The Irb Ecu, referring to an Institutional Review Board (IRB) approved Electronic Control Unit (ECU) research, ensures ethical and regulatory compliance in automotive research involving human subjects. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers advanced diagnostic tools, repair guidance, and technical support to help automotive professionals understand and navigate the complexities of IRB ECU related automotive systems. These resources enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficiency, making automotive repair more effective and compliant.
Contents
- 1. Understanding IRB (Institutional Review Board) in Automotive Research
- 1.1. Ethical Oversight in Automotive ECU Research
- 1.1.1. Key Responsibilities of an IRB
- 1.1.2. Impact on ECU Testing
- 1.2. Regulatory Framework for Automotive Research
- 1.2.1. Ensuring Compliance
- 2. ECU (Electronic Control Unit) Basics
- 2.1. Core Functions of an ECU
- 2.2. Advancements in ECU Technology
- 2.3. Common ECU Issues and Diagnostic Techniques
- 3. The Interplay of IRB ECU in Automotive Diagnostics
- 3.1. Ethical Considerations in Diagnostic Testing
- 3.2. Diagnostic Tools and IRB Compliance
- 3.3. Case Studies: IRB ECU in Action
- 4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for IRB ECU Systems
- 4.1. CAN Bus Diagnostics
- 4.2. ECU Programming and Reflashing
- 4.3. Data Logging and Analysis
- 5. The Role of CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in IRB ECU Diagnostics
- 5.1. Diagnostic Tools Offered
- 5.2. Training Programs
- 5.3. Technical Support and Resources
- 6. Future Trends in IRB ECU Automotive Diagnostics
- 6.1. The Role of AI and Machine Learning
- 6.2. The Growth of Remote Diagnostics
- 6.3. Cybersecurity Considerations
- 7. Best Practices for Maintaining IRB Compliance in Automotive Diagnostics
- 7.1. Informed Consent Procedures
- 7.2. Data Privacy and Security Measures
- 7.3. Regular Audits and Training
- 8. Common Mistakes to Avoid in IRB ECU Diagnostics
- 8.1. Ignoring Privacy Concerns
- 8.2. Neglecting Security Protocols
- 8.3. Lack of Documentation
- 9. The Economic Impact of Effective IRB ECU Diagnostics
- 9.1. Reduced Repair Time
- 9.2. Improved Vehicle Reliability
- 9.3. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
- 10. Resources and Support for Automotive Professionals
- 10.1. Industry Associations
- 10.2. Online Forums and Communities
- 10.3. Government Agencies
- FAQ: IRB ECU and Automotive Diagnostics
1. Understanding IRB (Institutional Review Board) in Automotive Research
What exactly does IRB stand for, and what’s its role in automotive research?
An IRB stands for Institutional Review Board, a committee established to review and approve research involving human subjects. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the primary purpose of an IRB is to protect the rights and welfare of human subjects recruited to participate in research activities. In the context of automotive research, this oversight ensures that any studies involving drivers, passengers, or mechanics adhere to ethical guidelines and regulatory requirements.
1.1. Ethical Oversight in Automotive ECU Research
How does IRB oversight impact the development and testing of automotive ECUs?
IRB oversight is critical in automotive research, especially when dealing with Electronic Control Units (ECUs). ECUs are sophisticated systems that control various functions in a vehicle, from engine management to safety features. When research involves testing these systems with human subjects, IRB approval is essential to guarantee that the studies are conducted ethically and safely.
1.1.1. Key Responsibilities of an IRB
What specific responsibilities does an IRB have in reviewing automotive research proposals?
The IRB’s responsibilities include:
- Reviewing Research Protocols: Evaluating study designs to ensure they minimize risks to participants.
- Informed Consent: Ensuring that participants are fully informed about the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits.
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Protecting participants’ personal information and data.
- Monitoring Ongoing Research: Continuously monitoring the research to ensure compliance with ethical standards and regulations.
According to 45 CFR 46.109, the IRB shall review and have authority to approve, require modifications in (to secure approval), or disapprove all research activities covered by this policy.
1.1.2. Impact on ECU Testing
How does IRB approval affect the practical aspects of ECU testing and validation?
