Completing a 2005 Bmw Z4 Obd2 Drive Cycle involves a series of specific driving conditions that allow your vehicle’s onboard computer to run diagnostics and confirm that all emission systems are functioning correctly, and CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive resources, including diagnostic tools and repair guides, to assist you with this process. By following the correct steps, you can address issues effectively, whether you’re a young auto repair enthusiast or an experienced garage owner, and you can explore our training programs to enhance your skills or utilize our remote support for complex repairs.
Contents
- 1: Understanding the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle
- 1.1: Why is the OBD2 Drive Cycle Important?
- 1.2: Common Reasons for Performing a Drive Cycle
- 2: Preparing for the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle
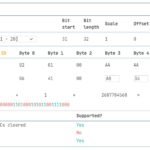
- 2.1: Checking for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 2.2: Fuel Level and Other Basic Checks
- 2.3: Understanding Specific Monitor Requirements
- 3: Step-by-Step Guide to Performing the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle
- 3.1: Initial Conditions
- 3.2: Starting the Engine and Idle Phase
- 3.3: Steady Speed Driving
- 3.4: Acceleration and Deceleration
- 3.5: Highway Driving
- 3.6: Final Idle Phase
- 3.7: Verifying Monitor Status
- 4: Troubleshooting Common Issues During the Drive Cycle
- 4.1: Common Reasons for Drive Cycle Failure
- 4.2: Verifying Driving Conditions
- 4.3: Diagnosing Mechanical and Electrical Issues
- 4.4: Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 4.5: When to Seek Professional Help
- 5: OBD2 Monitors Explained
- 5.1: Comprehensive Component Monitor (CCM)
- 5.2: Catalyst Monitor
- 5.3: Oxygen Sensor Monitor
- 5.4: EVAP Monitor
- 5.5: EGR Monitor
- 6: Tips for a Successful Drive Cycle
- 6.1: Choose the Right Environment
- 6.2: Use a Reliable OBD2 Scanner
- 6.3: Understand Your Vehicle’s Specific Requirements
- 6.4: Be Patient and Persistent
- 6.5: Document Your Progress
- 7: Benefits of Using CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 7.1: Comprehensive Guides and Resources
- 7.2: Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 7.3: Remote Support from Experienced Technicians
- 7.4: Specialized Training Programs
- 7.5: Success Stories and Testimonials
- 8: Staying Updated with Automotive Technology
- 8.1: Continuous Learning
- 8.2: Participating in Industry Events
- 8.3: Utilizing Online Resources
- 8.4: Reading Technical Publications
- 8.5: Networking with Other Professionals
- 9: Common Mistakes to Avoid During an OBD2 Drive Cycle
- 9.1: Failing to Meet Specific Driving Conditions
- 9.2: Neglecting to Check for Pre-Existing DTCs
- 9.3: Using Unreliable Diagnostic Tools
- 9.4: Ignoring the Fuel Level Requirement
- 9.5: Starting with a Warm Engine
- 9.6: Not Following the Recommended Idle Time
- 10: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle
- 10.1: What is an OBD2 Drive Cycle?
- 10.2: How Long Does a 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle Take?
- 10.3: What Tools Do I Need to Perform a Drive Cycle?
- 10.4: Can I Perform a Drive Cycle on a Dyno?
- 10.5: What Should I Do if the Drive Cycle Fails to Complete?
- 10.6: How Many Times Do I Need to Repeat the Drive Cycle?
- 10.7: Will Disconnecting the Battery Affect the OBD2 System?
- 10.8: Can Poor Fuel Quality Affect the Drive Cycle?
- 10.9: Is It Possible to Damage My Vehicle During a Drive Cycle?
- 10.10: Where Can I Find More Information About OBD2 Drive Cycles?
- Conclusion
1: Understanding the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle
What is the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle? The 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle is a series of driving conditions that allow the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system to check the functionality of its emission control systems. Completing this cycle is essential for clearing certain diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and ensuring your vehicle passes an emissions test.
1.1: Why is the OBD2 Drive Cycle Important?
The OBD2 drive cycle is crucial for several reasons:
- Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): After repairing an issue that triggered a DTC, the drive cycle helps confirm that the problem is resolved, and the code can be cleared.
