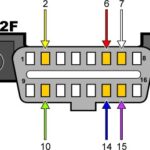
Taking information from an ECU is essential for modern car diagnostics; CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides tools, repair guides, and tech support to help you interpret ECU data accurately, ensuring effective car maintenance and repair. Our resources extend to technician training and remote support, enhancing your diagnostic capabilities and keeping you updated with the latest in automotive technology.
Contents
- 1. What is an ECU and Why is Extracting Data Important?
- 1.1 The Role of the ECU in Modern Vehicles
- 1.2 Why Accessing ECU Data is Crucial
- 1.3 Key Types of Data Available from the ECU
- 2. Essential Tools for Extracting ECU Information
- 2.1 Overview of OBD-II Scanners
- 2.2 Types of OBD-II Scanners
- 2.3 Diagnostic Software Options
- 2.4 Interface Cables and Adapters
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide to Taking Information from an ECU
- 3.1 Connecting the OBD-II Scanner
- 3.2 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.3 Interpreting DTCs
- 3.4 Accessing Live Sensor Data
- 3.5 Analyzing Freeze Frame Data
- 3.6 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 4. Advanced Techniques for ECU Data Extraction
- 4.1 ECU Flashing and Programming
- 4.2 Data Logging and Analysis
- 4.3 Using Oscilloscopes for Advanced Diagnostics
- 5. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- 5.1 Incorrect Interpretation of DTCs
- 5.2 Using Incompatible Tools
- 5.3 Failing to Update Software
- 5.4 Neglecting Battery Voltage
- 5.5 Incorrect Flashing Procedures
- 6. Maximizing the Benefits of ECU Data with CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 6.1 Utilizing Comprehensive Repair Guides
- 6.2 Accessing Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 6.3 Receiving Expert Technical Support
- 6.4 Enhancing Skills with Technician Training
- 6.5 Remote Support for Complex Issues
- 7. The Future of ECU Diagnostics
- 7.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
- 7.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 7.3. Enhanced Vehicle Cybersecurity
- 8. Real-World Applications and Case Studies
- 8.1 Diagnosing Intermittent Misfires
- 8.2 Improving Fuel Efficiency
- 8.3 Preventing Catastrophic Engine Failure
- 9. Compliance and Regulations
- 9.1 Data Privacy Laws
- 9.2 Right to Repair Laws
- 9.3 Emissions Regulations
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is an ECU and Why is Extracting Data Important?
The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is essentially the brain of a modern vehicle, managing various systems from the engine to the transmission and beyond. Extracting data from an ECU is critical for diagnosing issues, optimizing performance, and ensuring the vehicle operates within specified parameters. Accessing this data allows technicians and car enthusiasts to understand a vehicle’s real-time condition, historical performance, and potential problems.
1.1 The Role of the ECU in Modern Vehicles
The ECU, or Engine Control Unit, is responsible for monitoring and controlling nearly every aspect of a modern vehicle’s operation. According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), ECUs manage everything from fuel injection and ignition timing to anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and electronic stability control (ESC). This centralized control allows for optimized performance, reduced emissions, and enhanced safety features.
1.2 Why Accessing ECU Data is Crucial
Accessing ECU data is crucial for several reasons:
- Diagnostics: It allows technicians to identify the root cause of issues by reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and analyzing sensor data.
- Performance Tuning: Tuners can modify ECU parameters to increase horsepower, improve fuel efficiency, or alter other performance characteristics.
- Maintenance: By monitoring data such as oil temperature, coolant levels, and mileage, you can anticipate maintenance needs and prevent potential breakdowns.
- Security: ECU data can be used to track vehicle usage, monitor driver behavior, and even recover stolen vehicles, according to research from the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute.
1.3 Key Types of Data Available from the ECU
The ECU stores and provides access to various types of data, including:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific issues within the vehicle’s systems.
- Live Sensor Data: Real-time readings from sensors throughout the vehicle, such as engine speed (RPM), vehicle speed, oxygen sensor readings, and throttle position.
- Freeze Frame Data: A snapshot of sensor data captured at the moment a DTC was triggered.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): A unique identifier for the vehicle.
- Calibration Information: Data related to the ECU’s programming and configuration.
2. Essential Tools for Extracting ECU Information
To effectively extract data from an ECU, you need the right tools. These typically include OBD-II scanners, specialized diagnostic software, and interfaces that allow communication between your computer and the vehicle’s ECU.
2.1 Overview of OBD-II Scanners
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) scanners are the most common tools for accessing ECU data. They connect to the vehicle’s OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard, and allow you to read DTCs, view live data, and perform basic diagnostic tests.