IRB approval significantly impacts how ECU testing and validation are conducted. Researchers must design studies that prioritize the safety and well-being of participants. This may involve:
- Simulated Environments: Using driving simulators to replicate real-world conditions without exposing participants to actual risks.
- Limited On-Road Testing: Restricting on-road testing to controlled environments with experienced drivers and safety measures in place.
- Data Privacy: Implementing strict protocols for data collection and storage to protect participants’ privacy.
1.2. Regulatory Framework for Automotive Research
What are the primary regulations governing automotive research involving human subjects?
The regulatory framework for automotive research involving human subjects is primarily governed by:
- The Common Rule (45 CFR 46): A set of regulations outlining the basic provisions for protecting human subjects in research, including informed consent, IRB review, and record-keeping requirements.
- FDA Regulations (21 CFR Parts 50, 56): Regulations specific to research involving products regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), such as medical devices integrated into vehicles.
- State and Local Laws: Additional regulations that may apply depending on the location of the research.
1.2.1. Ensuring Compliance
How can automotive researchers ensure compliance with these regulations?
To ensure compliance, researchers should:
- Submit Research Proposals to the IRB: Obtain IRB approval before commencing any research involving human subjects.
- Develop Comprehensive Protocols: Create detailed research protocols that address all ethical and regulatory requirements.
- Obtain Informed Consent: Ensure that all participants provide informed consent before participating in the study.
- Maintain Accurate Records: Keep thorough records of all research activities, including IRB correspondence, consent forms, and data collection procedures.
2. ECU (Electronic Control Unit) Basics
What is an ECU, and what functions does it control in modern vehicles?
An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is a critical component in modern vehicles, acting as the central processing unit that manages and controls various systems. According to Robert Bosch GmbH, a leading automotive supplier, ECUs optimize engine performance, enhance safety, and improve fuel efficiency. ECUs use sensor data to adjust engine parameters, control transmission, manage braking systems, and regulate emissions.
2.1. Core Functions of an ECU
What are the primary systems managed by an ECU?
The core functions managed by an ECU include:
- Engine Management: Controlling fuel injection, ignition timing, and air-fuel mixture to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
- Transmission Control: Managing gear shifting and clutch engagement in automatic transmissions.
- Braking Systems: Regulating anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and traction control systems (TCS) to enhance vehicle safety.
- Emissions Control: Monitoring and controlling exhaust emissions to meet environmental regulations.
- Safety Systems: Managing airbag deployment, seatbelt pretensioners, and other safety features.
2.2. Advancements in ECU Technology
How have advancements in ECU technology improved vehicle performance and safety?
Advancements in ECU technology have significantly improved vehicle performance and safety. Modern ECUs are more powerful, faster, and capable of processing vast amounts of data in real-time. These advancements have led to:
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Precise control of engine parameters optimizes fuel consumption.
- Enhanced Safety: Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) such as adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking rely on sophisticated ECU algorithms.
- Reduced Emissions: More accurate emissions control systems minimize the release of harmful pollutants.
- Better Performance: Optimized engine and transmission control delivers smoother acceleration and improved handling.
2.3. Common ECU Issues and Diagnostic Techniques
What are some common issues that can affect ECU performance, and how are they diagnosed?
Common issues that can affect ECU performance include:
- Software Glitches: Bugs or errors in the ECU software can cause malfunctions or erratic behavior.
- Sensor Failures: Faulty sensors can provide incorrect data to the ECU, leading to inaccurate control adjustments.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring can disrupt communication between the ECU and other vehicle components.
- Power Supply Issues: Fluctuations in voltage or current can damage the ECU or cause it to malfunction.
Diagnostic techniques for ECU issues include:
- OBD-II Scanning: Using On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) scanners to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) stored in the ECU’s memory.
- Live Data Analysis: Monitoring real-time sensor data to identify anomalies or out-of-range values.
- Component Testing: Testing individual sensors and actuators to verify their functionality.
- Software Updates: Updating the ECU software to fix bugs or improve performance.
3. The Interplay of IRB ECU in Automotive Diagnostics
How does the combination of IRB considerations and ECU technology affect automotive diagnostics?
