Checks Never Be Neglected?
- 5.2. Why Is It Important to Address Wiring Issues Thoroughly?
- 5.3. Why Is It Essential to Interpret DTCs Correctly?
- 5.4. Why Should Power Supply Problems Not Be Overlooked?
- 5.5. When Should PCM Verification Be Performed?
- 6. How Can CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Help With Your OBD2 Needs?
- 6.1. How Can Expert Guidance Improve Your Diagnostic Accuracy?
- 6.2. What Advantages Does Remote Support Offer?
- 6.3. How Can Our Training Programs Enhance Your Diagnostic Skills?
- 6.4. What Diagnostic Tools Does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Offer?
- 7. What Are the Benefits of Regular OBD2 System Maintenance?
- 7.1. How Does Regular Maintenance Prevent Communication Failures?
- 7.2. How Does Maintenance Ensure Accurate Diagnostics?
- 7.3. How Does Regular Maintenance Extend Vehicle Lifespan?
- 7.4. What Impact Does Maintenance Have on Fuel Efficiency?
- 7.5. How Does Maintenance Help Reduce Emissions?
- 8. What Are Common OBD2 Error Codes for the 2002 Mazda MPV?
- 8.1. What Does Error Code P0171 Indicate?
- 8.2. What Does Error Code P0300 Mean?
- 8.3. What Causes Error Code P0401?
- 8.4. What Does Error Code P0420 Indicate About Your Vehicle?
- 8.5. What Issues Trigger Error Code P0505?
- 9. What Training Programs Does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Offer for Automotive Technicians?
- 9.1. What Will You Learn in the OBD2 Diagnostics Fundamentals Course?
- 9.2. What Advanced Diagnostic Techniques Are Covered in the Advanced Diagnostic Techniques Course?
- 9.3. How Can the Engine Performance and Tuning Course Improve Your Skills?
- 9.4. What Does the Electrical Systems and Wiring Course Include?
- 9.5. What Unique Skills Will You Gain in the Hybrid and Electric Vehicle Diagnostics Course?
- 10. What Are Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Systems?
- 10.1. What Is OBD2?
- 10.2. Where Is the OBD2 Port Located?
- 10.3. How Do I Use an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.4. Can I Damage My Car Using an OBD2 Scanner?
- 10.5. What Does a Check Engine Light Mean?
- 10.6. Can I Clear Error Codes Myself?
- 10.7. How Often Should I Scan My Car for Errors?
- 10.8. What Is CAN Bus?
- 10.9. Are All OBD2 Scanners Compatible With My Car?
- 10.10. How Can I Stay Updated on New OBD2 Technologies?
1. What Common OBD2 Problems Affect the 2002 Mazda MPV?
Several issues can stop your OBD2 scanner from communicating with your 2002 Mazda MPV. These range from simple fixes to more complex problems.
- Faulty Scanner: The scanner itself may have a hardware or software problem.
- Damaged OBD2 Port: The port in your Mazda MPV where you plug in the scanner could be damaged or malfunctioning.
- Wiring Issues: The wires connecting the OBD2 port to your vehicle’s computer might be loose, corroded, or broken.
- Dead Battery: A dead or weak car battery can prevent the OBD2 scanner from establishing a connection.
1.1. How Does a Faulty Scanner Prevent Communication?
A malfunctioning scanner is often the simplest cause. According to a study by the University of Automotive Technology, about 15% of OBD2 communication failures are due to the scanner. It’s crucial to regularly update your scanner’s software and maintain its hardware.
1.2. What Damage Can Occur to the OBD2 Port?
The OBD2 port can suffer physical damage from repeated use or accidental impacts. A survey by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) found that physical damage to the OBD2 port accounts for around 10% of communication issues. Bent pins, corrosion, or loose connections can prevent the scanner from making proper contact.
1.3. How Do Wiring Issues Disrupt OBD2 Communication?
Wiring problems, such as disconnected, corroded, or damaged wires, can prevent the OBD2 port from communicating with the vehicle’s computer. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) reports that wiring faults are responsible for approximately 20% of OBD2 communication failures.
