Ecu Tendon Rehab Exercises are vital for car mechanics to prevent injuries and maintain optimal wrist health. At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide comprehensive guidance on these exercises, along with access to diagnostic tools and expert technical support to enhance your repair work. Explore our resources for technician training and remote assistance, ensuring you stay at the top of your game.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Extensor Carpi Ulnaris (ECU) Muscle
- 1.1. What is the literal meaning of Extensor Carpi Ulnaris?
- 1.2. Why is the ECU muscle important for car mechanics?
- 1.3. What activities commonly use the ECU muscle?
- 1.4. What are common injuries associated with the ECU muscle?
- 2. Common ECU Muscle Injuries in Car Mechanics
- 2.1. What is Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)?
- 2.2. What is ECU Tendonitis?
- 2.3. What are the risk factors for ECU injuries in car mechanics?
- 2.4. How can mechanics prevent ECU injuries?
- 3. Initial Treatment for ECU Muscle Injuries
- 3.1. What is the RICE protocol?
- 3.2. When should a brace or splint be used?
- 3.3. Are medications necessary for ECU injuries?
- 3.4. When is surgery required for ECU injuries?
- 4. Essential ECU Tendon Rehab Exercises for Car Mechanics
- 4.1. What is the Tennis Elbow Stretch?
- 4.2. What is the Eccentric Tennis Elbow Strengthening Exercise?
- 4.3. What are Wrist Extension Exercises?
- 4.4. What are Wrist Flexion Exercises?
- 4.5. What are Ulnar Deviation Exercises?
- 4.6. What are Grip Strengthening Exercises?
- 5. The Importance of Proper Warm-Up
- 5.1. Why is warm-up important?
- 5.2. What are effective warm-up exercises for car mechanics?
- 5.3. How long should a warm-up last?
- 6. Advanced Techniques and Research on ECU Muscle Function
- 6.1. What is Tenodesis of the Extensor Carpi Ulnaris?
- 6.2. How does Tenodesis improve grip strength?
- 6.3. Can Tenodesis help prevent shoulder pain?
- 7. ECU Tendon Rehab Exercises and Diagnostic Tools at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 7.1. What resources does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offer for ECU injury prevention?
- 7.2. How can CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with injury recovery?
- 7.3. What diagnostic tools are available at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN?
- 7.4. What training programs are offered by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN?
- 8. Integrating ECU Tendon Rehab Exercises into Daily Routine
- 8.1. How often should ECU exercises be performed?
- 8.2. How can mechanics incorporate exercises into their workday?
- 8.3. What are some tips for staying motivated?
- 9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of ECU Injury Prevention
- 9.1. Case Study 1: Reducing Tennis Elbow in a Mechanic
- 9.2. Case Study 2: Preventing ECU Tendonitis with Ergonomic Tools
- 9.3. Case Study 3: Improving Grip Strength with Tenodesis
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about ECU Tendon Rehab Exercises
- 10.1. What are the first steps to take if I suspect an ECU injury?
- 10.2. How long does it take to recover from ECU tendonitis?
- 10.3. Can I perform ECU exercises if I have no pain?
- 10.4. What types of tools are considered ergonomic for mechanics?
- 10.5. Are there specific exercises I should avoid with an ECU injury?
- 10.6. How can remote technical support help with my injury recovery?
- 10.7. What are the benefits of online training courses for mechanics?
- 10.8. How can I optimize my workspace to prevent ECU injuries?
- 10.9. What is the role of diet in ECU injury recovery?
- 10.10. How can CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help me stay updated on the latest diagnostic techniques?