The intersection of IRB considerations and ECU technology significantly impacts automotive diagnostics. As vehicles become more complex and reliant on electronic systems, diagnostic procedures must adhere to ethical guidelines, especially when involving human subjects in testing or research. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides resources and tools to navigate this complex landscape effectively.
3.1. Ethical Considerations in Diagnostic Testing
What ethical issues arise when using diagnostic tools and procedures on vehicles driven by human subjects?
When diagnostic testing involves vehicles driven by human subjects, several ethical issues may arise:
- Privacy Concerns: Diagnostic tools can collect personal data about driving habits, vehicle usage, and location. Protecting this data is crucial to maintaining privacy.
- Safety Risks: Diagnostic procedures performed on vehicles in motion can pose safety risks to drivers and passengers.
- Informed Consent: Participants must be fully informed about the purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits of the diagnostic testing.
- Data Security: Ensuring that diagnostic data is stored and transmitted securely to prevent unauthorized access or misuse.
3.2. Diagnostic Tools and IRB Compliance
How can automotive diagnostic tools be used in compliance with IRB regulations?
To use automotive diagnostic tools in compliance with IRB regulations, researchers and technicians should:
- Anonymize Data: Remove or encrypt personal identifiers from diagnostic data to protect participants’ privacy.
- Use Secure Data Storage: Store diagnostic data in secure, password-protected databases with limited access.
- Obtain Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent from participants before collecting any diagnostic data.
- Minimize Risks: Perform diagnostic testing in controlled environments to minimize safety risks.
3.3. Case Studies: IRB ECU in Action
Can you provide examples of how IRB ECU principles are applied in real-world automotive diagnostic scenarios?
Several case studies illustrate the application of IRB ECU principles in real-world automotive diagnostic scenarios:
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) Testing: Researchers testing ADAS features must obtain IRB approval to ensure that the testing is conducted safely and ethically. This involves using driving simulators, limiting on-road testing, and protecting participants’ privacy.
- Remote Diagnostics: Technicians using remote diagnostic tools to access vehicle data must obtain informed consent from the vehicle owner and ensure that the data is transmitted securely.
- Data Logging: Companies collecting data from vehicles for research purposes must anonymize the data and obtain IRB approval to protect participants’ privacy.
4. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for IRB ECU Systems
What advanced diagnostic techniques are available for troubleshooting complex IRB ECU systems?
Advanced diagnostic techniques for troubleshooting complex IRB ECU systems include:
- Network Analysis: Analyzing communication between different ECUs to identify network issues or bottlenecks.
- Software Debugging: Using specialized software tools to debug ECU code and identify software glitches.
- Hardware Testing: Testing individual ECU components to verify their functionality.
- Simulation and Modeling: Using computer simulations to model ECU behavior and predict performance under different conditions.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training and resources to master these advanced techniques.
4.1. CAN Bus Diagnostics
How is CAN bus diagnostics used to troubleshoot communication issues in IRB ECU systems?
CAN (Controller Area Network) bus diagnostics is a critical technique for troubleshooting communication issues in IRB ECU systems. According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the CAN bus is a communication protocol that allows different ECUs in a vehicle to communicate with each other. CAN bus diagnostics involves:
- Monitoring CAN Bus Traffic: Using specialized tools to monitor the flow of data on the CAN bus.
- Identifying Communication Errors: Detecting errors in CAN bus communication, such as data corruption, missing messages, or bus contention.
- Isolating Faulty ECUs: Identifying ECUs that are not communicating properly or are causing errors on the CAN bus.
- Analyzing CAN Bus Signals: Using oscilloscopes or logic analyzers to analyze the electrical signals on the CAN bus.
4.2. ECU Programming and Reflashing
What is ECU programming and reflashing, and when is it necessary for IRB ECU systems?
ECU programming and reflashing involve updating or replacing the software in an ECU. This is necessary when:
- Fixing Software Bugs: Correcting errors in the ECU software that can cause malfunctions or erratic behavior.
- Improving Performance: Optimizing the ECU software to improve engine performance, fuel efficiency, or emissions control.
- Adding New Features: Enabling new features or functionalities in the vehicle.
