The 2005 F250 Diesel Obd2 Fuse is critical for diagnostics. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive guides, diagnostic tools, and expert support to help you locate and troubleshoot fuse-related issues efficiently, ensuring optimal vehicle performance. Explore our advanced remote assistance for complex problems and specialized technician training to enhance your diagnostic skills.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Importance of the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2005 F250 Diesel
- 1.1 Why is the OBD2 Fuse Important?
- 1.2 Common Symptoms of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
- 1.3 Potential Causes of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
- 2. Locating the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2005 F250 Diesel
- 2.1 Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Fuse Panel
- 2.2 Identifying the Correct Fuse
- 2.3 Tools Needed for Fuse Inspection
- 3. How to Inspect and Test the OBD2 Fuse
- 3.1 Visual Inspection of the Fuse
- 3.2 Using a Multimeter to Test Continuity
- 3.3 What to Do if the Fuse is Blown
- 4. Replacing the OBD2 Fuse: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 4.1 Choosing the Correct Replacement Fuse
- 4.2 Step-by-Step Fuse Replacement Process
- 4.3 Safety Precautions
- 5. Troubleshooting Common Issues After Fuse Replacement
- 5.1 The New Fuse Blows Immediately
- 5.2 The OBD2 Port Still Doesn’t Work
- 5.3 When to Seek Professional Help
- 6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for OBD2 Issues
- 6.1 Using a Professional Diagnostic Scanner
- 6.2 Checking the CAN Bus System
- 6.3 Electrical Testing and Wiring Diagrams
- 7. Preventive Measures to Avoid Future OBD2 Fuse Issues
- 7.1 Regular Inspection of the OBD2 Port
- 7.2 Using High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
- 7.3 Avoiding Overloading the OBD2 Circuit
- 8. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes for the 2005 F250 Diesel
- 8.1 P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected
- 8.2 P0603: Internal Control Module Keep Alive Memory (KAM) Error
- 8.3 P1000: OBD Systems Readiness Test Not Complete
- 9. The Role of CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in OBD2 Diagnostics
- 9.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Guides
- 9.2 Expert Remote Assistance
- 9.3 Technician Training Programs
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About 2005 F250 Diesel OBD2 Fuses
- 10.1 Where is the OBD2 port located on a 2005 Ford F250 diesel?
- 10.2 What amperage is the OBD2 fuse for a 2005 F250 diesel?
- 10.3 Can a blown OBD2 fuse affect other systems in the vehicle?
- 10.4 How do I know if my OBD2 port is not working?
- 10.5 What should I do if the new fuse blows immediately after replacing it?
- 10.6 Can I use a higher amperage fuse if I don’t have the exact replacement?
- 10.7 How often should I inspect my OBD2 port?
- 10.8 What tools do I need to replace an OBD2 fuse?
- 10.9 Can CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help me diagnose OBD2 issues remotely?
- 10.10 Do you offer training programs for automotive diagnostics?
1. Understanding the Importance of the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2005 F250 Diesel
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD2) system is a vital component in your 2005 Ford F-250 diesel, enabling technicians and vehicle owners to diagnose issues efficiently. The OBD2 port, powered by a dedicated fuse, allows communication between diagnostic tools and the vehicle’s computer. When this fuse blows, it can halt the diagnostic process, leaving you in the dark about potential problems.
1.1 Why is the OBD2 Fuse Important?
The OBD2 fuse safeguards the diagnostic system from electrical overloads. Without a functioning OBD2 port, you cannot:
- Read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
- Monitor live engine data
- Perform necessary system tests
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurate diagnostics can reduce repair times by up to 40%. A blown OBD2 fuse prevents this efficiency, potentially leading to prolonged downtime and increased repair costs.
1.2 Common Symptoms of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
Recognizing the symptoms of a blown OBD2 fuse is the first step in addressing the problem. Common signs include:
- The diagnostic scanner fails to power on when connected to the OBD2 port.
- No communication between the scanner and the vehicle’s computer.