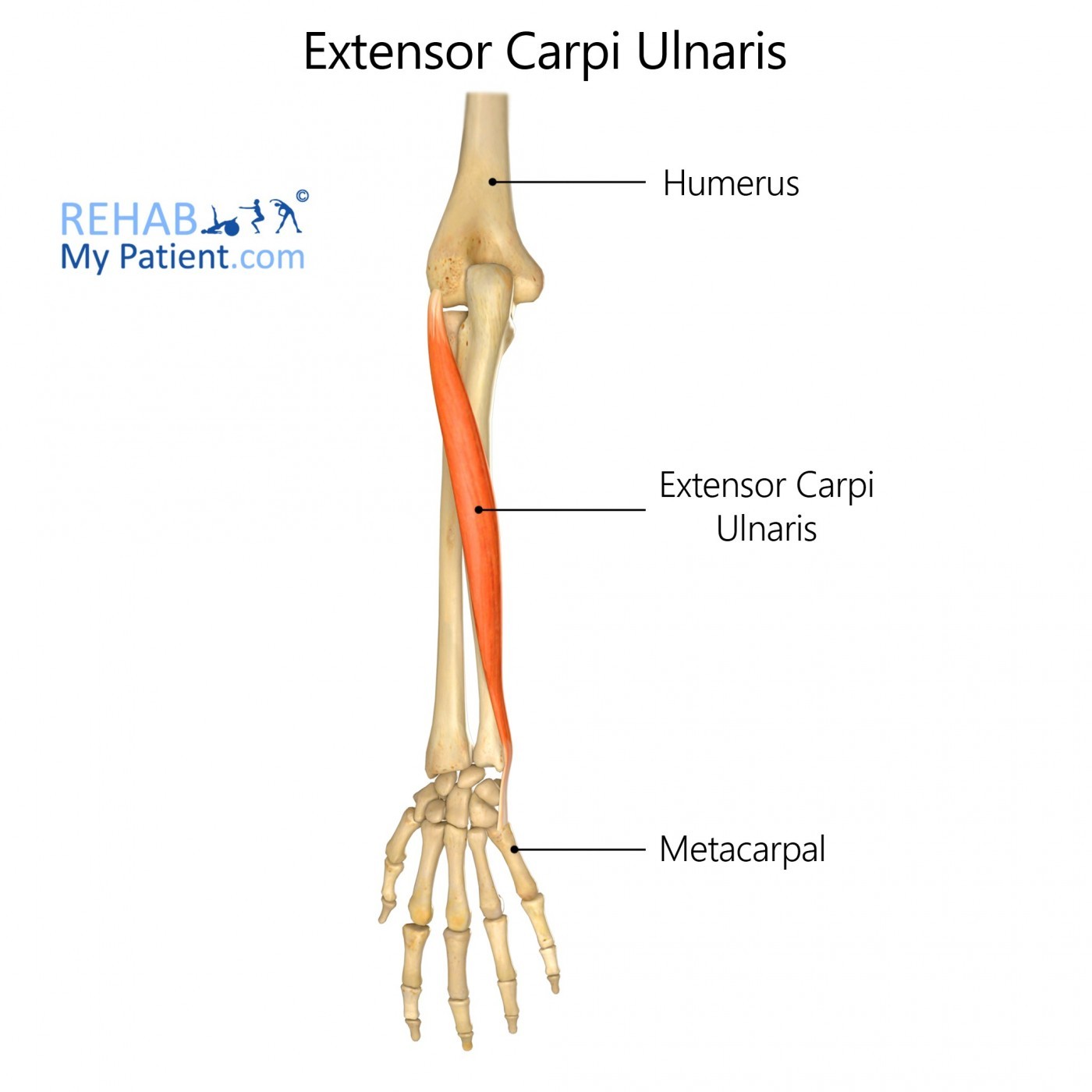
1. Understanding the Extensor Carpi Ulnaris (ECU) Muscle
The extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) is a skeletal muscle located on the ulnar (pinky) side of your forearm. It plays a crucial role in wrist extension and adduction (ulnar deviation).
1.1. What is the literal meaning of Extensor Carpi Ulnaris?
The literal meaning of “Extensor Carpi Ulnaris” is the muscle on the ulnar side that extends the wrist. This muscle’s primary functions are extending and adducting the wrist, making it essential for movements that bend the wrist backward and angle the hand toward the little finger.