- Emissions Testing: Many states require vehicles to pass an emissions test. The drive cycle ensures that all emission monitors are set to “ready,” which is necessary for passing the test.
- Vehicle Performance: Completing the drive cycle can help identify underlying issues that may affect your vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency.
1.2: Common Reasons for Performing a Drive Cycle
There are several scenarios where performing an OBD2 drive cycle becomes necessary:
- Battery Replacement: Disconnecting or replacing the car battery can reset the OBD2 system, requiring a drive cycle to reset the monitors.
- ECU Reset: Resetting the Engine Control Unit (ECU) for any reason will also require a drive cycle.
- Emissions-Related Repairs: After conducting repairs related to the emission system, such as replacing the oxygen sensor or catalytic converter, a drive cycle verifies the effectiveness of the repairs.
2: Preparing for the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle
How do I prepare for the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle? Before starting the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle, there are several preparatory steps to ensure a smooth and successful process. This includes verifying that there are no stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), ensuring that the fuel tank is at the appropriate level, and understanding the specific conditions required for each monitor to run.
2.1: Checking for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Before initiating the drive cycle, it’s essential to check for any existing DTCs using an OBD2 scanner.
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Connect the OBD2 Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port, usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Read the Codes: Follow the scanner’s instructions to read any stored DTCs.
- Record the Codes: Note down any codes present.
- Clear the Codes (If Necessary): If you have already addressed the issues related to the codes, clear them using the scanner.
Why This Step is Important: Addressing any existing issues before starting the drive cycle prevents false readings and ensures that the monitors can run correctly.
2.2: Fuel Level and Other Basic Checks
Ensuring the correct fuel level and performing basic checks are crucial before starting the drive cycle.
Fuel Level:
- The fuel tank should be between 1/4 and 3/4 full. This level helps ensure that the evaporative emission control system (EVAP) monitor can run without interference.
Other Basic Checks:
- Engine Temperature: Ensure the engine is cold before starting the drive cycle.
- Fluid Levels: Check and top off all essential fluids, including engine oil, coolant, and brake fluid.
- Tire Pressure: Verify that the tire pressure is at the recommended level.
2.3: Understanding Specific Monitor Requirements
Each monitor within the OBD2 system has specific conditions that must be met to run and complete its diagnostic checks. Understanding these requirements is essential for a successful drive cycle.
Key Monitors and Their Requirements:
- Catalyst Monitor: This monitor checks the efficiency of the catalytic converter. It typically requires a stable speed and load for a certain period.
- Oxygen Sensor Monitor: This monitor evaluates the performance of the oxygen sensors. It requires the engine to reach operating temperature and then idle for a specified time.
- EVAP Monitor: This monitor checks for fuel vapor leaks in the evaporative emission control system. It usually runs under specific fuel level and temperature conditions.
- EGR Monitor: This monitor assesses the functionality of the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system. It typically requires driving at moderate speeds with varying loads.
3: Step-by-Step Guide to Performing the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle
What are the exact steps for completing the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle? The 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle involves a detailed series of steps designed to test the functionality of your vehicle’s emission control systems; with assistance from CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can follow the procedure effectively, ensuring each step is performed accurately. This process typically includes a cold start, idle time, steady driving at various speeds, and periods of acceleration and deceleration.
3.1: Initial Conditions
Before starting the drive cycle, ensure the following conditions are met:
- Cold Start: The engine must be completely cold, meaning it has not been run for at least eight hours.
- Fuel Level: The fuel tank should be between 1/4 and 3/4 full.
- No DTCs: Verify that there are no stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). If there are, address them before proceeding.
3.2: Starting the Engine and Idle Phase
- Start the Engine: Start the engine without touching the accelerator pedal.
- Idle Time: Allow the engine to idle for approximately 2-3 minutes. This allows the engine to reach its normal operating temperature.
3.3: Steady Speed Driving
- Drive at a Steady Speed: Drive at a steady speed of 45-55 mph (72-88 km/h) for 15 minutes. This step helps the catalyst and oxygen sensor monitors to run.
- Avoid Sudden Acceleration or Deceleration: Maintain a constant speed and avoid sudden changes in throttle position.
3.4: Acceleration and Deceleration
- Decelerate: Without using the brake, release the accelerator and allow the vehicle to coast down to 20 mph (32 km/h).