- Error messages on the scanner indicating a connection failure.
It’s crucial to distinguish these symptoms from other potential issues, such as a faulty scanner or a damaged OBD2 port. A systematic approach, including checking the fuse, can save time and effort.
1.3 Potential Causes of a Blown OBD2 Fuse
Several factors can cause an OBD2 fuse to blow in your 2005 F-250 diesel. Understanding these causes can help prevent future occurrences:
- Short Circuit in the OBD2 Port: Physical damage or corrosion can lead to a short circuit.
- Faulty Diagnostic Tool: A malfunctioning scanner can draw excessive current, blowing the fuse.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or frayed wires connected to the OBD2 port can cause a short.
- Electrical Overload: Connecting devices that draw too much power through the OBD2 port.
Regular inspection and proper use of diagnostic tools are essential to maintaining the integrity of the OBD2 system.
2. Locating the OBD2 Fuse in Your 2005 F250 Diesel
Finding the OBD2 fuse is a straightforward process, but it requires knowing where to look. The 2005 Ford F-250 diesel has two main fuse boxes:
- Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel: Located inside the cab.
- Power Distribution Box: Found in the engine compartment.
The OBD2 fuse is typically located in the passenger compartment fuse panel.
2.1 Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the Fuse Panel
- Locate the Passenger Compartment: This fuse panel is usually found on the driver’s side, underneath the dashboard.
- Access the Fuse Panel: You may need a screwdriver to remove a protective cover.
- Identify the Fuse Layout Diagram: A diagram is usually printed on the inside of the cover or in the owner’s manual.
Following these steps will help you quickly access the fuse panel and identify the OBD2 fuse.
2.2 Identifying the Correct Fuse
Once you have accessed the fuse panel, use the fuse layout diagram to locate the OBD2 fuse. In the 2005 Ford F-250 diesel, the OBD2 fuse is often shared with the cigarette lighter. The fuse is typically labeled as “Cigar Lighter/OBD II” or similar.
| Fuse Number | Description | Amperage |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Cigar Lighter, OBD II | 20A |
Consulting the owner’s manual for the exact fuse number and amperage is always a good practice.
2.3 Tools Needed for Fuse Inspection
Before inspecting the fuse, gather the necessary tools:
- Fuse Puller: This tool makes removing fuses easier and prevents damage.
- Multimeter: To test the fuse for continuity.
- Flashlight: To provide better visibility in the fuse panel area.
Having these tools on hand will streamline the inspection process and ensure accuracy.
3. How to Inspect and Test the OBD2 Fuse
Once you have located the OBD2 fuse, the next step is to inspect and test it. This process involves visually examining the fuse and using a multimeter to confirm its functionality.
3.1 Visual Inspection of the Fuse
Begin by visually inspecting the fuse. Look for the following signs of damage:
- Broken Filament: A visible gap in the metal wire inside the fuse.
- Darkened or Burnt Appearance: Indicates the fuse has blown due to an overload.
If the filament is broken or the fuse looks burnt, it needs to be replaced.
3.2 Using a Multimeter to Test Continuity
A multimeter provides a more accurate way to test the fuse. Here’s how:
- Set the Multimeter: Turn the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a sound wave symbol).
- Test the Fuse: Place one probe on each of the fuse’s metal contacts.
- Check for Continuity: If the multimeter beeps or displays a value close to zero ohms, the fuse is good. If there is no sound or the display shows infinite resistance, the fuse is blown.
According to Fluke Corporation, a leading manufacturer of multimeters, using a multimeter to test fuses ensures accurate diagnostics and prevents misdiagnosis.
3.3 What to Do if the Fuse is Blown
If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the same amperage. It is crucial to use the correct amperage to avoid damaging the electrical system. After replacing the fuse, test the OBD2 port to ensure it is functioning correctly.