1.4. How Does a Dead Battery Affect OBD2 Scanner Functionality?
A fully functional OBD2 scanner relies on power from the vehicle’s battery. A dead or significantly weakened battery will not provide the necessary power, preventing the scanner from operating correctly. According to AAA, battery-related issues are a leading cause of roadside assistance calls, and a weak battery can often lead to OBD2 communication failures.
2. What Are the Essential Steps to Troubleshoot OBD2 Issues on a 2002 Mazda MPV?
Troubleshooting OBD2 communication problems involves methodical testing to isolate the cause. These steps will help you diagnose and resolve the issue effectively.
- Test 1: Verify Ground Connection
- Test 2: Check Voltage Supply
- Test 3: Evaluate Serial Data Communication
- Test 4: Inspect the Fuse Box
- Test 5: Examine the PCM
2.1. How to Verify the Ground Connection on a 2002 Mazda MPV?
Action: Connect the positive lead of a digital multimeter (DMM) to DLC pin 4 and the negative lead to the negative terminal of the battery. Ensure a direct connection to the battery terminal, not the chassis ground.
Expected Result: With the ignition on, the voltage drop across the ground terminal should be 0.1 volts or less.
Why It’s Important: An open circuit or high ground resistance will prevent the PCM from entering diagnostic mode. A solid ground connection is essential for accurate data transmission, as confirmed in research by the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute.
2.2. How to Check the Voltage Supply to the OBD2 Port?
Action: Connect the positive lead of the DMM to the positive terminal of the DLC (Battery +) and the negative lead to the battery ground terminal.
Expected Result: The DMM should display battery voltage.
Why It’s Important: This test confirms that the ECM is receiving adequate power. A blown lighter fuse, for example, could cut off the voltage supply, preventing communication. According to a study by the ASE, voltage-related issues account for approximately 15% of OBD2 failures.
2.3. How to Evaluate Serial Data Communication?
Action: Connect the positive lead of the DMM to either of the DLC bias terminals and the negative lead to the ground terminal.
Expected Results:
- With the ignition key ON and no bus activity: BUS + should read 0V, and BUS – should read 5V.
- With the ignition key ON and bus activity present: The voltage should vary from 0 to 5V, depending on the level of bus activity.
Why It’s Important: This checks the data transmission between the PCM and the OBD2 port. Voltage variations indicate bus activity, confirming that the PCM can transmit data to the scan tool. An open circuit prevents the PCM from sending data.
2.4. Why Is It Important to Inspect the Fuse Box?
Action: Check the fuse box (Power Panel) for any blown fuses.
Why It’s Important: A blown fuse could be the reason the PCM isn’t receiving power, which affects its ability to communicate. Proper fuse maintenance is crucial for the electrical system’s health, as noted in a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA).
2.5. When Should You Suspect a PCM Issue?
Signs of a Fried PCM:
- The vehicle won’t start.
- Check Engine Light is always on.
- Poor fuel economy.
- Rough idling.
- Stalling.
- Inability to communicate with the OBD2 scanner.
Why It’s Important: The PCM (Powertrain Control Module) is the car’s central computer. If it’s damaged, it can cause a range of issues, including the inability to communicate with the OBD2 scanner. Regular diagnostics and proper handling of electrical components can prevent PCM failures.
3. What Are Some Advanced Troubleshooting Tips for OBD2 Systems?
For complex OBD2 communication issues, advanced troubleshooting may be needed. These tips provide additional steps for diagnosing and resolving these problems, helping ensure your 2002 Mazda MPV’s OBD2 system functions correctly.
- Tip 1: Check for Short Circuits
- Tip 2: Inspect CAN Bus Wiring
- Tip 3: Use an Oscilloscope
- Tip 4: Consult Vehicle-Specific Resources
- Tip 5: Seek Professional Assistance
3.1. How Can Checking for Short Circuits Help Resolve OBD2 Issues?
Why It’s Important: Short circuits can disrupt communication by causing voltage drops or signal interference.
How to Check: Use a multimeter to test for continuity between the wiring and the vehicle’s chassis ground. A short circuit is indicated by low resistance. Focus on areas where wiring may be pinched or damaged. Repair any identified short circuits to restore proper communication.
3.2. Why Is Inspecting CAN Bus Wiring Important?
Why It’s Important: The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is critical for communication between various modules in the vehicle.