- Accelerate: Gently accelerate back to 55 mph (88 km/h).
- Repeat: Repeat this acceleration and deceleration sequence several times over a period of about 5 minutes.
3.5: Highway Driving
- Drive on the Highway: Drive at a steady speed of 60-70 mph (96-112 km/h) for approximately 5 minutes.
- Maintain Steady Throttle: Ensure the throttle position remains as constant as possible.
3.6: Final Idle Phase
- Idle Again: After the highway driving phase, safely pull over and allow the engine to idle for another 2-3 minutes.
- Check Monitors: Use an OBD2 scanner to check the status of the OBD2 monitors.
3.7: Verifying Monitor Status
- Connect the OBD2 Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBD2 port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine.
- Check Monitor Status: Use the scanner to check the status of the OBD2 monitors. The monitors should indicate “ready” or “complete.”
- Repeat if Necessary: If some monitors are not yet ready, repeat the drive cycle, paying close attention to the specific conditions required for the remaining monitors.
4: Troubleshooting Common Issues During the Drive Cycle
What should I do if the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle doesn’t complete? If the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle does not complete successfully, troubleshooting the issue involves addressing several potential factors that may be preventing the monitors from setting; CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides the tools and expertise to diagnose and resolve these problems effectively. This includes verifying the correct driving conditions, checking for underlying mechanical or electrical issues, and using advanced diagnostic equipment to pinpoint specific faults.
4.1: Common Reasons for Drive Cycle Failure
Several factors can prevent the OBD2 drive cycle from completing successfully:
- Incorrect Driving Conditions: Failing to meet the specific speed, time, and throttle requirements for each monitor.
- Underlying Mechanical Issues: Problems with the engine, transmission, or emission control components can prevent the monitors from running.
- Electrical Issues: Faulty sensors, wiring problems, or a malfunctioning ECU can disrupt the OBD2 system.
- Fuel Quality: Poor fuel quality can affect the performance of the engine and emission control systems.
4.2: Verifying Driving Conditions
One of the most common reasons for drive cycle failure is not adhering to the specific driving conditions required for each monitor.
Tips for Verification:
- Speed and Throttle: Use cruise control to maintain a steady speed during the steady-state driving phases.
- Timing: Ensure you drive for the specified duration for each phase of the drive cycle.
- Environment: Perform the drive cycle on a road with minimal traffic to avoid interruptions.
4.3: Diagnosing Mechanical and Electrical Issues
If the driving conditions are met but the drive cycle still fails, there may be underlying mechanical or electrical issues.
Diagnostic Steps:
- Check Sensors: Use an OBD2 scanner to check the readings from the oxygen sensors, mass airflow sensor, and other relevant sensors.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for any signs of damaged or corroded wiring, especially around the sensors and ECU.
- Vacuum Leaks: Check for vacuum leaks, which can affect engine performance and emission control.
- Fuel System: Inspect the fuel injectors and fuel pump for proper operation.
- Consult a Professional: If you are unable to diagnose the issue, consult a professional mechanic. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN can connect you with experienced technicians for remote support.
4.4: Using Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Advanced diagnostic tools can provide more detailed information about the OBD2 system and help pinpoint specific faults.
Types of Tools:
- Professional OBD2 Scanners: These scanners offer advanced features such as live data streaming, component testing, and freeze frame data.
- Multimeters: Use a multimeter to check the voltage and resistance of sensors and wiring.
- Oscilloscopes: An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the waveforms of sensor signals and identify any anomalies.
4.5: When to Seek Professional Help
If you have tried troubleshooting the issue and the drive cycle still fails to complete, it may be necessary to seek professional help.
Reasons to Seek Professional Assistance:
- Complex Issues: If you suspect a complex mechanical or electrical issue, a professional mechanic has the expertise and tools to diagnose and repair the problem.
- Time Constraints: If you need to complete the drive cycle quickly for an emissions test, a professional can expedite the process.
- Lack of Experience: If you are not comfortable working on your vehicle, it is best to leave the job to a professional. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers remote support services to assist you with complex repairs.