- Replacing Faulty ECUs: Programming a new ECU to replace a faulty one.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive training and resources to perform ECU programming and reflashing safely and effectively.
4.3. Data Logging and Analysis
How is data logging and analysis used to diagnose intermittent issues in IRB ECU systems?
Data logging and analysis involve recording data from various sensors and systems in a vehicle over a period of time. This data can then be analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that can help diagnose intermittent issues. Data logging and analysis is particularly useful for:
- Identifying Intermittent Problems: Detecting issues that occur sporadically or under specific conditions.
- Analyzing System Behavior: Understanding how different systems in the vehicle interact with each other.
- Monitoring Performance Over Time: Tracking the performance of various systems over time to identify degradation or wear.
- Validating Repairs: Verifying that repairs have been effective in resolving the issue.
5. The Role of CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in IRB ECU Diagnostics
How does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN support automotive professionals in diagnosing and repairing IRB ECU systems?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN plays a vital role in supporting automotive professionals in diagnosing and repairing IRB ECU systems by providing:
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Offering a range of advanced diagnostic tools, including OBD-II scanners, CAN bus analyzers, and ECU programmers.
- Comprehensive Training: Providing comprehensive training programs on ECU diagnostics, programming, and repair.
- Technical Support: Offering technical support from experienced automotive technicians.
- Repair Guidance: Providing access to a vast library of repair manuals, wiring diagrams, and technical bulletins.
5.1. Diagnostic Tools Offered
What types of diagnostic tools does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offer for IRB ECU systems?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide range of diagnostic tools for IRB ECU systems, including:
| Tool | Description | Features |
|---|---|---|
| OBD-II Scanners | Handheld devices that read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) from the ECU. | Reads and clears DTCs, displays live data, performs component testing. |
| CAN Bus Analyzers | Tools that monitor and analyze communication on the CAN bus. | Detects communication errors, identifies faulty ECUs, analyzes CAN bus signals. |
| ECU Programmers | Devices that update or replace the software in an ECU. | Flashes ECU software, programs new ECUs, performs software updates. |
| Multimeters | Electronic instruments that measure voltage, current, and resistance. | Tests electrical circuits, verifies sensor functionality, diagnoses wiring problems. |
| Oscilloscopes | Electronic instruments that display electrical signals as waveforms. | Analyzes CAN bus signals, detects signal abnormalities, diagnoses electrical issues. |
| Data Loggers | Devices that record data from various sensors and systems in a vehicle over a period of time. | Records sensor data, analyzes system behavior, identifies intermittent problems. |
| Diagnostic Software | Software applications that provide access to ECU data, diagnostic tests, and repair information. | Performs diagnostic tests, displays live data, provides repair information, updates ECU software. |
5.2. Training Programs
What training programs does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provide for automotive professionals working with IRB ECU systems?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training programs for automotive professionals working with IRB ECU systems, including:
- ECU Diagnostics: A course that covers the fundamentals of ECU diagnostics, including how to use OBD-II scanners, CAN bus analyzers, and other diagnostic tools.
- ECU Programming: A course that teaches how to program and reflash ECUs safely and effectively.
- CAN Bus Diagnostics: A course that covers the fundamentals of CAN bus diagnostics, including how to monitor CAN bus traffic, identify communication errors, and isolate faulty ECUs.
- Advanced Diagnostics: A course that covers advanced diagnostic techniques, such as network analysis, software debugging, and hardware testing.
5.3. Technical Support and Resources
What types of technical support and resources does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offer to its customers?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide range of technical support and resources to its customers, including:
- Technical Support Hotline: A phone hotline staffed by experienced automotive technicians.
- Online Knowledge Base: A searchable database of technical articles, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides.
- Repair Manuals: Access to a vast library of repair manuals, wiring diagrams, and technical bulletins.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostic services performed by experienced technicians.
6. Future Trends in IRB ECU Automotive Diagnostics
What are the emerging trends in automotive diagnostics related to IRB ECU systems?
Emerging trends in automotive diagnostics related to IRB ECU systems include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using AI to analyze diagnostic data and identify potential issues before they cause problems.
- Machine Learning (ML): Using ML to develop predictive maintenance algorithms that can anticipate when components are likely to fail.