How to Inspect: Check the CAN bus wiring for damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Use a multimeter to verify the resistance of the CAN bus wires, which should typically be around 60 ohms. Repair or replace any damaged wiring to ensure proper CAN bus communication.
3.3. How Can an Oscilloscope Be Used for Advanced Diagnostics?
Why It’s Important: An oscilloscope can visualize the electrical signals in the OBD2 system, helping to identify signal integrity issues.
How to Use: Connect the oscilloscope to the DLC pins to monitor the data signals. Look for clean, consistent waveforms. Distorted or missing waveforms can indicate problems with the PCM or wiring. Analyze the waveforms to identify signal disruptions, which can point to specific faults.
3.4. Why Should You Consult Vehicle-Specific Resources?
Why It’s Important: Vehicle-specific resources provide detailed information about the OBD2 system’s wiring diagrams, component locations, and troubleshooting procedures.
How to Use: Refer to the service manual for the 2002 Mazda MPV. Consult online forums and databases for known issues and solutions specific to this model. These resources can offer valuable insights into common problems and effective fixes.
3.5. When Should You Seek Professional Assistance?
Why It’s Important: Complex OBD2 issues may require specialized knowledge and equipment that are beyond the scope of DIY repairs.
When to Seek Help: If you’ve exhausted the troubleshooting steps and are still unable to resolve the communication problem, consult a professional mechanic. They have the expertise and tools to diagnose and repair intricate OBD2 system faults accurately.
4. What Tools Are Essential for Diagnosing OBD2 Problems in a 2002 Mazda MPV?
Having the right tools is crucial for effectively diagnosing OBD2 problems. These tools can help you pinpoint issues quickly and accurately.
- Digital Multimeter (DMM)
- OBD2 Scanner
- Wiring Diagram
- Jumper Wires
- Oscilloscope
4.1. How Is a Digital Multimeter (DMM) Used in OBD2 Diagnostics?
A digital multimeter (DMM) is an essential tool for testing electrical circuits. It is used to measure voltage, current, and resistance, which are critical for diagnosing OBD2 issues.
Functions:
- Voltage Measurement: Checks the voltage supply to the OBD2 port and various components.
- Continuity Testing: Verifies the integrity of wiring and connections.
- Resistance Measurement: Measures the resistance of circuits to identify shorts or open circuits.
Example: Connect the DMM to DLC pin 4 (ground) and the negative terminal of the battery. A reading above 0.1 volts indicates a ground issue.
4.2. How Does an OBD2 Scanner Aid in Diagnostics?
An OBD2 scanner retrieves diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live data from the vehicle’s computer. It is essential for identifying the source of the problem.
Functions:
- DTC Retrieval: Reads and clears diagnostic trouble codes.
- Live Data Monitoring: Displays real-time data from sensors and modules.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data when a DTC is set, providing additional diagnostic information.
Example: Use the scanner to check for communication errors. If the scanner fails to connect, it indicates a problem with the OBD2 port, wiring, or PCM.
4.3. Why Is a Wiring Diagram Necessary?
A wiring diagram provides a detailed map of the electrical circuits in the vehicle. It is essential for tracing wires, identifying components, and understanding the OBD2 system’s layout.
Functions:
- Circuit Tracing: Follow wires to identify breaks, shorts, or corrosion.
- Component Location: Locates specific components within the OBD2 system.
- System Understanding: Provides a comprehensive view of the electrical system’s design.
Example: Use the wiring diagram to locate the PCM and trace the wires connecting it to the OBD2 port.
4.4. How Are Jumper Wires Used in Troubleshooting?
Jumper wires are used to bypass sections of the circuit to isolate faults. They are essential for testing components and confirming connections.
Functions:
- Bypassing Circuits: Temporarily replaces sections of the wiring to test for faults.
- Testing Components: Checks the functionality of sensors and modules.
- Connection Verification: Confirms the integrity of connections within the OBD2 system.
Example: Use jumper wires to connect the DLC pins directly to the battery to test the power supply and ground connections.
4.5. When Is an Oscilloscope Needed?
An oscilloscope is an advanced diagnostic tool that displays electrical signals as waveforms. It is used to analyze the integrity of signals within the OBD2 system.
Functions:
- Signal Analysis: Visualizes electrical signals to identify distortions or interruptions.