5: OBD2 Monitors Explained
What are the different OBD2 monitors and what do they do? OBD2 monitors are diagnostic programs within your vehicle’s onboard computer that continuously check the performance of various emission control systems; CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed explanations and resources to help you understand each monitor and its function. These monitors ensure that your vehicle complies with emission standards and operates efficiently.
5.1: Comprehensive Component Monitor (CCM)
The Comprehensive Component Monitor (CCM) is an umbrella term for all non-continuous monitors that check various components and systems in the vehicle. These monitors run once per driving cycle when specific conditions are met.
Key Components Monitored by CCM:
- Fuel System: Checks the fuel delivery system for proper operation.
- Misfire Monitor: Detects engine misfires, which can damage the catalytic converter.
- EGR System: Evaluates the performance of the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system.
- Oxygen Sensors: Monitors the performance of the oxygen sensors.
5.2: Catalyst Monitor
The catalyst monitor assesses the efficiency of the catalytic converter in reducing harmful emissions.
Functionality:
- Efficiency Check: Compares the oxygen levels before and after the catalytic converter to determine its efficiency.
- Operating Conditions: Requires a stable speed and load for a certain period to accurately assess the catalyst’s performance.
- Failure Codes: If the catalyst is not functioning efficiently, it will trigger a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
5.3: Oxygen Sensor Monitor
The oxygen sensor monitor evaluates the performance of the oxygen sensors, which are crucial for maintaining the correct air-fuel mixture.
Functionality:
- Response Time: Checks the response time of the oxygen sensors to changes in the air-fuel mixture.
- Heater Circuit: Monitors the heater circuit of the oxygen sensors to ensure they reach operating temperature quickly.
- Voltage Range: Verifies that the oxygen sensors are operating within the specified voltage range.
5.4: EVAP Monitor
The EVAP (Evaporative Emission Control System) monitor checks for fuel vapor leaks in the evaporative emission control system.
Functionality:
- Leak Detection: Uses pressure or vacuum to detect leaks in the fuel tank, fuel lines, and vapor recovery system.
- Purge Valve: Monitors the operation of the purge valve, which controls the flow of fuel vapor to the engine.
- Fuel Tank Pressure: Verifies that the fuel tank pressure is within the specified range.
5.5: EGR Monitor
The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) monitor assesses the functionality of the Exhaust Gas Recirculation system, which reduces NOx emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the engine.
Functionality:
- Flow Rate: Measures the flow rate of exhaust gas through the EGR valve.
- Valve Position: Monitors the position of the EGR valve to ensure it is opening and closing correctly.
- Temperature: Checks the temperature of the exhaust gas entering the EGR system.
6: Tips for a Successful Drive Cycle
What are some tips for ensuring a successful 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle? Ensuring a successful 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle involves careful planning and execution; CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides essential tips to help you achieve the desired results efficiently. This includes choosing the right environment, using reliable diagnostic tools, and understanding your vehicle’s specific requirements.
6.1: Choose the Right Environment
Selecting the right environment is crucial for performing a successful OBD2 drive cycle.
Factors to Consider:
- Traffic: Choose a road with minimal traffic to avoid interruptions and maintain a steady speed.
- Road Conditions: Select a road with smooth pavement to minimize vibrations and ensure accurate sensor readings.
- Safety: Prioritize safety by performing the drive cycle in a controlled environment and adhering to all traffic laws.
6.2: Use a Reliable OBD2 Scanner
A reliable OBD2 scanner is essential for monitoring the progress of the drive cycle and verifying the status of the OBD2 monitors.
Features to Look For:
- Live Data Streaming: Allows you to monitor sensor readings in real-time.
- Monitor Status: Displays the status of each OBD2 monitor.
- DTC Reading and Clearing: Allows you to read and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
6.3: Understand Your Vehicle’s Specific Requirements
Each vehicle has specific requirements for performing the OBD2 drive cycle. Consult your vehicle’s service manual or a reliable online resource to understand these requirements.
Key Information to Look For:
- Specific Monitor Conditions: Understand the specific speed, time, and throttle requirements for each monitor.
- Cold Start Procedure: Follow the recommended cold start procedure for your vehicle.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Familiarize yourself with common issues and troubleshooting tips for your vehicle.
6.4: Be Patient and Persistent
The OBD2 drive cycle can be time-consuming and may require multiple attempts to complete successfully. Be patient and persistent, and don’t give up if the monitors don’t set on the first try.
