Does Audi Use Obd2? Absolutely! Audi, like all cars sold in the USA after 1996, uses the OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) system. This allows you to tap into your vehicle’s computer to diagnose problems, monitor performance, and even reset certain functions. At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we can guide you on how to use OBD2 effectively for your Audi, offering comprehensive diagnostic solutions, repair guidance, and expert technical support. Our remote assistance and technician training programs are designed to empower you with the knowledge to keep your Audi running smoothly.
Contents
- 1. Understanding OBD2 and Its Importance for Audi Vehicles
- 1.1 What is OBD2?
- 1.2 Why is OBD2 Important for Audi Owners?
- 1.3 How to Access the OBD2 Port in Your Audi
- 2. Essential OBD2 Functions for Audi Diagnostics
- 2.1 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 2.2 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
- 2.3 Reading Freeze Frame Data
- 2.4 Live Data Streaming
- 3. Special Functions for Audi Vehicles via OBD2
- 3.1 Oil Reset
- 3.2 Electronic Parking Brake (EPB) Reset
- 3.3 Battery Registration
- 3.4 Steering Angle Sensor (SAS) Calibration
- 3.5 Throttle Body Adaptation
- 3.6 Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Regeneration
- 4. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Audi
- 4.1 Basic Code Readers vs. Advanced Scanners
- 4.2 Key Features to Look For
- 4.3 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Audi Vehicles
- 5. Common Audi Diagnostic Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
- 5.1 Engine-Related Codes
- 5.2 Transmission-Related Codes
- 5.3 ABS/Brake-Related Codes
- 5.4 Airbag-Related Codes
- 5.5 Electrical System Codes
- 6. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing and Repairing Common Audi Issues Using OBD2
- 6.1 Step 1: Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- 6.2 Step 2: Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 6.3 Step 3: Research the DTCs
- 6.4 Step 4: Inspect the Suspect Components
- 6.5 Step 5: Repair or Replace the Faulty Components
- 6.6 Step 6: Clear the DTCs
- 6.7 Step 7: Test the Vehicle
- 6.8 Example: Diagnosing a Misfire (P0301)
- 7. Maximizing the Benefits of OBD2 with CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 7.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Solutions
- 7.2 Detailed Repair Guidance
- 7.3 Expert Technical Support
- 7.4 Technician Training Programs
- 8. Future Trends in Audi Diagnostics and OBD2 Technology
- 8.1 Enhanced OBD2 (EOBD2)
- 8.2 Wireless OBD2 Adapters
- 8.3 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
- 8.4 Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
- 8.5 Cybersecurity Considerations
- 9. Maintaining Your Audi’s Health with Proactive OBD2 Monitoring
- 9.1 Regular Scanning
- 9.2 Monitoring Live Data
- 9.3 Tracking Maintenance Intervals
- 9.4 Addressing DTCs Promptly
- 9.5 Staying Informed
- 10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Audi and OBD2
1. Understanding OBD2 and Its Importance for Audi Vehicles
The OBD2 system is a standardized system that provides access to a wealth of information about your vehicle’s performance and health. For Audi owners, understanding and utilizing OBD2 can save time and money on repairs, as well as provide valuable insights into the vehicle’s condition.
1.1 What is OBD2?
OBD2 is an acronym for On-Board Diagnostics II, a standardized system implemented in all cars sold in the United States after January 1, 1996. Its primary purpose is to monitor the performance of the engine and related components to ensure emissions compliance. The OBD2 system consists of:
- Sensors: Numerous sensors throughout the vehicle monitor various parameters such as engine speed, coolant temperature, oxygen levels, and more.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The ECU, also known as the car’s computer, collects and processes data from the sensors.
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): When the ECU detects a problem, it stores a specific DTC indicating the nature of the issue.
- Standardized Connector: A 16-pin connector, typically located under the dashboard, allows access to the OBD2 system using a scan tool.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the OBD2 system was mandated to ensure vehicles meet stringent emissions standards. A study by the EPA in 2019 revealed that effective use of OBD2 can reduce vehicle emissions by up to 20%.