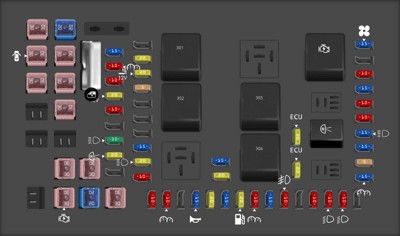 2005 Ford F-250 fuse box diagram Passenger compartment fuse panel
2005 Ford F-250 fuse box diagram Passenger compartment fuse panel
4. Replacing the OBD2 Fuse: A Step-by-Step Guide
Replacing the OBD2 fuse is a simple task, but it must be done correctly to avoid further electrical issues. Follow these steps to ensure a successful fuse replacement.
4.1 Choosing the Correct Replacement Fuse
Using the correct replacement fuse is crucial. Refer to the owner’s manual or the fuse panel diagram to determine the correct amperage. Using a fuse with a higher amperage can damage the electrical system, while a lower amperage fuse may blow prematurely.
| Original Fuse Amperage | Replacement Fuse Amperage |
|---|---|
| 20A | 20A |
Always double-check the amperage rating to ensure compatibility.
4.2 Step-by-Step Fuse Replacement Process
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the vehicle’s ignition is turned off to prevent electrical surges.
- Remove the Blown Fuse: Use the fuse puller to gently remove the blown fuse from the fuse panel.
- Insert the New Fuse: Align the new fuse with the empty slot and gently push it in until it is fully seated.
- Test the OBD2 Port: Connect a diagnostic scanner to the OBD2 port to ensure it is functioning correctly.
Following these steps will ensure a smooth and safe fuse replacement process.
4.3 Safety Precautions
When working with electrical components, it is essential to take safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: For added safety, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to prevent electrical shock.
- Avoid Wet Conditions: Do not work on the electrical system in wet or damp conditions.
Adhering to these safety precautions will minimize the risk of electrical accidents.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues After Fuse Replacement
Even after replacing the fuse, you may encounter additional issues. Troubleshooting these problems can help you identify underlying causes and prevent future fuse failures.
5.1 The New Fuse Blows Immediately
If the new fuse blows immediately after replacement, it indicates a persistent short circuit or overload in the system. Common causes include:
- Short Circuit in the Wiring: Inspect the wiring connected to the OBD2 port for damage or fraying.
- Faulty OBD2 Port: A damaged OBD2 port can cause a short circuit.
- Overloaded Circuit: Too many devices drawing power from the same circuit.
Addressing these issues will prevent the new fuse from blowing repeatedly.
5.2 The OBD2 Port Still Doesn’t Work
If the OBD2 port still doesn’t work after replacing the fuse, consider the following:
- Check the Ground Connection: Ensure the OBD2 port has a good ground connection.
- Inspect the Wiring Harness: Look for damaged or disconnected wires in the harness.
- Test the OBD2 Port with Another Scanner: Rule out the possibility of a faulty scanner.
Systematic troubleshooting will help you identify the root cause of the problem.
5.3 When to Seek Professional Help
If you are unable to resolve the issue after troubleshooting, it is best to seek professional help. A qualified technician can diagnose and repair complex electrical problems that may be beyond the scope of a DIY repair.
 2005 Ford F-250 fuse box diagram Power distribution box
2005 Ford F-250 fuse box diagram Power distribution box
6. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for OBD2 Issues
For more complex OBD2 issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary. These techniques require specialized tools and a deeper understanding of the vehicle’s electrical system.
6.1 Using a Professional Diagnostic Scanner
A professional diagnostic scanner offers advanced features such as:
- Live Data Monitoring: View real-time data from various sensors and modules.
- Bi-Directional Control: Perform tests and activate components to diagnose issues.
- Advanced Code Reading: Access manufacturer-specific codes and enhanced diagnostics.
According to Bosch Automotive Service Solutions, professional diagnostic scanners can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency.
6.2 Checking the CAN Bus System
The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is a communication network that allows various modules in the vehicle to communicate. Issues with the CAN bus can affect the OBD2 system. To check the CAN bus:
- Use an Oscilloscope: Monitor the CAN bus signals for proper voltage and waveform.