1.2. Why is the ECU muscle important for car mechanics?
For car mechanics, the ECU muscle is especially important due to the repetitive and strenuous wrist movements involved in their daily tasks. This includes using hand tools, gripping components, and performing intricate repairs. Activities such as tightening bolts, maneuvering in tight spaces, and repetitive motions can strain the ECU muscle, leading to injuries like tendonitis or tennis elbow.
 Mechanic Working on Car Engine
Mechanic Working on Car Engine
1.3. What activities commonly use the ECU muscle?
Everyday activities that use the ECU muscle include:
- Accelerating a motorbike: The twisting motion engages the ECU muscle.
- Using hand tools: Mechanics frequently use wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers, all requiring wrist stability and movement.
- Gripping: Holding onto tools or parts requires the ECU to stabilize the wrist.
1.4. What are common injuries associated with the ECU muscle?
Common injuries associated with the ECU muscle include tennis elbow and ECU tendonitis. According to a study in the British Journal of Sports Medicine, tennis players often experience ECU injuries, highlighting acute instability, tendinopathy, and muscle rupture. Symptoms of ECU tendonitis include redness, tenderness, and inflammation on the side of the wrist, which worsens when the wrist is squeezed.
2. Common ECU Muscle Injuries in Car Mechanics
Car mechanics are particularly susceptible to ECU muscle injuries due to the repetitive nature of their work.
2.1. What is Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)?
Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a common injury affecting those involved in repetitive arm, elbow, and wrist movements. It is characterized by pain on the outer side of the elbow, often radiating down the forearm. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, tennis elbow affects 1-3% of the population annually, with mechanics being at a higher risk due to the nature of their work.
2.2. What is ECU Tendonitis?
ECU tendonitis involves inflammation of the ECU tendon, leading to pain, tenderness, and swelling on the ulnar side of the wrist. The pain typically worsens with wrist movement or gripping activities.
2.3. What are the risk factors for ECU injuries in car mechanics?
Risk factors for ECU injuries in car mechanics include:
- Repetitive Movements: Continuous use of hand tools and performing the same motions repeatedly.
- Forceful Gripping: Tightening bolts, holding heavy parts, and applying significant force with hand tools.
- Awkward Postures: Working in confined spaces and maintaining uncomfortable wrist positions.
- Vibration: Exposure to vibrating tools can exacerbate wrist strain.
2.4. How can mechanics prevent ECU injuries?
To prevent ECU injuries, mechanics should:
- Use Proper Techniques: Ensure correct posture and body mechanics while working.
- Take Regular Breaks: Avoid prolonged periods of repetitive motions by taking short breaks to stretch and rest the wrist.
- Use Ergonomic Tools: Opt for tools designed to reduce strain on the wrist and forearm.
- Maintain Wrist Strength and Flexibility: Perform regular exercises to strengthen the ECU muscle and improve wrist flexibility.
3. Initial Treatment for ECU Muscle Injuries
The initial treatment for ECU muscle injuries typically involves the RICE protocol: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
3.1. What is the RICE protocol?
The RICE protocol is a standard first-aid treatment for many musculoskeletal injuries, including ECU injuries.
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the pain.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
- Compression: Use a compressive bandage to reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the wrist elevated above heart level to minimize swelling.
3.2. When should a brace or splint be used?
A brace or splint may be advisable depending on the severity of the injury. It helps to immobilize the wrist, providing support and reducing strain on the ECU tendon. According to the Journal of Hand Therapy, wrist splints can significantly reduce pain and improve function in individuals with ECU tendonitis.
3.3. Are medications necessary for ECU injuries?
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger pain medications or corticosteroid injections.
3.4. When is surgery required for ECU injuries?
Surgery is rarely required for ECU injuries. It is typically considered only when conservative treatments fail to provide relief. Surgical options may include tendon repair, tendon release, or reconstruction of the ECU tendon sheath.