2.2 Types of OBD-II Scanners
There are several types of OBD-II scanners available, each with varying capabilities:
- Basic Code Readers: These are entry-level scanners that can read and clear DTCs. They are suitable for basic diagnostics and DIY enthusiasts.
- Mid-Range Scanners: These offer additional features such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and the ability to perform some basic tests.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: These are advanced tools used by professional technicians. They offer comprehensive diagnostic capabilities, including bidirectional control, advanced coding, and access to manufacturer-specific data.
2.3 Diagnostic Software Options
In addition to OBD-II scanners, diagnostic software can provide more in-depth access to ECU data. These software solutions often include advanced features such as:
- Detailed DTC Information: Comprehensive explanations of DTCs, including possible causes and troubleshooting steps.
- Advanced Data Analysis: Tools for analyzing live data, graphing sensor readings, and identifying trends.
- Bi-Directional Control: The ability to send commands to the ECU to activate components, perform tests, and reset systems.
- ECU Programming: The ability to reprogram or update the ECU’s software.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive guides and support for selecting and using the best diagnostic software for your needs.
2.4 Interface Cables and Adapters
To connect your OBD-II scanner or computer to the vehicle’s ECU, you’ll need the appropriate interface cables and adapters. These may include:
- OBD-II Cables: Standard cables for connecting to the OBD-II port.
- USB Interfaces: Cables that connect the OBD-II scanner to a computer via USB.
- Bluetooth Adapters: Wireless adapters that allow you to connect to the ECU using a smartphone or tablet.
- Manufacturer-Specific Adapters: Some vehicles may require proprietary adapters to access certain ECU functions.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Taking Information from an ECU
Extracting data from an ECU involves a series of steps, from connecting the scanner to interpreting the data. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
3.1 Connecting the OBD-II Scanner
- Locate the OBD-II Port: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned off before connecting the scanner.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD-II scanner to the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
3.2 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Power on the Scanner: Follow the scanner’s instructions to power it on.
- Select “Read Codes”: Navigate the scanner’s menu to find the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option.
- View the Codes: The scanner will display any stored DTCs. Record these codes for further analysis.
3.3 Interpreting DTCs
DTCs are five-character codes that provide information about specific issues. The first character indicates the system affected:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission)
- B: Body (interior, exterior)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension)
- U: Network (communication systems)
The remaining characters provide more specific information about the fault. Consult a repair manual or online database, such as those available at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, to understand the meaning of each code and potential causes.
3.4 Accessing Live Sensor Data
- Select “Live Data”: Navigate the scanner’s menu to find the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option.
- Choose Parameters: Select the specific sensor data you want to monitor, such as RPM, vehicle speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- View the Data: The scanner will display real-time data from the selected sensors.
3.5 Analyzing Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data provides a snapshot of sensor readings at the moment a DTC was triggered. This can be valuable for diagnosing intermittent issues.
- Select “Freeze Frame”: Navigate the scanner’s menu to find the “Freeze Frame” option.
- View the Data: The scanner will display the stored freeze frame data associated with a specific DTC.
3.6 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
After addressing the underlying issue, you can clear the DTCs from the ECU.
- Select “Clear Codes”: Navigate the scanner’s menu to find the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option.
- Confirm the Action: Follow the scanner’s prompts to confirm that you want to clear the codes.
- Verify the Codes are Cleared: After clearing the codes, re-read them to ensure they have been successfully erased.
Table: Common OBD-II Codes and Their Meanings
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, vacuum leaks, wiring issues |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leaks, faulty oxygen sensor, fuel system issues |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak) | Loose or damaged fuel cap, cracked or damaged EVAP hoses, faulty purge valve |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Dirty or faulty idle air control valve, vacuum leaks, throttle body issues |
| B1000 | Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Internal Failure | Faulty ECU, wiring issues, poor connections |
| C0035 | Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Faulty wheel speed sensor, wiring issues, damaged sensor ring |
| U0100 | Lost Communication With ECU | Wiring issues, faulty ECU, CAN bus problems |
4. Advanced Techniques for ECU Data Extraction
For more in-depth diagnostics and performance tuning, advanced techniques are required. These techniques often involve specialized software and hardware, as well as a deeper understanding of vehicle systems.
4.1 ECU Flashing and Programming
ECU flashing, also known as reprogramming, involves replacing the ECU’s existing software with a modified version. This can be done to improve performance, adjust for modifications, or fix software bugs.
Tools Required:
- ECU Flashing Software: Software specific to the vehicle’s make and model.
- Interface Cable: A specialized cable for connecting to the ECU.
- Stable Power Supply: To prevent interruptions during the flashing process.