- Check for Open or Short Circuits: Inspect the CAN bus wiring for damage or corrosion.
- Verify Module Communication: Ensure all modules are communicating properly on the CAN bus.
Addressing CAN bus issues can resolve many OBD2-related problems.
6.3 Electrical Testing and Wiring Diagrams
Electrical testing and wiring diagrams are essential for diagnosing complex OBD2 issues. Use a multimeter to test voltage, resistance, and continuity in the OBD2 circuit. Refer to the vehicle’s wiring diagrams to trace the circuit and identify potential faults.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed wiring diagrams and electrical testing guides to assist technicians and DIYers in diagnosing OBD2 issues.
7. Preventive Measures to Avoid Future OBD2 Fuse Issues
Preventing future OBD2 fuse issues involves regular maintenance and careful use of diagnostic tools. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
7.1 Regular Inspection of the OBD2 Port
Regularly inspect the OBD2 port for:
- Physical Damage: Look for cracks, breaks, or corrosion.
- Loose Connections: Ensure the connector is securely attached.
- Cleanliness: Keep the port free from dirt and debris.
Regular inspections can help identify potential issues before they cause a fuse to blow.
7.2 Using High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
Using high-quality diagnostic tools can prevent electrical overloads and damage to the OBD2 system. Choose tools from reputable manufacturers that meet industry standards.
| Feature | High-Quality Tool | Low-Quality Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Overload Protection | Yes | No |
| Software Updates | Regular | Infrequent |
| Build Quality | Durable | Flimsy |
Investing in high-quality tools can save you time and money in the long run.
7.3 Avoiding Overloading the OBD2 Circuit
Avoid overloading the OBD2 circuit by:
- Using Only Necessary Devices: Do not connect multiple devices to the OBD2 port simultaneously.
- Checking Power Requirements: Ensure devices connected to the OBD2 port do not draw excessive power.
- Disconnecting Devices When Not in Use: Disconnect devices when they are not actively being used.
By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of future OBD2 fuse issues.
8. Common OBD2 Trouble Codes for the 2005 F250 Diesel
Understanding common OBD2 trouble codes for the 2005 F250 diesel can help you diagnose issues more efficiently. Here are some of the most common codes:
8.1 P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected
This code indicates that the EGR system is not functioning correctly. Possible causes include:
- Faulty EGR Valve: The EGR valve may be stuck or malfunctioning.
- Clogged EGR Passages: Carbon buildup can restrict EGR flow.
- Defective EGR Sensor: The EGR sensor may be providing inaccurate readings.
According to a study by Delphi Technologies, a malfunctioning EGR system can reduce fuel efficiency by up to 15%.
8.2 P0603: Internal Control Module Keep Alive Memory (KAM) Error
This code indicates an issue with the vehicle’s computer memory. Possible causes include:
- Low Battery Voltage: Insufficient voltage can cause memory loss.
- Faulty PCM: The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) may be defective.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged or disconnected wires can cause memory loss.
Addressing this code promptly can prevent further issues with the vehicle’s computer.
8.3 P1000: OBD Systems Readiness Test Not Complete
This code indicates that the OBD system has not completed all required tests. Possible causes include:
- Recent Battery Disconnection: Disconnecting the battery resets the OBD system.
- Recent Code Clearing: Clearing codes resets the OBD system.
- Drive Cycle Not Completed: The vehicle may not have completed a full drive cycle.
Completing a drive cycle can resolve this code and ensure the OBD system is functioning correctly.
9. The Role of CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN in OBD2 Diagnostics
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of services to assist technicians and vehicle owners with OBD2 diagnostics, including:
9.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Guides
We provide detailed diagnostic guides for various vehicle makes and models, including the 2005 Ford F-250 diesel. Our guides cover:
- OBD2 Fuse Location: Precise location of the OBD2 fuse in different vehicles.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and repairing OBD2 issues.
- Code Definitions: Clear explanations of common OBD2 trouble codes.