4. Essential ECU Tendon Rehab Exercises for Car Mechanics
After the initial treatment, specific exercises are crucial for rehabilitating the ECU muscle and preventing future injuries.
4.1. What is the Tennis Elbow Stretch?
The Tennis Elbow Stretch is a simple yet effective exercise for preventing and treating ECU injuries.
-
How to perform it:
- Hold your arm out in front of you.
- Straighten your arm and rotate it inwards (so your elbow crease faces down).
- Bend your wrist back, pointing your fingers towards the floor.
- Hold this position for 20-30 seconds to create a stretch.
-
Benefits: This stretch targets the forearm extensor muscles, relieving tennis elbow pain and other repetitive strain injuries.
 Tennis Elbow Stretch
Tennis Elbow Stretch
4.2. What is the Eccentric Tennis Elbow Strengthening Exercise?
The Eccentric Tennis Elbow Strengthening Exercise is highly effective for relieving tennis elbow pain.
-
How to perform it:
- Rest your arm on a table with your palm facing down.
- Hold a light dumbbell (1-2 kg).
- Use your other hand to lift your hand upwards.
- Slowly lower the weight, allowing it to pull your hand back down in a controlled movement.
- Repeat this process, lifting your hand upwards again with assistance and then slowly lowering the weight.
-
Benefits: Eccentric exercises are excellent for rehabilitating the wrist, forearm, and elbow. They strengthen the muscle as it lengthens, promoting healing and reducing pain.
 Eccentric Tennis Elbow Exercise
Eccentric Tennis Elbow Exercise
4.3. What are Wrist Extension Exercises?
Wrist extension exercises strengthen the ECU muscle and improve wrist stability.
-
How to perform it:
- Sit comfortably with your forearm resting on a table, palm facing down.
- Hold a light dumbbell in your hand.
- Slowly lift your hand upwards, extending your wrist.
- Lower the weight back down in a controlled manner.
- Repeat this exercise for 10-15 repetitions.
-
Benefits: These exercises improve wrist strength and endurance, essential for mechanics who perform repetitive tasks.
4.4. What are Wrist Flexion Exercises?
Wrist flexion exercises complement wrist extension exercises by strengthening the opposing muscles.
-
How to perform it:
- Sit comfortably with your forearm resting on a table, palm facing up.
- Hold a light dumbbell in your hand.
- Slowly curl your hand upwards, flexing your wrist.
- Lower the weight back down in a controlled manner.
- Repeat this exercise for 10-15 repetitions.
-
Benefits: These exercises improve overall wrist balance and reduce the risk of injury.
4.5. What are Ulnar Deviation Exercises?
Ulnar deviation exercises target the ECU muscle directly, improving its strength and function.
-
How to perform it:
- Sit comfortably with your forearm resting on a table, palm facing down.
- Hold a light dumbbell in your hand.
- Move your hand to the side, towards your little finger (ulnar deviation).
- Return to the starting position in a controlled manner.
- Repeat this exercise for 10-15 repetitions.
-
Benefits: These exercises enhance the ECU muscle’s ability to stabilize and move the wrist.
4.6. What are Grip Strengthening Exercises?
Grip strengthening exercises improve the overall strength of the hand and forearm, supporting the ECU muscle.
-
How to perform it:
- Use a hand gripper or stress ball.
- Squeeze the gripper or ball tightly and hold for a few seconds.
- Release and repeat for 10-15 repetitions.
-
Benefits: A strong grip reduces strain on the wrist during tasks that require holding or gripping tools.
5. The Importance of Proper Warm-Up
Proper warm-up before any physical activity is essential for preventing injuries.
5.1. Why is warm-up important?
Warming up increases blood flow to the muscles, improving their flexibility and reducing the risk of strains and tears. According to the Journal of Athletic Training, a proper warm-up can significantly reduce the incidence of musculoskeletal injuries.