- Cloud-Based Diagnostics: Storing diagnostic data in the cloud for easy access and analysis.
- Remote Diagnostics: Performing diagnostic tests remotely using telematics and connected car technologies.
6.1. The Role of AI and Machine Learning
How will AI and machine learning impact the future of IRB ECU automotive diagnostics?
AI and machine learning will revolutionize IRB ECU automotive diagnostics by:
- Improving Diagnostic Accuracy: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of diagnostic data to identify patterns and anomalies that human technicians may miss.
- Predicting Failures: ML algorithms can predict when components are likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing breakdowns.
- Automating Diagnostic Tasks: AI can automate many diagnostic tasks, freeing up technicians to focus on more complex repairs.
- Enhancing Remote Diagnostics: AI can enhance remote diagnostic capabilities by providing technicians with real-time insights into vehicle performance.
6.2. The Growth of Remote Diagnostics
How will remote diagnostics change the way automotive repairs are performed on IRB ECU systems?
Remote diagnostics will transform the way automotive repairs are performed on IRB ECU systems by:
- Enabling Faster Repairs: Technicians can diagnose issues remotely, reducing the time it takes to identify and fix problems.
- Reducing Downtime: Remote diagnostics can help prevent breakdowns by identifying potential issues before they cause problems.
- Improving Customer Service: Remote diagnostics can provide customers with faster, more convenient service.
- Expanding Service Areas: Remote diagnostics can enable technicians to service vehicles in remote locations or areas where they do not have a physical presence.
6.3. Cybersecurity Considerations
What cybersecurity considerations are important when working with IRB ECU systems?
Cybersecurity is a critical consideration when working with IRB ECU systems. As vehicles become more connected and reliant on electronic systems, they become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Important cybersecurity considerations include:
- Protecting ECU Software: Securing ECU software to prevent unauthorized access or modification.
- Securing CAN Bus Communication: Encrypting CAN bus communication to prevent eavesdropping or tampering.
- Protecting Diagnostic Data: Storing diagnostic data in secure, password-protected databases with limited access.
- Updating Security Patches: Regularly updating ECU software with the latest security patches.
7. Best Practices for Maintaining IRB Compliance in Automotive Diagnostics
What are the best practices for maintaining IRB compliance when performing automotive diagnostics?
Maintaining IRB compliance is crucial when performing automotive diagnostics, especially when dealing with human subjects. Here are some best practices:
7.1. Informed Consent Procedures
How to ensure that informed consent procedures are followed when collecting data from vehicles driven by human subjects?
To ensure informed consent procedures are followed:
- Provide Clear Information: Clearly explain the purpose of the data collection, the types of data being collected, how the data will be used, and who will have access to the data.
- Obtain Voluntary Consent: Ensure that participants are free to choose whether or not to participate in the data collection.
- Document Consent: Obtain written consent from participants and keep a record of the consent.
- Provide Contact Information: Provide participants with contact information for someone who can answer their questions about the data collection.
7.2. Data Privacy and Security Measures
What measures should be in place to protect the privacy and security of data collected during automotive diagnostics?
To protect data privacy and security:
- Anonymize Data: Remove or encrypt personal identifiers from diagnostic data to protect participants’ privacy.
- Use Secure Data Storage: Store diagnostic data in secure, password-protected databases with limited access.
- Implement Data Encryption: Encrypt diagnostic data to prevent unauthorized access or misuse.
- Comply with Privacy Regulations: Comply with all applicable privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.
7.3. Regular Audits and Training
Why are regular audits and training important for maintaining IRB compliance in automotive diagnostics?
Regular audits and training are essential for maintaining IRB compliance because:
- Audits Ensure Compliance: Audits help identify areas where compliance is lacking and allow for corrective action.
- Training Keeps Staff Informed: Training keeps staff up-to-date on the latest regulations and best practices.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular audits and training promote a culture of continuous improvement in compliance.
8. Common Mistakes to Avoid in IRB ECU Diagnostics
What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with IRB ECU systems and diagnostic data?
When working with IRB ECU systems and diagnostic data, it’s essential to avoid these common mistakes:
8.1. Ignoring Privacy Concerns
How can overlooking privacy concerns lead to non-compliance and ethical issues?