Tips for Staying Patient:
- Plan Ahead: Allocate enough time to complete the drive cycle without feeling rushed.
- Stay Focused: Avoid distractions while driving and focus on meeting the specific requirements of each monitor.
- Take Breaks: If you become frustrated, take a break and come back to the drive cycle later.
6.5: Document Your Progress
Keep a record of your progress during the drive cycle, including the date, time, and conditions under which each monitor was run. This documentation can be helpful for troubleshooting any issues and tracking your progress over time.
Information to Document:
- Date and Time: Record the date and time of each drive cycle attempt.
- Driving Conditions: Note the speed, time, and throttle position during each phase of the drive cycle.
- Monitor Status: Record the status of each OBD2 monitor after each attempt.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Note any DTCs that are triggered during the drive cycle.
7: Benefits of Using CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
How does CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help with OBD2 drive cycles and automotive diagnostics? CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive support for OBD2 drive cycles and automotive diagnostics through detailed guides, advanced diagnostic tools, remote support, and specialized training programs. We are dedicated to helping both novice and experienced technicians improve their skills and efficiently resolve complex automotive issues.
7.1: Comprehensive Guides and Resources
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information to help you understand and perform OBD2 drive cycles.
Resources Include:
- Detailed Guides: Step-by-step instructions for performing OBD2 drive cycles on various vehicle makes and models.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Solutions to common issues that can prevent the drive cycle from completing.
- OBD2 Monitor Explanations: Clear explanations of each OBD2 monitor and its function.
7.2: Advanced Diagnostic Tools
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides access to a wide range of advanced diagnostic tools to help you diagnose and repair automotive issues.
Tools Available:
| Tool | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| OBD2 Scanners | Reads and clears diagnostic trouble codes, displays live data, and monitors the status of OBD2 monitors. | Helps identify issues quickly and accurately. |
| Multimeters | Checks the voltage and resistance of sensors and wiring. | Essential for diagnosing electrical issues. |
| Oscilloscopes | Analyzes the waveforms of sensor signals to identify anomalies. | Provides detailed information about sensor performance. |
| Compression Testers | Measures the compression in each cylinder to identify engine problems. | Helps diagnose engine issues such as worn piston rings or leaking valves. |
| Fuel Pressure Testers | Measures the fuel pressure to ensure the fuel system is operating correctly. | Essential for diagnosing fuel system issues. |
7.3: Remote Support from Experienced Technicians
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers remote support from experienced technicians to help you diagnose and repair complex automotive issues.
Benefits of Remote Support:
- Expert Advice: Get expert advice from experienced technicians.
- Real-Time Assistance: Receive real-time assistance during the diagnostic and repair process.
- Cost-Effective: Remote support is often more cost-effective than hiring a local mechanic.
7.4: Specialized Training Programs
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers specialized training programs to help you improve your automotive diagnostic and repair skills.
Training Programs Include:
- OBD2 Diagnostics: Learn how to diagnose and repair OBD2-related issues.
- Engine Management Systems: Understand the operation of engine management systems and how to troubleshoot them.
- Electrical Systems: Learn how to diagnose and repair electrical issues in modern vehicles.
7.5: Success Stories and Testimonials
Many technicians and garage owners have benefited from using CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Success Stories:
- Technician A: “I was struggling to complete an OBD2 drive cycle on a BMW Z4. Thanks to the detailed guides and remote support from CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, I was able to identify and repair the issue quickly.”
- Garage Owner B: “The advanced diagnostic tools from CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN have helped my technicians diagnose and repair vehicles more efficiently, increasing our shop’s productivity and profitability.”
By leveraging the resources and services offered by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can improve your automotive diagnostic skills and efficiently resolve complex issues.
8: Staying Updated with Automotive Technology
How can I stay updated with the latest automotive technology and diagnostic techniques? Staying updated with the latest automotive technology and diagnostic techniques is essential for any technician or garage owner; CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides numerous resources to help you keep pace with these advancements. This includes continuous learning through training programs, participating in industry events, and utilizing online resources.
8.1: Continuous Learning
The automotive industry is constantly evolving, so it’s important to commit to continuous learning.