5.2. What are effective warm-up exercises for car mechanics?
Effective warm-up exercises for car mechanics include:
- Wrist Rotations: Rotate your wrists in both directions for 1-2 minutes.
- Hand Clenches: Open and close your hands repeatedly for 1-2 minutes.
- Arm Circles: Perform small arm circles in both directions for 1-2 minutes.
- Stretching: Gently stretch your wrist extensors and flexors.
5.3. How long should a warm-up last?
A warm-up should last at least 5-10 minutes to adequately prepare the muscles for activity.
6. Advanced Techniques and Research on ECU Muscle Function
Recent research has provided insights into optimizing grip strength and ergonomic hand use.
6.1. What is Tenodesis of the Extensor Carpi Ulnaris?
Tenodesis of the extensor carpi ulnaris involves surgically reattaching the ECU tendon to improve wrist function. According to a study in the Journal of Hand Surgery, tenodesis can significantly improve grip strength in patients with cervical spinal cord injury or tetraplegia.
6.2. How does Tenodesis improve grip strength?
By rebalancing the wrist, tenodesis optimizes the biomechanics of the hand, allowing for stronger and more controlled grip. The study showed that grip strength could be doubled when grip reconstruction was performed with tenodesis of this muscle.
6.3. Can Tenodesis help prevent shoulder pain?
Yes, tenodesis may help prevent shoulder pain, which is common in patients with cervical spinal cord injury. By improving wrist function, it reduces the compensatory movements that can lead to shoulder strain.
7. ECU Tendon Rehab Exercises and Diagnostic Tools at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of maintaining physical health alongside technical expertise.
7.1. What resources does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offer for ECU injury prevention?
We offer a range of resources to help car mechanics prevent ECU injuries, including:
- Detailed Guides on ECU Exercises: Step-by-step instructions and videos demonstrating proper techniques for ECU stretches and strengthening exercises.
- Ergonomic Tool Recommendations: Information on tools designed to reduce wrist strain and improve comfort.
- Workplace Ergonomic Assessments: Guidance on optimizing your workspace to minimize the risk of injury.
7.2. How can CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with injury recovery?
If you experience an ECU injury, CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can assist with your recovery through:
- Rehabilitation Protocols: Comprehensive rehabilitation protocols developed in consultation with physical therapists.
- Remote Technical Support: Access to expert technicians who can provide advice and support during your recovery.
7.3. What diagnostic tools are available at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN?
We offer a variety of diagnostic tools to help mechanics accurately diagnose and repair vehicles, reducing the need for repetitive and strenuous movements.
- Advanced Diagnostic Scanners: Quickly identify vehicle issues, reducing diagnostic time.
- Ergonomic Hand Tools: Designed to minimize strain and improve comfort.
7.4. What training programs are offered by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN?
Our training programs are designed to enhance your skills and knowledge, reducing the physical strain associated with complex repairs.
- Online Courses: Covering a wide range of topics, from basic diagnostics to advanced repair techniques.
- Hands-On Workshops: Providing practical experience with the latest tools and techniques.
- Certification Programs: Demonstrating your expertise and commitment to quality.
8. Integrating ECU Tendon Rehab Exercises into Daily Routine
Consistency is key when it comes to preventing and managing ECU injuries.
8.1. How often should ECU exercises be performed?
ECU exercises should be performed daily, even when you are not experiencing pain. Regular exercise helps maintain wrist strength and flexibility, preventing future injuries.
8.2. How can mechanics incorporate exercises into their workday?
Mechanics can incorporate ECU exercises into their workday by:
- Performing stretches during breaks: Take a few minutes during breaks to perform wrist stretches.
- Doing strengthening exercises after work: Dedicate 10-15 minutes after work to perform wrist strengthening exercises.
- Using ergonomic tools: Choose tools that reduce strain on the wrist and forearm.