Ignoring privacy concerns can lead to non-compliance and ethical issues because:
- Violates Privacy Regulations: It can violate privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.
- Damages Trust: It can damage trust with customers and participants.
- Results in Legal Penalties: It can result in legal penalties and fines.
8.2. Neglecting Security Protocols
What are the potential consequences of neglecting security protocols when handling diagnostic data?
Neglecting security protocols can have serious consequences:
- Data Breaches: It can lead to data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Compromised Systems: It can compromise vehicle systems and put drivers at risk.
- Reputational Damage: It can damage the reputation of the organization.
8.3. Lack of Documentation
Why is proper documentation essential for demonstrating compliance with IRB regulations?
Proper documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance because:
- Provides Evidence: It provides evidence that compliance procedures are being followed.
- Supports Audits: It supports audits and allows for verification of compliance.
- Facilitates Training: It facilitates training and ensures that staff are following the correct procedures.
9. The Economic Impact of Effective IRB ECU Diagnostics
How does effective IRB ECU diagnostics contribute to cost savings and increased efficiency in the automotive industry?
Effective IRB ECU diagnostics contributes to significant cost savings and increased efficiency in the automotive industry:
9.1. Reduced Repair Time
How does accurate diagnostics lead to faster repair times and lower labor costs?
Accurate diagnostics leads to faster repair times and lower labor costs by:
- Identifying the Root Cause: Quickly identifying the root cause of the problem.
- Avoiding Unnecessary Repairs: Avoiding unnecessary repairs or component replacements.
- Streamlining the Repair Process: Streamlining the repair process and reducing the time it takes to fix the vehicle.
9.2. Improved Vehicle Reliability
What is the relationship between effective diagnostics and the overall reliability of vehicles equipped with IRB ECUs?
Effective diagnostics improves vehicle reliability by:
- Preventing Breakdowns: Preventing breakdowns and unexpected repairs.
- Extending Vehicle Lifespan: Extending the lifespan of the vehicle.
- Reducing Warranty Claims: Reducing warranty claims and repair costs for manufacturers.
9.3. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
How does prompt and accurate diagnostics contribute to higher levels of customer satisfaction?
Prompt and accurate diagnostics contributes to higher customer satisfaction by:
- Resolving Issues Quickly: Resolving issues quickly and efficiently.
- Providing Transparent Service: Providing transparent service and clear explanations of the problem.
- Building Trust: Building trust with customers and creating a positive service experience.
10. Resources and Support for Automotive Professionals
What resources and support are available for automotive professionals working with IRB ECU systems?
Automotive professionals working with IRB ECU systems can access a variety of resources and support:
10.1. Industry Associations
Which industry associations offer guidance and support for automotive diagnostics and repair?
Several industry associations offer guidance and support:
- SAE International: SAE International provides standards, technical information, and training for automotive engineers and technicians.
- ASE (National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence): ASE certifies automotive technicians and provides training and resources for professional development.
- NASTF (National Automotive Service Task Force): NASTF promotes access to vehicle security and diagnostic information for independent repair shops.
10.2. Online Forums and Communities
What are some popular online forums and communities where automotive professionals can share knowledge and seek assistance?
Popular online forums and communities include:
- iATN (International Automotive Technicians Network): A professional network for automotive technicians.
- Automotive Forums: A general forum for automotive enthusiasts and professionals.
- Reddit’s r/MechanicAdvice: A subreddit where people can ask for advice on automotive repairs.
10.3. Government Agencies
Which government agencies provide regulations and guidelines related to automotive safety and emissions?
Government agencies that provide regulations and guidelines include:
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency): The EPA regulates vehicle emissions and fuel efficiency.
- NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration): NHTSA regulates vehicle safety and crashworthiness.
By understanding the intricacies of IRB ECU systems and utilizing the resources and support available through CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, automotive professionals can enhance their diagnostic capabilities, ensure compliance, and provide superior service to their customers.