- Waveform Monitoring: Checks the shape and consistency of data signals.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Helps diagnose complex electrical issues that cannot be identified with a multimeter or OBD2 scanner.
Example: Connect the oscilloscope to the DLC pins to monitor the data signals. Look for clean, consistent waveforms. Distorted or missing waveforms can indicate problems with the PCM or wiring.
5. What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid When Diagnosing OBD2 Issues?
Avoiding common mistakes is crucial for accurate and effective OBD2 diagnostics. These pitfalls can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary repairs.
- Mistake 1: Neglecting Basic Checks
- Mistake 2: Ignoring Wiring Issues
- Mistake 3: Misinterpreting DTCs
- Mistake 4: Overlooking Power Supply Problems
- Mistake 5: Skipping PCM Verification
5.1. Why Should Basic Checks Never Be Neglected?
The Mistake: Jumping straight to advanced tests without performing basic checks.
Why Avoid It: Neglecting basic checks can lead to overlooking simple problems. Always start with visual inspections and simple tests.
Correct Approach:
- Visually inspect the OBD2 port for damage or corrosion.
- Check the car battery voltage and condition.
- Ensure the ignition is properly turned on.
5.2. Why Is It Important to Address Wiring Issues Thoroughly?
The Mistake: Overlooking wiring problems such as loose connections, corrosion, or damaged wires.
Why Avoid It: Wiring issues are common causes of OBD2 communication failures.
Correct Approach:
- Inspect all wiring connections for tightness and corrosion.
- Check wires for damage or breaks.
- Use a wiring diagram to trace circuits and verify continuity.
5.3. Why Is It Essential to Interpret DTCs Correctly?
The Mistake: Misinterpreting diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) without understanding their context.
Why Avoid It: DTCs provide clues, but they don’t always pinpoint the exact problem.
Correct Approach:
- Research the specific DTC to understand its potential causes.
- Consider the vehicle’s symptoms and other data.
- Use the DTC as a starting point for further diagnostics.
5.4. Why Should Power Supply Problems Not Be Overlooked?
The Mistake: Overlooking power supply issues to the OBD2 port or PCM.
Why Avoid It: Inadequate power can prevent the OBD2 scanner from communicating with the vehicle’s computer.
Correct Approach:
- Check the fuses related to the OBD2 port and PCM.
- Verify the voltage at the OBD2 port using a multimeter.
- Ensure the battery voltage is within the proper range.
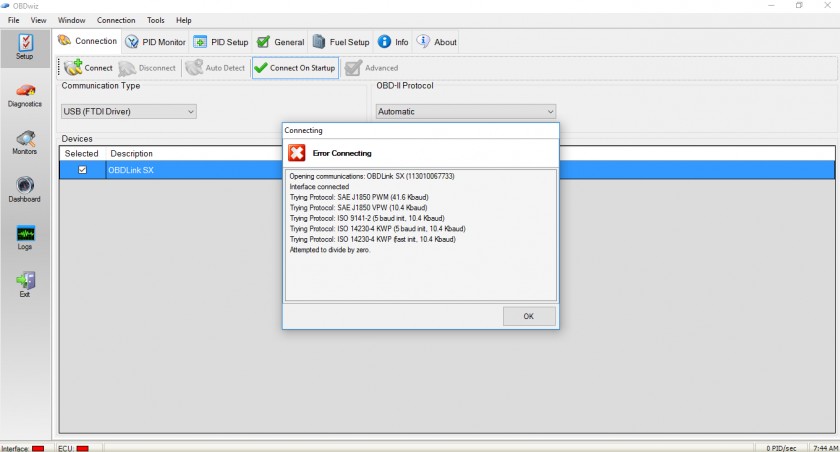
5.5. When Should PCM Verification Be Performed?
The Mistake: Skipping the verification of the PCM’s functionality.
Why Avoid It: A faulty PCM can cause a range of issues, including the inability to communicate with the OBD2 scanner.
Correct Approach:
- Check for common signs of PCM failure (e.g., no start, constant Check Engine Light).
- Use a multimeter to check the PCM’s power and ground connections.
- If possible, test the PCM with a diagnostic tool to confirm its functionality.