1.2 Why is OBD2 Important for Audi Owners?
For Audi owners, OBD2 offers several key benefits:
- Early Problem Detection: OBD2 allows you to identify potential issues before they escalate into major repairs.
- Informed Decision-Making: Understanding the DTCs helps you make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance.
- Cost Savings: By diagnosing and addressing problems early, you can avoid costly repairs down the road.
- Performance Monitoring: OBD2 can provide insights into your Audi’s performance, allowing you to optimize fuel efficiency and driving experience.
- DIY Repairs: With the right tools and knowledge, you can perform some repairs yourself, saving on labor costs.
The Kelley Blue Book (KBB) suggests that regular OBD2 scans can extend the lifespan of your vehicle by identifying maintenance needs early.
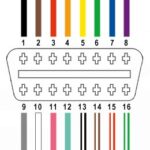
1.3 How to Access the OBD2 Port in Your Audi
The OBD2 port in an Audi is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Here’s how to find it:
- Locate the Area: Look under the dashboard, near the steering column or around the center console area on the driver’s side.
- Check the Manual: If you’re having trouble finding it, consult your Audi’s owner’s manual for the exact location.
- Use a Flashlight: In some models, the port might be hidden from plain view. Use a flashlight to illuminate the area for better visibility.
- Identify the Port: The OBD2 port is a 16-pin, trapezoid-shaped connector.
Once you’ve located the port, you can plug in an OBD2 scanner or code reader to access the vehicle’s diagnostic data. At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we provide guidance and support to help you confidently navigate this process.
2. Essential OBD2 Functions for Audi Diagnostics
OBD2 provides numerous functions that are invaluable for diagnosing and maintaining your Audi. Understanding these functions will empower you to take control of your vehicle’s health.
2.1 Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Reading DTCs is one of the most basic and essential functions of OBD2. DTCs are codes stored by the ECU when it detects a problem. These codes provide clues about the nature and location of the issue.
- How it Works: When a sensor detects a reading outside of the normal range, the ECU registers a DTC. The code is a five-character alphanumeric string (e.g., P0301).
- Importance: DTCs help you pinpoint the source of the problem, whether it’s a faulty sensor, a misfiring cylinder, or an emissions issue.
- Example: A P0301 code indicates a misfire in cylinder 1. This could be due to a faulty spark plug, ignition coil, or fuel injector.
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), accurately interpreting DTCs is crucial for effective automotive diagnostics.
2.2 Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Clearing DTCs involves erasing the stored codes from the ECU’s memory. This function is useful after you’ve addressed the underlying issue.
- How it Works: Using an OBD2 scanner, you can send a command to the ECU to clear the stored DTCs.
- Importance: Clearing codes can reset the check engine light and allow you to monitor if the problem recurs.
- Caution: Always diagnose and repair the underlying issue before clearing codes. Simply clearing the codes without addressing the problem will only result in the light coming back on.
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) recommends documenting all DTCs before clearing them to maintain a record of past issues.
2.3 Reading Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a DTC was triggered.
- How it Works: When a DTC is stored, the ECU also saves relevant data such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel trim.
- Importance: Freeze frame data provides valuable context for diagnosing intermittent problems or issues that are difficult to reproduce.
- Example: If you have a misfire code that only occurs at high speeds, the freeze frame data can show the engine speed and load conditions at the time of the misfire, helping you identify the cause.
A report by Consumer Reports highlights the importance of freeze frame data in diagnosing complex automotive issues.
2.4 Live Data Streaming
Live data streaming allows you to monitor various parameters in real-time as the vehicle is running.
- How it Works: The OBD2 scanner displays real-time data from various sensors, such as engine speed, throttle position, oxygen sensor readings, and more.
- Importance: Live data streaming is essential for diagnosing performance issues, identifying sensor malfunctions, and verifying the effectiveness of repairs.