Ready to elevate your automotive diagnostics skills and ensure IRB compliance? Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance, advanced diagnostic tools, and comprehensive training programs. Our team is dedicated to helping you navigate the complexities of IRB ECU systems and provide top-notch service to your customers. Reach out to us at our U.S. support office located at 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States, or connect with us via WhatsApp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN to learn more and get started on your journey to diagnostic excellence.
FAQ: IRB ECU and Automotive Diagnostics
-
What is IRB ECU in automotive diagnostics?
An IRB ECU refers to the ethical oversight and regulatory compliance applied to Electronic Control Unit (ECU) research in vehicles involving human subjects, ensuring their rights and safety are protected. -
Why is IRB approval necessary for ECU testing?
IRB approval is necessary to ensure ECU testing is conducted ethically and safely, with informed consent from participants, protecting their privacy and minimizing risks. -
What are the key functions controlled by an ECU?
Key functions include engine management, transmission control, braking systems, emissions control, and safety systems, all managed by the ECU using sensor data. -
How do advanced diagnostic tools comply with IRB regulations?
Advanced diagnostic tools comply by anonymizing data, using secure storage, obtaining informed consent, and minimizing safety risks during testing. -
What is CAN bus diagnostics, and how does it help?
CAN bus diagnostics monitors communication between ECUs, identifying errors and faulty units, ensuring proper data flow and system functionality. -
What is ECU programming and reflashing used for?
ECU programming and reflashing updates or replaces ECU software to fix bugs, improve performance, add new features, or replace faulty ECUs. -
How do AI and machine learning enhance ECU diagnostics?
AI and machine learning improve diagnostic accuracy, predict failures, automate tasks, and enhance remote diagnostics by analyzing vast amounts of data. -
What are the benefits of remote diagnostics in automotive repair?
Remote diagnostics enable faster repairs, reduce downtime, improve customer service, and expand service areas by allowing technicians to diagnose issues remotely. -
What cybersecurity measures are crucial for IRB ECU systems?
Crucial measures include protecting ECU software, securing CAN bus communication, safeguarding diagnostic data, and regularly updating security patches to prevent cyberattacks. -
How does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN support automotive professionals in IRB ECU diagnostics?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides advanced tools, comprehensive training, technical support, and repair guidance to help professionals effectively diagnose and repair IRB ECU systems.
 Kathryn Verbanac headshot, Professor at the Division of Surgical Oncology
Kathryn Verbanac headshot, Professor at the Division of Surgical Oncology
 Specimen Request Process flowchart, detailing steps for obtaining specimens
Specimen Request Process flowchart, detailing steps for obtaining specimens
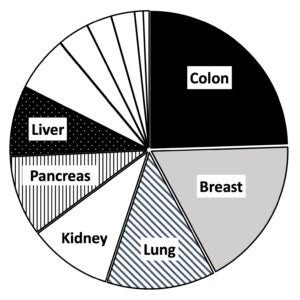 NCTC Tissues chart, showing the distribution of tissue types available from the North Carolina Tissue Consortium
NCTC Tissues chart, showing the distribution of tissue types available from the North Carolina Tissue Consortium
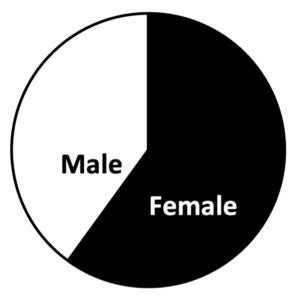 Enrolled Participants chart, showing the gender distribution of participants in the North Carolina Tissue Consortium
Enrolled Participants chart, showing the gender distribution of participants in the North Carolina Tissue Consortium
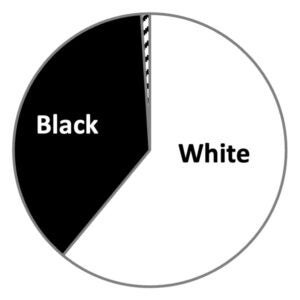 Enrolled Participants chart, showing the race distribution of participants in the North Carolina Tissue Consortium
Enrolled Participants chart, showing the race distribution of participants in the North Carolina Tissue Consortium
 Yaolin Zhou headshot, Associate Professor and Head of Molecular Pathology
Yaolin Zhou headshot, Associate Professor and Head of Molecular Pathology