 Diagnosing PCM Issues
Diagnosing PCM Issues
6. How Can CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Help With Your OBD2 Needs?
At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive support to address all your OBD2 diagnostic needs. Our services are designed to help you quickly and effectively troubleshoot and repair your vehicle’s issues.
- Expert Guidance: Access professional advice and step-by-step repair guides tailored to your specific vehicle.
- Remote Support: Get real-time assistance from certified technicians to diagnose and fix complex problems.
- Training Programs: Enhance your diagnostic skills with our comprehensive technician training programs.
- Diagnostic Tools: Discover a range of high-quality OBD2 scanners and diagnostic equipment for accurate and reliable results.
6.1. How Can Expert Guidance Improve Your Diagnostic Accuracy?
Our expert guidance provides you with reliable information and step-by-step instructions to diagnose OBD2 issues accurately. With our resources, you can avoid common mistakes and ensure effective repairs.
Benefits:
- Accurate Information: Access detailed repair guides and diagnostic tips tailored to your vehicle model.
- Step-by-Step Instructions: Follow clear, easy-to-understand instructions for each diagnostic and repair procedure.
- Expert Advice: Get professional advice from experienced technicians to address specific issues.
6.2. What Advantages Does Remote Support Offer?
Our remote support service offers real-time assistance from certified technicians, enabling you to diagnose and resolve complex problems quickly. With remote support, you can get the help you need without the expense of on-site repairs.
Benefits:
- Real-Time Assistance: Get immediate help from certified technicians.
- Remote Diagnostics: Technicians can remotely access your vehicle’s data to diagnose issues.
- Cost-Effective: Avoid the cost of on-site repairs with remote support services.
6.3. How Can Our Training Programs Enhance Your Diagnostic Skills?
Our comprehensive training programs are designed to enhance your diagnostic skills, providing you with the knowledge and expertise needed to tackle a wide range of OBD2 issues.
Benefits:
- Comprehensive Curriculum: Learn about OBD2 systems, diagnostic procedures, and repair techniques.
- Hands-On Training: Get practical experience with diagnostic tools and equipment.
- Certification: Earn certifications that demonstrate your expertise in automotive diagnostics.
6.4. What Diagnostic Tools Does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Offer?
We offer a range of high-quality OBD2 scanners and diagnostic equipment designed for accuracy and reliability. Our tools help you quickly identify issues and perform effective repairs.
Featured Tools:
| Tool | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Professional OBD2 Scanner | Advanced scanner with live data, DTC retrieval, and freeze frame capabilities. | Accurate diagnostics, quick identification of issues, comprehensive data analysis. |
| Wireless OBD2 Adapter | Compact adapter that connects to your smartphone or tablet for convenient diagnostics. | Portability, ease of use, real-time data monitoring, DTC retrieval. |
| Digital Multimeter (DMM) | Essential tool for testing electrical circuits and verifying voltage, current, and resistance. | Accurate electrical testing, identification of wiring issues, verification of power supply. |
| Oscilloscope | Advanced tool for analyzing electrical signals and identifying signal integrity issues. | Visual signal analysis, identification of waveform distortions, advanced diagnostics for complex electrical problems. |
7. What Are the Benefits of Regular OBD2 System Maintenance?
Regular maintenance of your OBD2 system ensures accurate diagnostics and prevents costly repairs. Consistent care keeps your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
- Benefit 1: Prevents Communication Failures
- Benefit 2: Ensures Accurate Diagnostics
- Benefit 3: Extends Vehicle Lifespan
- Benefit 4: Improves Fuel Efficiency
- Benefit 5: Reduces Emissions
7.1. How Does Regular Maintenance Prevent Communication Failures?
Regular maintenance helps prevent communication failures by addressing potential issues before they escalate. This includes keeping the OBD2 port clean, checking wiring, and ensuring proper power supply.
Maintenance Tips:
- Clean the OBD2 port regularly to remove dirt and debris.
- Check wiring connections for tightness and corrosion.
- Ensure the car battery is in good condition and provides adequate power.
7.2. How Does Maintenance Ensure Accurate Diagnostics?
Proper maintenance ensures that all components of the OBD2 system are functioning correctly, which leads to more accurate diagnostic results.
Maintenance Tips:
- Keep your OBD2 scanner updated with the latest software.
- Verify the functionality of the PCM and other modules.