- Example: Monitoring the oxygen sensor readings can help diagnose fuel trim issues or catalytic converter problems.
According to Bosch Automotive Handbook, live data streaming is an indispensable tool for modern automotive diagnostics.
3. Special Functions for Audi Vehicles via OBD2
Beyond the basic functions, many advanced OBD2 scanners offer special functions tailored to specific makes and models, including Audi. These functions can significantly enhance your ability to diagnose and maintain your vehicle.
3.1 Oil Reset
The oil reset function allows you to reset the oil service indicator after performing an oil change.
- How it Works: The OBD2 scanner sends a command to the ECU to reset the oil life counter.
- Importance: Resetting the oil service indicator ensures that the vehicle’s maintenance reminders are accurate.
- Note: Some Audi models may require manual reset procedures in addition to the OBD2 function.
3.2 Electronic Parking Brake (EPB) Reset
The EPB reset function is necessary when replacing brake pads on vehicles equipped with electronic parking brakes.
- How it Works: The OBD2 scanner retracts the EPB calipers to allow for brake pad replacement and then recalibrates the system after the new pads are installed.
- Importance: Proper EPB reset is crucial for ensuring the parking brake functions correctly and to prevent damage to the system.
According to ZF, a leading supplier of automotive components, incorrect EPB procedures can lead to premature brake wear and system malfunctions.
3.3 Battery Registration
Battery registration is required when replacing the battery in many newer Audi models.
- How it Works: The OBD2 scanner informs the ECU that a new battery has been installed, allowing the charging system to adapt to the new battery’s characteristics.
- Importance: Battery registration ensures proper charging and extends the life of the new battery.
- Consequences of Not Registering: Failing to register the battery can lead to overcharging, undercharging, and premature battery failure.
Varta, a leading battery manufacturer, emphasizes the importance of proper battery registration for optimal performance and longevity.
3.4 Steering Angle Sensor (SAS) Calibration
SAS calibration is necessary after replacing the steering angle sensor or performing certain suspension repairs.
- How it Works: The OBD2 scanner recalibrates the SAS to ensure the stability control system functions correctly.
- Importance: Proper SAS calibration is crucial for the accurate operation of the stability control system, which helps prevent accidents.
- Symptoms of Incorrect Calibration: Issues with the stability control system, ABS, and tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) can arise if the SAS is not correctly calibrated.
3.5 Throttle Body Adaptation
Throttle body adaptation is required after cleaning or replacing the throttle body.
- How it Works: The OBD2 scanner relearns the throttle body’s idle position to ensure smooth engine operation.
- Importance: Proper throttle body adaptation prevents issues such as stalling, rough idling, and poor throttle response.
3.6 Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Regeneration
DPF regeneration is a process to clean the diesel particulate filter, which traps soot from the exhaust.
- How it Works: The OBD2 scanner initiates a regeneration cycle, which burns off the accumulated soot.
- Importance: Regular DPF regeneration is essential for maintaining optimal engine performance and preventing costly repairs.
4. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Your Audi
Selecting the appropriate OBD2 scanner is crucial for effectively diagnosing and maintaining your Audi. There are many options available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools.
4.1 Basic Code Readers vs. Advanced Scanners
- Basic Code Readers: These are simple, inexpensive devices that can read and clear DTCs. They are suitable for basic diagnostics and resetting the check engine light.
- Advanced Scanners: These offer a wider range of functions, including live data streaming, special functions, and bidirectional control. They are better suited for more in-depth diagnostics and repairs.
4.2 Key Features to Look For
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your Audi model and year.
- Functions: Consider the functions you need, such as live data streaming, special functions, and bidirectional control.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear instructions.
- Updates: Choose a scanner that can be updated with the latest software and vehicle data.
- Customer Support: Opt for a brand with good customer support and a strong reputation.
4.3 Recommended OBD2 Scanners for Audi Vehicles
Some popular OBD2 scanners that are well-suited for Audi vehicles include:
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: A versatile scanner with a wide range of functions and excellent compatibility.