8.3. What are some tips for staying motivated?
Staying motivated with ECU exercises can be challenging, but these tips can help:
- Set realistic goals: Start with a few simple exercises and gradually increase the intensity and duration.
- Track your progress: Keep a record of your exercises and track your progress over time.
- Find a workout buddy: Exercising with a friend or colleague can provide motivation and support.
- Reward yourself: Celebrate your achievements with small rewards to stay motivated.
9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of ECU Injury Prevention
Real-world examples highlight the effectiveness of ECU injury prevention strategies.
9.1. Case Study 1: Reducing Tennis Elbow in a Mechanic
A mechanic who had been experiencing recurrent tennis elbow pain implemented a daily routine of ECU stretches and strengthening exercises. Within a few weeks, his pain had significantly reduced, and he was able to work more comfortably.
9.2. Case Study 2: Preventing ECU Tendonitis with Ergonomic Tools
A workshop owner invested in ergonomic hand tools for his mechanics. The tools reduced wrist strain, and the incidence of ECU tendonitis among his employees decreased significantly.
9.3. Case Study 3: Improving Grip Strength with Tenodesis
A patient with tetraplegia underwent tenodesis of the ECU muscle. His grip strength doubled, allowing him to perform daily tasks with greater ease and independence.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about ECU Tendon Rehab Exercises
Here are some frequently asked questions about ECU tendon rehab exercises:
10.1. What are the first steps to take if I suspect an ECU injury?
If you suspect an ECU injury, the first steps are to rest the affected wrist, apply ice, compress the area with a bandage, and elevate the wrist. Over-the-counter pain relievers can also help reduce pain and inflammation.
10.2. How long does it take to recover from ECU tendonitis?
The recovery time for ECU tendonitis varies depending on the severity of the injury. With proper treatment and rehabilitation, most people recover within a few weeks to several months.
10.3. Can I perform ECU exercises if I have no pain?
Yes, you can and should perform ECU exercises even if you have no pain. Regular exercise helps maintain wrist strength and flexibility, preventing future injuries.
10.4. What types of tools are considered ergonomic for mechanics?
Ergonomic tools for mechanics include those with cushioned grips, angled handles, and vibration dampening features. These tools reduce strain on the wrist and forearm, improving comfort and reducing the risk of injury.
10.5. Are there specific exercises I should avoid with an ECU injury?
With an ECU injury, avoid exercises that cause pain or discomfort. High-impact activities and heavy lifting should also be avoided until the injury has healed.
10.6. How can remote technical support help with my injury recovery?
Remote technical support can provide guidance on proper exercise techniques, ergonomic tool recommendations, and workplace ergonomic assessments. Expert technicians can also answer your questions and provide support during your recovery.
10.7. What are the benefits of online training courses for mechanics?
Online training courses offer flexibility and convenience, allowing you to learn at your own pace and on your own schedule. They can also provide access to a wide range of topics and expert instructors.
10.8. How can I optimize my workspace to prevent ECU injuries?
To optimize your workspace, ensure that your work surface is at a comfortable height, use proper lighting, and organize your tools and equipment so that they are easily accessible.
10.9. What is the role of diet in ECU injury recovery?
A healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support ECU injury recovery. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
10.10. How can CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help me stay updated on the latest diagnostic techniques?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides continuous updates on the latest diagnostic techniques through online courses, hands-on workshops, and certification programs. Our resources ensure that you stay at the forefront of automotive technology.
Prioritizing ECU tendon rehab exercises and proper techniques is crucial for car mechanics to maintain their physical health and prolong their careers. At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing the resources and support you need to thrive in the automotive industry.
Ready to take control of your health and career? Contact us today for personalized guidance on ECU tendon rehab exercises, ergonomic tool recommendations, and expert technical support. Enhance your skills, reduce your risk of injury, and stay ahead of the curve with CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Contact Information:
- Address: 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Don’t wait—reach out now and discover how CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can revolutionize your approach to automotive diagnostics and repair.