Ways to Learn:
- Training Programs: Enroll in training programs offered by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN to learn about the latest diagnostic techniques and technologies.
- Online Courses: Take online courses from reputable sources to expand your knowledge.
- Certifications: Pursue certifications from industry organizations such as ASE (Automotive Service Excellence) to demonstrate your expertise.
8.2: Participating in Industry Events
Attending industry events is a great way to network with other professionals and learn about the latest trends and technologies.
Types of Events:
- Trade Shows: Attend trade shows such as SEMA (Specialty Equipment Market Association) to see the latest products and technologies.
- Conferences: Participate in conferences to learn from industry experts and attend workshops and seminars.
- Workshops: Attend hands-on workshops to learn new skills and techniques.
8.3: Utilizing Online Resources
The internet is a vast resource for automotive information. Utilize online resources to stay updated with the latest news, trends, and technologies.
Online Resources:
- Industry Websites: Visit industry websites such as Automotive Engineering International and Motor Age to read articles and news about the latest developments.
- Forums: Participate in online forums to ask questions and share your knowledge with other professionals.
- Blogs: Read blogs from industry experts to stay informed about the latest trends and technologies.
- CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN: Regularly check our website for updated guides, resources, and training programs.
8.4: Reading Technical Publications
Technical publications provide in-depth information about automotive systems and technologies.
Types of Publications:
- Service Manuals: Consult service manuals for detailed information about specific vehicles.
- Technical Journals: Read technical journals to stay updated with the latest research and developments.
- Industry Magazines: Subscribe to industry magazines to read articles about new technologies and techniques.
8.5: Networking with Other Professionals
Networking with other professionals is a great way to learn from their experiences and stay updated with the latest trends.
Ways to Network:
- Industry Events: Network with other professionals at industry events.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums to connect with other professionals.
- Professional Organizations: Join professional organizations such as the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) to network with other engineers and technicians.
By committing to continuous learning, participating in industry events, utilizing online resources, reading technical publications, and networking with other professionals, you can stay updated with the latest automotive technology and diagnostic techniques. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to support you on this journey with our comprehensive resources and training programs.
9: Common Mistakes to Avoid During an OBD2 Drive Cycle
What are the common mistakes to avoid during a 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle? During a 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle, avoiding common mistakes is critical for achieving accurate and reliable results; CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN highlights these pitfalls to ensure you conduct the process effectively. Common errors include failing to meet specific driving conditions, neglecting to check for pre-existing DTCs, and using unreliable diagnostic tools.
9.1: Failing to Meet Specific Driving Conditions
One of the most common mistakes is not adhering to the specific driving conditions required for each OBD2 monitor. Each monitor has its own set of conditions that must be met in order for it to run and complete its diagnostic check.
How to Avoid:
- Consult the Vehicle’s Service Manual: Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the exact driving conditions required for each monitor.
- Use Cruise Control: Use cruise control to maintain a steady speed during the steady-state driving phases.
- Monitor the Throttle Position: Ensure the throttle position remains as constant as possible.
9.2: Neglecting to Check for Pre-Existing DTCs
Another common mistake is starting the drive cycle without first checking for any pre-existing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes can interfere with the drive cycle and prevent the monitors from setting.
How to Avoid:
- Use an OBD2 Scanner: Use an OBD2 scanner to check for any stored DTCs before starting the drive cycle.
- Address Any Issues: If any DTCs are present, address the underlying issues before proceeding with the drive cycle.
- Clear the Codes (If Necessary): If you have already addressed the issues, clear the DTCs using the scanner.
9.3: Using Unreliable Diagnostic Tools
Using unreliable diagnostic tools can lead to inaccurate readings and prevent the drive cycle from completing successfully.
How to Avoid:
- Use a Reputable OBD2 Scanner: Invest in a high-quality OBD2 scanner from a reputable brand.
- Check Sensor Readings: Verify that the sensor readings are accurate and within the specified range.
- Calibrate Your Tools: Calibrate your diagnostic tools regularly to ensure they are providing accurate readings.
9.4: Ignoring the Fuel Level Requirement
The fuel level in the tank can affect the operation of the EVAP monitor. Ignoring the fuel level requirement can prevent the EVAP monitor from running.
How to Avoid:
- Maintain Proper Fuel Level: Ensure the fuel tank is between 1/4 and 3/4 full before starting the drive cycle.