- Veepeak OBDCheck BLE: A Bluetooth scanner that connects to your smartphone or tablet.
- OBDeleven: A popular choice among Audi enthusiasts, offering advanced features and customization options.
- Launch X431 V+: A professional-grade scanner with extensive coverage and advanced diagnostic capabilities.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers expert advice on selecting the best OBD2 scanner for your specific needs.
5. Common Audi Diagnostic Trouble Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding common Audi DTCs can help you quickly identify and address problems with your vehicle.
5.1 Engine-Related Codes
- P0300 – Random Misfire Detected: Indicates that the engine is misfiring randomly.
- P0301 to P0306 – Cylinder Misfire Detected (Cylinders 1 to 6): Indicates a misfire in a specific cylinder.
- P0171 – System Too Lean (Bank 1): Indicates that the air-fuel mixture is too lean on bank 1.
- P0174 – System Too Lean (Bank 2): Indicates that the air-fuel mixture is too lean on bank 2.
- P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1): Indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
5.2 Transmission-Related Codes
- P0715 – Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction: Indicates a problem with the input speed sensor.
- P0722 – Output Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal: Indicates a problem with the output speed sensor.
- P0730 – Incorrect Gear Ratio: Indicates that the transmission is not shifting properly.
5.3 ABS/Brake-Related Codes
- C0040 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction: Indicates a problem with the right front wheel speed sensor.
- C0041 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Range/Performance: Indicates a problem with the range or performance of the right front wheel speed sensor.
5.4 Airbag-Related Codes
- B0001 – Driver Airbag Deployment Control: Indicates a problem with the driver airbag deployment control.
- B0002 – Passenger Airbag Deployment Control: Indicates a problem with the passenger airbag deployment control.
5.5 Electrical System Codes
- U0100 – Lost Communication with ECM/PCM: Indicates a loss of communication with the engine control module (ECM) or powertrain control module (PCM).
- U0155 – Lost Communication with Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC) Control Module: Indicates a loss of communication with the instrument panel cluster.
Refer to your Audi’s service manual or consult with a professional technician for a comprehensive list of DTCs and their meanings. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides access to detailed repair guides and technical support to help you diagnose and resolve these issues.
6. Step-by-Step Guide to Diagnosing and Repairing Common Audi Issues Using OBD2
Using OBD2 to diagnose and repair your Audi can be a straightforward process if you follow these steps:
6.1 Step 1: Connect the OBD2 Scanner
- Locate the OBD2 port under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug the OBD2 scanner into the port.
- Turn the ignition key to the “on” position (but do not start the engine).
6.2 Step 2: Read the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” menu on the scanner.
- The scanner will display any stored DTCs.
- Record the DTCs and their descriptions.
6.3 Step 3: Research the DTCs
- Use the DTCs to research the possible causes of the problem.
- Consult your Audi’s service manual, online forums, or a professional technician for more information.
6.4 Step 4: Inspect the Suspect Components
- Based on your research, inspect the components that are likely causing the problem.
- Check for damaged wiring, loose connections, or faulty sensors.
6.5 Step 5: Repair or Replace the Faulty Components
- Repair or replace any faulty components as needed.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation and calibration.
6.6 Step 6: Clear the DTCs
- After completing the repairs, clear the DTCs using the OBD2 scanner.
- Navigate to the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” menu on the scanner.
6.7 Step 7: Test the Vehicle
- Start the engine and test the vehicle to ensure the problem has been resolved.
- Monitor the vehicle’s performance and check for any recurring DTCs.
6.8 Example: Diagnosing a Misfire (P0301)
- Connect the OBD2 scanner and read the codes. You find a P0301 code, indicating a misfire in cylinder 1.
- Research the DTC. You learn that a misfire can be caused by a faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector, or vacuum leak.
- Inspect the suspect components. You check the spark plug, ignition coil, and fuel injector for cylinder 1.
- Repair or replace the faulty components. You find that the spark plug is fouled and replace it.