Procedure:
- Connect the Interface Cable: Connect the cable between your computer and the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Launch the Flashing Software: Open the ECU flashing software and select the appropriate vehicle and ECU type.
- Select the Firmware: Choose the firmware file you want to flash to the ECU.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: Carefully follow the software’s instructions to initiate the flashing process.
- Verify the Flash: After the flash is complete, verify that the new firmware has been successfully installed.
Caution: ECU flashing can be risky and should only be performed by experienced technicians. Incorrect flashing can damage the ECU and render the vehicle inoperable. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers training and support to ensure you can perform ECU flashing safely and effectively.
4.2 Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging involves recording ECU data over a period of time while the vehicle is in operation. This data can then be analyzed to identify performance issues, diagnose problems, or fine-tune engine parameters.
Tools Required:
- Data Logging Software: Software that can record and analyze ECU data.
- OBD-II Interface: A device that connects to the OBD-II port and transmits data to the software.
Procedure:
- Connect the Interface: Connect the OBD-II interface to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Launch the Data Logging Software: Open the data logging software and select the parameters you want to record.
- Start Logging: Begin recording data while driving the vehicle under various conditions.
- Analyze the Data: After logging, analyze the data using the software’s graphing and analysis tools to identify trends and anomalies.
4.3 Using Oscilloscopes for Advanced Diagnostics
Oscilloscopes are advanced diagnostic tools that allow you to visualize electrical signals in real-time. This can be useful for diagnosing issues with sensors, actuators, and other electronic components.
How to Use an Oscilloscope:
- Connect the Oscilloscope: Connect the oscilloscope probes to the circuit you want to test.
- Set the Time and Voltage Scales: Adjust the oscilloscope’s settings to display the signal clearly.
- Analyze the Waveform: Observe the waveform to identify any abnormalities, such as signal dropouts, noise, or incorrect voltage levels.
According to a study by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), oscilloscopes can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce troubleshooting time.
5. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Extracting data from an ECU can be complex, and it’s easy to make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
5.1 Incorrect Interpretation of DTCs
Misinterpreting DTCs can lead to incorrect diagnoses and unnecessary repairs. Always consult a reliable repair manual or database, such as those provided by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, to understand the meaning of each code.
5.2 Using Incompatible Tools
Using the wrong OBD-II scanner or software can result in inaccurate data or even damage to the ECU. Ensure that the tools you are using are compatible with the vehicle’s make and model.
5.3 Failing to Update Software
Outdated diagnostic software may not have the latest DTC definitions or vehicle information. Regularly update your software to ensure accurate and reliable diagnostics.
5.4 Neglecting Battery Voltage
Low battery voltage can interfere with ECU communication and cause inaccurate readings. Ensure the vehicle’s battery is fully charged before performing diagnostics.
5.5 Incorrect Flashing Procedures
Incorrect ECU flashing procedures can damage the ECU and render the vehicle inoperable. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and use a stable power supply.
6. Maximizing the Benefits of ECU Data with CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a range of resources to help you maximize the benefits of ECU data extraction, including comprehensive repair guides, advanced diagnostic tools, and expert technical support.
6.1 Utilizing Comprehensive Repair Guides
Our repair guides offer detailed information on diagnosing and repairing a wide range of vehicle issues. These guides include step-by-step instructions, wiring diagrams, and troubleshooting tips to help you resolve problems quickly and effectively.
6.2 Accessing Advanced Diagnostic Tools
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers access to advanced diagnostic tools that can provide in-depth insights into your vehicle’s systems. These tools include professional-grade OBD-II scanners, data logging software, and ECU flashing tools.
6.3 Receiving Expert Technical Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert technical support and guidance. Whether you need help interpreting DTCs, analyzing data, or performing advanced diagnostics, we are here to assist you. Contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance.
6.4 Enhancing Skills with Technician Training
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive technician training programs designed to enhance your diagnostic skills and keep you up-to-date with the latest automotive technology. Our training programs cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Basic Diagnostics: Understanding OBD-II systems, reading DTCs, and interpreting live data.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Using oscilloscopes, data logging, and ECU flashing techniques.
- Vehicle Systems: In-depth knowledge of engine, transmission, brake, and electrical systems.
6.5 Remote Support for Complex Issues
For complex diagnostic issues, CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides remote support services. Our technicians can remotely access your diagnostic tools and provide real-time guidance to help you resolve even the most challenging problems.
7. The Future of ECU Diagnostics
The field of ECU diagnostics is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging all the time. Staying up-to-date with these advancements is essential for automotive technicians and enthusiasts.
7.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
AI is increasingly being used to enhance ECU diagnostics. AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential issues before they become major problems. These tools can also provide technicians with more accurate and efficient troubleshooting guidance.