Our comprehensive guides are designed to simplify the diagnostic process and help you resolve issues quickly and efficiently.
9.2 Expert Remote Assistance
Our team of experienced technicians offers remote assistance to help you diagnose and repair complex OBD2 issues. We can:
- Provide Real-Time Guidance: Assist you with troubleshooting steps in real-time.
- Interpret Diagnostic Data: Help you understand and interpret diagnostic data from your scanner.
- Offer Expert Advice: Provide expert advice on repair procedures and best practices.
With our remote assistance, you can access expert knowledge and support from the comfort of your own garage.
9.3 Technician Training Programs
We offer specialized technician training programs to enhance your diagnostic skills. Our programs cover:
- OBD2 System Fundamentals: Comprehensive overview of the OBD2 system and its components.
- Advanced Diagnostic Techniques: Hands-on training in advanced diagnostic techniques.
- Troubleshooting Common Issues: Practical training in troubleshooting common OBD2 issues.
Our training programs are designed to equip you with the knowledge and skills you need to excel in the automotive industry.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About 2005 F250 Diesel OBD2 Fuses
10.1 Where is the OBD2 port located on a 2005 Ford F250 diesel?
The OBD2 port on a 2005 Ford F250 diesel is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is usually near the steering column or slightly to the left.
10.2 What amperage is the OBD2 fuse for a 2005 F250 diesel?
The OBD2 fuse for a 2005 F250 diesel is usually a 20A fuse. However, it’s always best to check your vehicle’s owner’s manual or the fuse box diagram for the exact amperage.
10.3 Can a blown OBD2 fuse affect other systems in the vehicle?
Yes, a blown OBD2 fuse can affect other systems if it shares a circuit with other components, such as the cigarette lighter. Replacing the fuse is crucial to restore functionality to these systems.
10.4 How do I know if my OBD2 port is not working?
You’ll know your OBD2 port is not working if your diagnostic scanner fails to power on when connected, or if the scanner displays a “no communication” error message.
10.5 What should I do if the new fuse blows immediately after replacing it?
If a new fuse blows immediately, there’s likely a short circuit in the wiring or a faulty component connected to the OBD2 circuit. Inspect the wiring and OBD2 port for damage.
10.6 Can I use a higher amperage fuse if I don’t have the exact replacement?
No, you should never use a fuse with a higher amperage. This can cause damage to the electrical system and potentially lead to a fire. Always use the correct amperage fuse.
10.7 How often should I inspect my OBD2 port?
You should inspect your OBD2 port regularly, especially if you frequently use it for diagnostics. Check for physical damage, loose connections, and cleanliness.
10.8 What tools do I need to replace an OBD2 fuse?
To replace an OBD2 fuse, you’ll need a fuse puller, a new fuse with the correct amperage, and a flashlight to see inside the fuse box. A multimeter can be helpful to test the fuse.
10.9 Can CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help me diagnose OBD2 issues remotely?
Yes, CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert remote assistance to help you diagnose and repair complex OBD2 issues. Our technicians can provide real-time guidance and expert advice.
10.10 Do you offer training programs for automotive diagnostics?
Yes, we offer specialized technician training programs to enhance your diagnostic skills, covering OBD2 system fundamentals, advanced diagnostic techniques, and troubleshooting common issues.
Ensuring your 2005 F250 diesel’s OBD2 system is functioning correctly is crucial for maintaining its performance and longevity. By understanding the importance of the OBD2 fuse, knowing how to locate and replace it, and following preventive measures, you can avoid common issues and keep your vehicle running smoothly. For advanced diagnostics, expert assistance, and comprehensive training, turn to CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN.
Is your 2005 F250 diesel giving you trouble? Don’t let a blown fuse keep you in the dark. Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our office at 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States, for expert diagnostic tools, step-by-step repair guidance, and remote technical support. Our training programs can help you master advanced diagnostic techniques, ensuring you’re always ready to tackle any automotive challenge. Let CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN be your trusted partner in automotive excellence. Visit CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN now.