- Clear the DTCs. You clear the P0301 code using the OBD2 scanner.
- Test the vehicle. You start the engine and find that the misfire is gone.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides detailed step-by-step guides and video tutorials to help you diagnose and repair common Audi issues using OBD2.
7. Maximizing the Benefits of OBD2 with CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a range of services and resources to help you maximize the benefits of OBD2 for your Audi.
7.1 Comprehensive Diagnostic Solutions
We provide access to a wide range of OBD2 scanners and diagnostic tools, tailored to meet the needs of Audi owners and technicians.
- Scanner Recommendations: We offer expert advice on selecting the best OBD2 scanner for your specific needs and budget.
- Tool Training: We provide training on how to use OBD2 scanners effectively to diagnose and repair Audi vehicles.
7.2 Detailed Repair Guidance
We offer detailed repair guides and technical information to help you troubleshoot and repair common Audi issues.
- Step-by-Step Instructions: Our guides provide clear, step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and repairing various problems.
- Video Tutorials: We offer video tutorials that demonstrate key diagnostic and repair procedures.
7.3 Expert Technical Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert technical support and guidance.
- Remote Assistance: We offer remote diagnostic assistance to help you troubleshoot complex issues.
- Online Forums: Our online forums provide a platform for sharing knowledge and asking questions.
7.4 Technician Training Programs
We offer comprehensive technician training programs to help you enhance your diagnostic and repair skills.
- OBD2 Training: Our training programs cover the fundamentals of OBD2 and advanced diagnostic techniques.
- Audi-Specific Training: We offer specialized training on diagnosing and repairing Audi vehicles.
By leveraging the resources and expertise available at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can unlock the full potential of OBD2 and keep your Audi running smoothly for years to come.
8. Future Trends in Audi Diagnostics and OBD2 Technology
The field of automotive diagnostics is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging all the time. Staying up-to-date with these developments is essential for Audi owners and technicians alike.
8.1 Enhanced OBD2 (EOBD2)
EOBD2 is an enhanced version of OBD2 that provides more detailed diagnostic information and supports a wider range of vehicles.
- Benefits: EOBD2 offers improved accuracy, faster data transfer, and more comprehensive coverage.
- Availability: Many newer OBD2 scanners support EOBD2 functionality.
8.2 Wireless OBD2 Adapters
Wireless OBD2 adapters connect to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allowing you to view diagnostic data on your mobile device.
- Benefits: Wireless adapters offer greater convenience and flexibility compared to traditional wired scanners.
- Popular Options: Veepeak OBDCheck BLE, BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool.
8.3 Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostics platforms store diagnostic data in the cloud, allowing you to access it from anywhere and share it with other technicians.
- Benefits: Cloud-based diagnostics enable remote collaboration, data analysis, and improved diagnostic accuracy.
- Examples: Bosch Connected Workshop, Snap-on Cloud.
8.4 Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Diagnostics
AI is being used to develop advanced diagnostic tools that can automatically identify and diagnose problems based on the data collected from the vehicle.
- Benefits: AI-powered diagnostics can significantly reduce diagnostic time and improve accuracy.
- Examples: Diagnostic apps that use machine learning to analyze DTCs and suggest possible causes and solutions.
8.5 Cybersecurity Considerations
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming an increasingly important consideration for automotive diagnostics.
- Risks: Hackers could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in the OBD2 system to gain access to the vehicle’s control systems.
- Mitigation: Manufacturers are implementing security measures to protect the OBD2 system from cyberattacks.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to staying at the forefront of these technological advancements, providing our customers with the latest diagnostic solutions and training.
9. Maintaining Your Audi’s Health with Proactive OBD2 Monitoring
Proactive OBD2 monitoring can help you catch potential problems early, preventing costly repairs and ensuring your Audi remains in top condition.
9.1 Regular Scanning
- Frequency: Scan your Audi’s OBD2 system at least once a month, or more frequently if you notice any unusual symptoms.