7.2. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostic platforms allow technicians to access vehicle data and diagnostic tools from anywhere with an internet connection. This can improve collaboration, streamline workflows, and enable remote diagnostics.
7.3. Enhanced Vehicle Cybersecurity
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming an increasingly important concern. Modern diagnostic tools include features to protect against unauthorized access to the ECU and other vehicle systems.
8. Real-World Applications and Case Studies
To illustrate the practical benefits of extracting ECU data, here are a few real-world applications and case studies:
8.1 Diagnosing Intermittent Misfires
A vehicle owner complained of intermittent misfires that were difficult to diagnose. By using data logging software, a technician was able to record ECU data while driving the vehicle. The data revealed that the misfires were occurring under specific driving conditions, such as during acceleration. Further analysis of the data identified a faulty fuel injector as the cause of the misfires.
8.2 Improving Fuel Efficiency
A fleet operator wanted to improve the fuel efficiency of their vehicles. By using ECU data, they were able to identify driving behaviors that were contributing to poor fuel economy, such as excessive idling and hard acceleration. By implementing driver training programs, they were able to reduce these behaviors and improve fuel efficiency by 15%.
8.3 Preventing Catastrophic Engine Failure
A vehicle owner noticed that their engine was running hotter than usual. By monitoring ECU data, they were able to identify a failing water pump before it caused catastrophic engine failure. By replacing the water pump in a timely manner, they were able to avoid costly repairs and downtime.
9. Compliance and Regulations
When extracting data from an ECU, it’s important to be aware of any applicable compliance and regulations. These may include:
9.1 Data Privacy Laws
Data privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, may apply to the collection and use of vehicle data. Ensure that you are complying with these laws when extracting and using ECU data.
9.2 Right to Repair Laws
Right to repair laws, which are being considered in many jurisdictions, aim to ensure that independent repair shops have access to the same diagnostic and repair information as authorized dealers. These laws can impact the availability of ECU data and diagnostic tools.
9.3 Emissions Regulations
Emissions regulations, such as those enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, may require that vehicles meet certain emissions standards. Modifying ECU parameters to bypass these regulations can result in fines and penalties.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the most common reason for needing to extract data from an ECU?
The most common reason is for diagnosing vehicle issues by reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and analyzing live sensor data to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
Q2: Can I extract ECU data myself, or do I need a professional?
You can extract ECU data yourself with an OBD-II scanner, but interpreting the data and performing advanced diagnostics often requires professional expertise. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers tools and support for both DIY enthusiasts and professional technicians.
Q3: What type of OBD-II scanner should I buy?
The type of scanner you need depends on your diagnostic needs. Basic code readers are suitable for simple tasks, while professional-grade scanners offer comprehensive capabilities for advanced diagnostics.
Q4: Is it safe to flash or reprogram my ECU?
ECU flashing can be risky if not done correctly. It’s essential to follow manufacturer instructions and use reliable software. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides training to ensure safe and effective ECU flashing.
Q5: How can I improve my skills in ECU diagnostics?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers technician training programs that cover basic and advanced diagnostics, ensuring you stay up-to-date with the latest automotive technology.
Q6: What kind of support does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provide for ECU diagnostics?
We offer comprehensive repair guides, advanced diagnostic tools, expert technical support, and remote assistance for complex issues. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate help.
Q7: How often should I update my diagnostic software?
You should update your diagnostic software regularly to ensure accurate DTC definitions, access to the latest vehicle information, and optimal performance.
Q8: What are the potential risks of misinterpreting DTCs?
Misinterpreting DTCs can lead to incorrect diagnoses, unnecessary repairs, and wasted time and money. Always consult a reliable repair manual or database, such as those provided by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Q9: Can ECU data be used for performance tuning?
Yes, ECU data can be used to modify engine parameters, increase horsepower, improve fuel efficiency, and adjust other performance characteristics. However, this should be done by experienced professionals to avoid damaging the engine.
Q10: What are the legal considerations when extracting and using ECU data?
Be aware of data privacy laws and right-to-repair laws in your jurisdiction. Ensure that you are complying with these regulations when extracting and using ECU data.
Extracting information from an ECU is a powerful tool for diagnosing and maintaining modern vehicles. With the right tools, techniques, and support from CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can unlock the full potential of ECU data and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Are you ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics and repair process? Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today! Call us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for expert guidance, advanced tools, and comprehensive training. Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a passionate DIY enthusiast, we have the solutions you need to succeed. Don’t wait—empower yourself with the knowledge and resources to keep your vehicle performing at its best! Our office is located at 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States.