- Avoid Overfilling: Avoid overfilling the fuel tank, as this can also affect the EVAP monitor.
9.5: Starting with a Warm Engine
Starting the drive cycle with a warm engine can prevent some monitors from running. The engine must be cold for certain monitors to activate.
How to Avoid:
- Ensure a Cold Start: Allow the engine to cool down completely (at least eight hours) before starting the drive cycle.
- Check Engine Temperature: Verify that the engine temperature is below a certain threshold before starting the drive cycle.
9.6: Not Following the Recommended Idle Time
Failing to follow the recommended idle time can prevent the monitors from setting properly.
How to Avoid:
- Allow Proper Idle Time: Allow the engine to idle for the specified duration at the beginning and end of the drive cycle.
- Monitor Engine Temperature: Monitor the engine temperature during the idle phases to ensure it reaches the specified operating temperature.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can increase your chances of completing the OBD2 drive cycle successfully and ensuring your vehicle is ready for an emissions test. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides the resources and support you need to navigate the drive cycle process with confidence.
10: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle
What are some frequently asked questions about the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle? Here are some frequently asked questions about the 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle, along with detailed answers provided by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. These FAQs cover common issues, troubleshooting tips, and best practices for ensuring a successful drive cycle.
10.1: What is an OBD2 Drive Cycle?
An OBD2 drive cycle is a series of specific driving conditions that allow your vehicle’s onboard computer to run diagnostics and confirm that all emission systems are functioning correctly. It is required to reset the OBD2 system after certain repairs or battery replacements.
10.2: How Long Does a 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 Drive Cycle Take?
The duration of a 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle can vary, but it typically takes between 30 minutes to one hour to complete. However, it may take multiple attempts to get all the monitors to set.
10.3: What Tools Do I Need to Perform a Drive Cycle?
To perform a drive cycle, you will need:
- An OBD2 scanner to check for DTCs and monitor the status of the OBD2 monitors.
- The vehicle’s service manual for specific driving conditions.
- A safe and suitable driving environment.
10.4: Can I Perform a Drive Cycle on a Dyno?
Yes, you can perform a drive cycle on a dyno, but it requires specialized equipment and expertise. It is generally easier to perform the drive cycle on the road.
10.5: What Should I Do if the Drive Cycle Fails to Complete?
If the drive cycle fails to complete, check for common issues such as incorrect driving conditions, pre-existing DTCs, or mechanical problems. Consult the troubleshooting section of this guide or seek professional help.
10.6: How Many Times Do I Need to Repeat the Drive Cycle?
You may need to repeat the drive cycle multiple times to get all the monitors to set. Be patient and persistent, and ensure you are meeting the specific driving conditions for each monitor.
10.7: Will Disconnecting the Battery Affect the OBD2 System?
Yes, disconnecting the battery will reset the OBD2 system and erase any stored DTCs or monitor status. You will need to perform a drive cycle to reset the monitors.
10.8: Can Poor Fuel Quality Affect the Drive Cycle?
Yes, poor fuel quality can affect the performance of the engine and emission control systems, which can prevent the drive cycle from completing successfully. Use high-quality fuel from a reputable source.
10.9: Is It Possible to Damage My Vehicle During a Drive Cycle?
It is unlikely to damage your vehicle during a drive cycle if you follow the recommended procedures and drive safely. However, if you suspect a mechanical issue, it is best to consult a professional mechanic.
10.10: Where Can I Find More Information About OBD2 Drive Cycles?
You can find more information about OBD2 drive cycles on CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, as well as in your vehicle’s service manual and other reliable online resources.
Conclusion
Completing a 2005 BMW Z4 OBD2 drive cycle is essential for ensuring your vehicle’s emission systems are functioning correctly and that it passes an emissions test. By following the step-by-step guide and tips provided by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can successfully perform the drive cycle and address any issues that may arise. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, our resources and support are here to help you every step of the way.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s diagnostics and ensure peak performance? Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance, advanced diagnostic tools, and comprehensive training programs tailored to your needs. Call us now at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States. You can also connect with us via Whatsapp for immediate assistance or explore our website at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for more information. Let us help you elevate your automotive expertise and achieve unparalleled diagnostic accuracy!