Are you curious about how OBD2 scanners work and how they can help you maintain your vehicle? At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we specialize in providing comprehensive solutions, including advanced diagnostic tools, detailed repair guides, and expert technical support, ensuring your vehicle stays in top condition. This guide will delve into the workings of OBD2 scanners, their benefits, and how you can leverage them for efficient vehicle maintenance, focusing on technician training and remote support.
Contents
- 1. What is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does it Work?
- 1.1 Key Functions of an OBD2 Scanner
- 1.2 The Communication Process
- 1.3 Supported Communication Protocols
- 1.4 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- 2. Why Use an OBD2 Scanner?
- 2.1 Early Problem Detection
- 2.2 Cost Savings
- 2.3 Improved Fuel Efficiency
- 2.4 Emission Control Compliance
- 2.5 Enhanced Vehicle Performance
- 3. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.1 Preparation
- 3.2 Power On and Connect
- 3.3 Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- 3.4 Interpret the Codes
- 3.5 Clear the Codes (Optional)
- 3.6 Monitor Real-Time Data (Optional)
- 4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
- 5. Advanced Features of OBD2 Scanners
- 5.1 Real-Time Data Streaming
- 5.2 Freeze Frame Data
- 5.3 Oxygen Sensor Testing
- 5.4 EVAP System Testing
- 5.5 ABS and Airbag System Diagnostics
- 6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 6.1 Budget
- 6.2 Features
- 6.3 Compatibility
- 6.4 Ease of Use
- 6.5 Brand Reputation
- 7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
- 7.1 Ignoring the Manual
- 7.2 Clearing Codes Without Diagnosing the Problem
- 7.3 Misinterpreting the Codes
- 7.4 Neglecting Real-Time Data
- 7.5 Using an Incompatible Scanner
- 8. The Future of OBD2 Technology
- 8.1 Enhanced Connectivity
- 8.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- 8.3 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
- 8.4 Integration with Electric Vehicles (EVs)
- 9. OBD2 Scanner and CAN Bus Connection
- 10. Maximize Your Vehicle Performance with OBD2 Scanners
- FAQ: Your Questions About OBD2 Scanners Answered
- 1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
- 2. How does an OBD2 scanner work?
- 3. What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
- 4. Where is the OBD2 port located in my car?
- 5. Can I clear codes with an OBD2 scanner?
- 6. What is real-time data monitoring?
- 7. What is freeze frame data?
- 8. Are all OBD2 scanners compatible with all cars?
- 9. What are some common OBD2 codes?
- 10. Where can I get training on how to use an OBD2 scanner?
1. What is an OBD2 Scanner and How Does it Work?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to access the data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics system, helping to identify and troubleshoot potential issues. The scanner connects to the car’s OBD2 port, reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and provides real-time data about various vehicle systems.
The OBD2 system, mandated in the USA since 1996, constantly monitors various parameters within a vehicle’s engine and other systems. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley’s Institute of Transportation Studies in 2022, OBD2 systems have significantly improved vehicle diagnostics, leading to quicker and more accurate identification of issues. When the system detects a problem, it generates a DTC, which can be accessed using an OBD2 scanner. This process helps mechanics and vehicle owners diagnose and fix problems, ensuring optimal vehicle performance and reducing emissions.
1.1 Key Functions of an OBD2 Scanner
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identifies the specific problem the vehicle has detected.
- Clearing DTCs: Resets the check engine light after repairs are made.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: Displays live data from various sensors in the vehicle, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Freeze Frame Data: Captures data from the moment a DTC was triggered, providing a snapshot of the conditions at the time of the fault.
- Vehicle Information Retrieval: Provides vehicle identification number (VIN) and other important information.
1.2 The Communication Process
When an OBD2 scanner is connected to the vehicle’s OBD2 port, it initiates a communication process with the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU), also known as the car’s computer. The scanner sends a request for data, and the ECU responds with the requested information. This communication follows specific protocols, ensuring compatibility between the scanner and the vehicle.