- Benefits: Regular scanning can help you identify minor issues before they escalate into major problems.
9.2 Monitoring Live Data
- Parameters: Monitor key parameters such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and fuel trim to identify potential performance issues.
- Benefits: Live data monitoring can help you detect problems such as vacuum leaks, faulty sensors, and clogged fuel injectors.
9.3 Tracking Maintenance Intervals
- Reminders: Use the OBD2 scanner to track maintenance intervals and reset service reminders.
- Benefits: Tracking maintenance intervals ensures that you perform necessary maintenance tasks on time, preventing premature wear and tear.
9.4 Addressing DTCs Promptly
- Response: Address any DTCs promptly to prevent further damage or performance issues.
- Benefits: Addressing DTCs promptly can help you avoid costly repairs and maintain your Audi’s resale value.
9.5 Staying Informed
- Updates: Stay informed about the latest recalls, technical service bulletins (TSBs), and software updates for your Audi.
- Benefits: Staying informed can help you identify and address potential issues before they affect your vehicle.
By following these proactive OBD2 monitoring tips, you can keep your Audi running smoothly and reliably for years to come. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is your partner in proactive vehicle maintenance, providing the tools, information, and support you need to keep your Audi in top condition.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Audi and OBD2
Here are some frequently asked questions about Audi and OBD2:
1. Can I use any OBD2 scanner on my Audi?
Yes, any standard OBD2 scanner should work on your Audi, as long as it complies with the OBD2 protocol mandated for all cars sold in the US after 1996. However, advanced functions like oil reset, EPB reset, or battery registration may require a scanner that specifically supports Audi vehicles.
2. Where is the OBD2 port located in my Audi?
The OBD2 port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Refer to your Audi’s owner’s manual for the exact location.
3. What does a check engine light mean on my Audi?
A check engine light indicates that the OBD2 system has detected a problem. The light can be triggered by a wide range of issues, from minor problems like a loose gas cap to more serious issues like a faulty catalytic converter.
4. Can I clear the check engine light myself using an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, you can clear the check engine light using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s crucial to diagnose and repair the underlying issue first. If you simply clear the code without addressing the problem, the light will likely come back on.
5. What are some common OBD2 codes for Audi vehicles?
Common OBD2 codes for Audi vehicles include P0300 (Random Misfire Detected), P0301-P0306 (Cylinder Misfire Detected), P0171 (System Too Lean, Bank 1), and P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold, Bank 1).
6. Do I need to register a new battery in my Audi?
Yes, many newer Audi models require battery registration when replacing the battery. Failing to register the battery can lead to overcharging, undercharging, and premature battery failure.
7. What is the electronic parking brake (EPB) reset function?
The EPB reset function is necessary when replacing brake pads on vehicles equipped with electronic parking brakes. The OBD2 scanner retracts the EPB calipers to allow for brake pad replacement and then recalibrates the system after the new pads are installed.
8. Can I perform a diesel particulate filter (DPF) regeneration using an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, some advanced OBD2 scanners offer the ability to initiate a DPF regeneration cycle. This process burns off accumulated soot from the diesel particulate filter, helping to maintain optimal engine performance.
9. Where can I find reliable information about Audi diagnostics and repairs?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive diagnostic solutions, repair guidance, and expert technical support for Audi vehicles.
10. How can CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN help me with my Audi diagnostic needs?
At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we offer a range of services and resources to help you maximize the benefits of OBD2 for your Audi, including scanner recommendations, detailed repair guides, expert technical support, and technician training programs.
By understanding OBD2 and utilizing the resources available at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can take control of your Audi’s health and enjoy worry-free driving for years to come.
Ready to take control of your Audi’s health? Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance, comprehensive diagnostic solutions, and top-notch technical support. Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a DIY enthusiast, we have the tools and expertise to help you keep your Audi running smoothly. Reach out to us at our US support office: 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States, or connect via Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN to explore our range of services and training programs. Let us help you unlock the full potential of your Audi!