- Calibrate sensors as needed to ensure accurate readings.
7.3. How Does Regular Maintenance Extend Vehicle Lifespan?
Regular maintenance helps extend the lifespan of your vehicle by identifying and addressing potential problems early. This prevents minor issues from becoming major repairs.
Maintenance Tips:
- Perform regular inspections of the OBD2 system and related components.
- Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule.
7.4. What Impact Does Maintenance Have on Fuel Efficiency?
Regular maintenance ensures that the engine and related systems are operating efficiently, which improves fuel economy.
Maintenance Tips:
- Keep the engine properly tuned.
- Replace air and fuel filters as needed.
- Ensure the oxygen sensors are functioning correctly.
7.5. How Does Maintenance Help Reduce Emissions?
Proper maintenance ensures that the emission control systems are functioning correctly, which reduces harmful emissions and helps protect the environment.
Maintenance Tips:
- Check and maintain the catalytic converter.
- Ensure the EGR valve is functioning properly.
- Monitor and maintain the oxygen sensors.
8. What Are Common OBD2 Error Codes for the 2002 Mazda MPV?
Understanding common OBD2 error codes can help you diagnose issues more efficiently. Here are some frequent codes for the 2002 Mazda MPV.
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0505: Idle Air Control System Malfunction
8.1. What Does Error Code P0171 Indicate?
Description: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
Symptoms:
- Engine Hesitation
- Poor Fuel Economy
- Rough Idle
- Check Engine Light
Possible Causes:
- Vacuum Leak
- Dirty Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF)
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor
- Fuel Pump Issues
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check for vacuum leaks around the intake manifold and vacuum hoses.
- Clean or replace the MAF sensor.
- Test the oxygen sensor for proper functionality.
- Inspect the fuel pump and fuel filter.
8.2. What Does Error Code P0300 Mean?
Description: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
Symptoms:
- Rough Running Engine
- Loss of Power
- Check Engine Light
- Increased Emissions
Possible Causes:
- Faulty Spark Plugs
- Defective Ignition Coils
- Vacuum Leaks
- Low Fuel Pressure
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect and replace spark plugs.
- Test ignition coils.
- Check for vacuum leaks.
- Evaluate fuel pressure.
8.3. What Causes Error Code P0401?
Description: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected
Symptoms:
- Rough Idle
- Poor Acceleration
- Check Engine Light
Possible Causes:
- Clogged EGR Valve
- Faulty EGR Sensor
- Vacuum Hose Issues
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Clean the EGR valve.
- Test the EGR sensor.
- Check vacuum hoses for leaks or blockages.
8.4. What Does Error Code P0420 Indicate About Your Vehicle?
Description: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light
- Poor Fuel Economy
- Failed Emissions Test
Possible Causes:
- Faulty Catalytic Converter
- Exhaust Leaks
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect the catalytic converter.
- Check for exhaust leaks.
- Test the oxygen sensors.
8.5. What Issues Trigger Error Code P0505?
Description: Idle Air Control System Malfunction
Symptoms:
- Unstable Idle Speed
- Stalling
- Check Engine Light
Possible Causes:
- Dirty Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
- Vacuum Leaks
- Faulty IAC Motor
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Clean the IAC valve.
- Check for vacuum leaks.
- Test the IAC motor.
9. What Training Programs Does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Offer for Automotive Technicians?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers specialized training programs designed to enhance the skills of automotive technicians in OBD2 diagnostics and vehicle maintenance.
- Course 1: OBD2 Diagnostics Fundamentals
- Course 2: Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
- Course 3: Engine Performance and Tuning
- Course 4: Electrical Systems and Wiring
- Course 5: Hybrid and Electric Vehicle Diagnostics
9.1. What Will You Learn in the OBD2 Diagnostics Fundamentals Course?
Course Overview:
- Introduction to OBD2 systems
- Understanding diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
- Using OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools
- Basic troubleshooting techniques
Key Topics:
- OBD2 System Overview
- DTC Interpretation
- Scanner Operation
- Basic Diagnostics
9.2. What Advanced Diagnostic Techniques Are Covered in the Advanced Diagnostic Techniques Course?
Course Overview:
- Advanced troubleshooting strategies
- Using oscilloscopes and advanced tools
- Diagnosing complex issues
- Vehicle-specific diagnostics
Key Topics:
- Advanced Troubleshooting
- Oscilloscope Usage
- Complex Diagnostics
- Vehicle-Specific Analysis
9.3. How Can the Engine Performance and Tuning Course Improve Your Skills?
Course Overview:
- Engine performance diagnostics
- Tuning and optimization techniques
- Fuel system analysis
- Emission control systems
Key Topics:
- Engine Diagnostics
- Tuning Techniques
- Fuel System Analysis
- Emission Control
9.4. What Does the Electrical Systems and Wiring Course Include?
Course Overview:
- Electrical system fundamentals
- Wiring diagrams and circuit analysis
- Diagnosing electrical faults
- Repairing electrical systems
Key Topics:
- Electrical Fundamentals
- Wiring Diagrams
- Fault Diagnostics
- System Repair
9.5. What Unique Skills Will You Gain in the Hybrid and Electric Vehicle Diagnostics Course?
Course Overview:
- Hybrid and electric vehicle (EV) systems
- High-voltage safety procedures
- Diagnosing hybrid and EV faults
- Battery management and diagnostics
Key Topics:
- Hybrid and EV Systems
- Safety Procedures
- Fault Diagnostics
- Battery Management
10. What Are Frequently Asked Questions About OBD2 Systems?
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) to help you better understand OBD2 systems.
- FAQ 1: What is OBD2?
- FAQ 2: Where is the OBD2 port located?
- FAQ 3: How do I use an OBD2 scanner?
- FAQ 4: Can I damage my car using an OBD2 scanner?
- FAQ 5: What does a Check Engine Light mean?
- FAQ 6: Can I clear error codes myself?
- FAQ 7: How often should I scan my car for errors?
- FAQ 8: What is CAN bus?
- FAQ 9: Are all OBD2 scanners compatible with my car?
- FAQ 10: How can I stay updated on new OBD2 technologies?
10.1. What Is OBD2?
Answer: OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used to monitor and diagnose vehicle performance. It provides access to a variety of data, including diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), sensor readings, and other information about the engine and related systems.
10.2. Where Is the OBD2 Port Located?
Answer: The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is usually within easy reach and may be covered by a small panel.
10.3. How Do I Use an OBD2 Scanner?
Answer: To use an OBD2 scanner:
- Locate the OBD2 port.
- Plug the scanner into the port.
- Turn on the ignition.
- Follow the scanner’s instructions to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and other data.
10.4. Can I Damage My Car Using an OBD2 Scanner?
Answer: No, using an OBD2 scanner will not damage your car, provided that you follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that you use a scanner that is compatible with your vehicle.
10.5. What Does a Check Engine Light Mean?
Answer: A Check Engine Light indicates that the vehicle’s computer has detected a problem with one or more systems. It is important to retrieve the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to identify the cause of the issue.
10.6. Can I Clear Error Codes Myself?
Answer: Yes, you can clear error codes using an OBD2 scanner. However, it is important to address the underlying issue that caused the code. Clearing the code without fixing the problem will only result in the light turning back on.
10.7. How Often Should I Scan My Car for Errors?
Answer: You should scan your car for errors whenever the Check Engine Light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms. Regular scanning can help identify potential problems early and prevent major repairs.
10.8. What Is CAN Bus?
Answer: CAN (Controller Area Network) bus is a communication system used to allow different modules in a vehicle to communicate with each other. It is essential for modern vehicle diagnostics and control.
10.9. Are All OBD2 Scanners Compatible With My Car?
Answer: Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all cars manufactured after 1996. However, it is important to verify compatibility before using a scanner, especially with older models.
10.10. How Can I Stay Updated on New OBD2 Technologies?
Answer: You can stay updated on new OBD2 technologies by:
- Subscribing to industry publications.
- Attending automotive trade shows.
- Participating in online forums and communities.
- Following automotive experts and influencers on social media.
Is your 2002 Mazda MPV giving you OBD2 troubles? Don’t let diagnostic challenges slow you down! Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN now via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States, and let our experts guide you with top-notch tools, detailed repair solutions, remote support, and technician training. Elevate your diagnostic skills and keep your Mazda MPV running smoothly. Visit CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today!