1.3 Supported Communication Protocols
According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), various communication protocols are used in OBD2 systems:
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| SAE J1850 PWM | Primarily used in Ford vehicles, this protocol communicates at 41.6 kbps, using Pulse Width Modulation. |
| SAE J1850 VPW | Favored by General Motors, it operates at speeds of 10.4/31.6 kbps with a Variable Pulse Width. |
| ISO 9141-2 | A choice for Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles, this protocol facilitates asynchronous serial communication at 10.4 kbps. |
| ISO 14230 KWP2000 | Also known as the Keyword Protocol 2000, it extends the capabilities of ISO 9141-2 by offering speeds up to 10.4 kbps. |
| ISO 15765 CAN | The backbone of modern vehicle diagnostics, this protocol is mandatory for all vehicles sold in the US from 2008 onwards. Operating at 250 kbit/s or 500 kbit/s. |
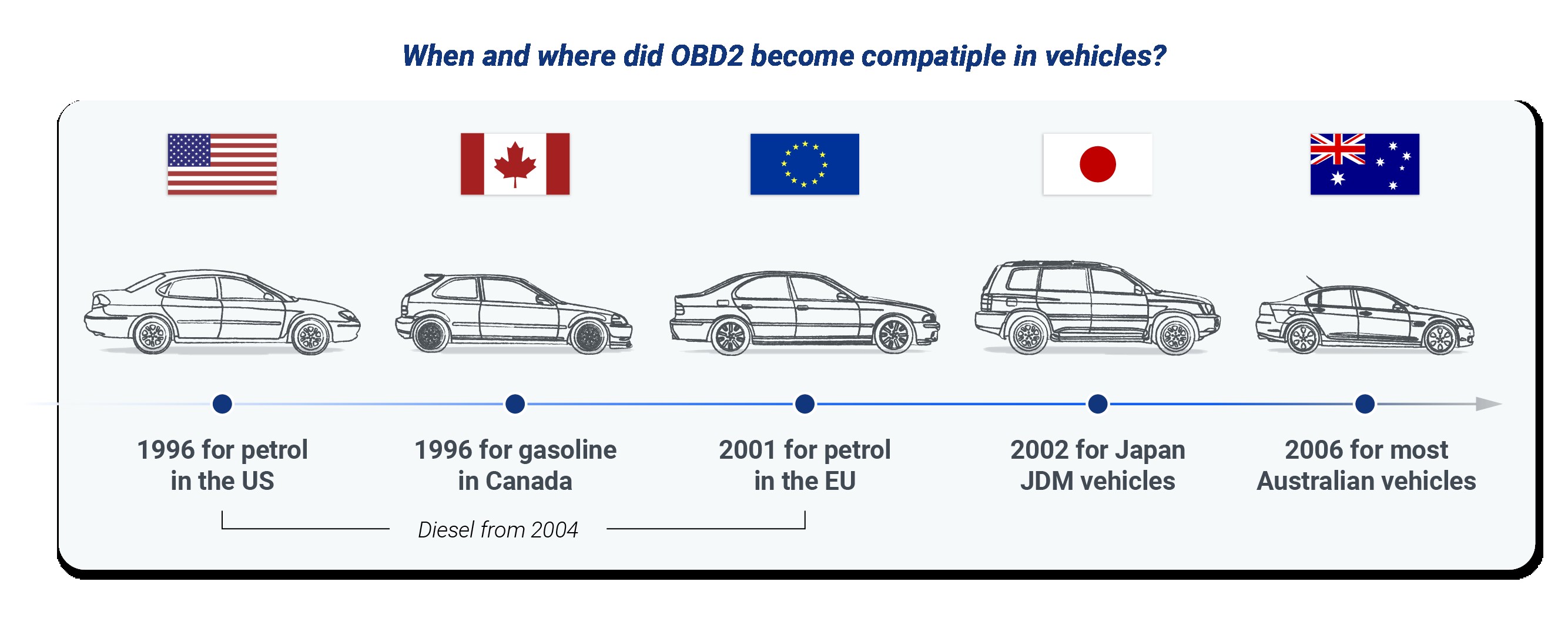 OBD-II vehicle compatibility
OBD-II vehicle compatibility
1.4 Types of OBD2 Scanners
- Code Readers: Basic scanners that only read and clear DTCs.
- Handheld Scanners: Portable devices with more advanced features like real-time data monitoring and freeze frame data.
- PC-Based Scanners: Software that connects to a laptop or PC via a cable, offering extensive diagnostic capabilities.
- Wireless Scanners: Connect to smartphones or tablets via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, providing flexibility and convenience.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a variety of OBD2 scanners to meet different needs, from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools. We provide detailed guidance and support to help you choose the right scanner for your specific requirements.
2. Why Use an OBD2 Scanner?
Using an OBD2 scanner offers several advantages, whether you’re a professional mechanic or a vehicle owner.
2.1 Early Problem Detection
OBD2 scanners allow for the early detection of potential problems, preventing minor issues from escalating into major repairs. Regular use of an OBD2 scanner can help identify issues such as a faulty oxygen sensor or a misfiring engine before they cause significant damage.
2.2 Cost Savings
By diagnosing and addressing issues early, OBD2 scanners can save you money on costly repairs. According to a 2021 report by the American Automobile Association (AAA), proactive vehicle maintenance can reduce repair costs by as much as $500 per year. Using an OBD2 scanner to identify and fix minor issues can prevent them from turning into expensive problems.
2.3 Improved Fuel Efficiency
OBD2 scanners can help improve fuel efficiency by identifying issues that may be affecting your vehicle’s fuel consumption. For example, a faulty oxygen sensor can cause your engine to run less efficiently, leading to decreased fuel economy. By identifying and replacing the faulty sensor, you can restore your vehicle’s fuel efficiency.
2.4 Emission Control Compliance
OBD2 systems are designed to monitor and control vehicle emissions. Using an OBD2 scanner can help ensure that your vehicle is compliant with emission standards, avoiding potential fines and penalties.
2.5 Enhanced Vehicle Performance
By diagnosing and addressing issues affecting your vehicle’s performance, OBD2 scanners can help improve overall vehicle performance. Whether it’s a misfiring engine or a faulty sensor, fixing these issues can result in smoother acceleration, better handling, and increased power.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive training and support to help you maximize the benefits of using OBD2 scanners. Our expert technicians can guide you through the diagnostic process, helping you identify and address issues efficiently.
3. How to Use an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
Using an OBD2 scanner is a straightforward process. Here’s a detailed guide:
3.1 Preparation
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the vehicle is turned off before connecting the scanner.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the OBD2 port.
3.2 Power On and Connect
- Turn the Ignition to the “On” Position: Without starting the engine.
- Power On the Scanner: Follow the scanner’s instructions to power it on and establish a connection with the vehicle’s ECU.
3.3 Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Select “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes”: From the scanner’s menu.
- View the Codes: The scanner will display any stored DTCs. Record these codes for further investigation.
3.4 Interpret the Codes
- Consult a DTC Lookup Resource: Use a reliable resource to look up the meaning of each code.
- Understand the Issue: Each code corresponds to a specific problem within the vehicle.
3.5 Clear the Codes (Optional)
- Select “Clear Codes”: From the scanner’s menu.
- Confirm the Action: The scanner will prompt you to confirm that you want to clear the codes.
- Start the Engine and Check: Ensure the check engine light remains off. If it comes back on, the issue persists.
3.6 Monitor Real-Time Data (Optional)
- Select “Live Data” or “Real-Time Data”: From the scanner’s menu.
- Choose Parameters: Select the parameters you want to monitor, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Analyze the Data: Observe the data to identify any abnormalities.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed repair guides and technical support to help you interpret DTCs and monitor real-time data effectively. Our resources provide step-by-step instructions and troubleshooting tips to ensure accurate diagnostics and repairs.
4. Common OBD2 Codes and Their Meanings
Understanding common OBD2 codes is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics. Here are some of the most frequent codes and their meanings:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, fuel injector issue, low fuel pressure |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leak, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, exhaust leak, faulty oxygen sensor |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected | Faulty EGR valve, clogged EGR passages, vacuum leak |
| P0113 | Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input | Faulty intake air temperature sensor, wiring issue |
| P0011 | A Camshaft Position – Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1) | Faulty camshaft position sensor, oil control valve, timing chain issue |
| P0102 | Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input | Dirty or faulty mass air flow sensor, vacuum leak, wiring issue |
| P0301-P0306 | Cylinder 1-6 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leak, low compression |
According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) in 2023, these are some of the most commonly reported OBD2 codes. Knowing these codes and their potential causes can help you diagnose and address issues quickly.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive DTC database and expert technical support to help you interpret OBD2 codes accurately. Our resources include detailed descriptions, possible causes, and troubleshooting tips for thousands of DTCs.
5. Advanced Features of OBD2 Scanners
Modern OBD2 scanners offer a range of advanced features that can significantly enhance your diagnostic capabilities.
5.1 Real-Time Data Streaming
Real-time data streaming allows you to monitor various parameters of your vehicle in real-time. This feature is invaluable for diagnosing intermittent issues and observing how different systems interact.
5.2 Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions at the moment a DTC was triggered. This data can provide valuable clues about the cause of the problem.
5.3 Oxygen Sensor Testing
Oxygen sensor testing allows you to evaluate the performance of your vehicle’s oxygen sensors. This is crucial for maintaining optimal fuel efficiency and emission control.
5.4 EVAP System Testing
EVAP system testing helps you identify leaks in your vehicle’s evaporative emissions control system. This is important for preventing fuel vapor from escaping into the atmosphere.
5.5 ABS and Airbag System Diagnostics
Some advanced OBD2 scanners can also diagnose issues with your vehicle’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) and airbag system. This can help ensure that these critical safety systems are functioning properly.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers advanced OBD2 scanners with these features and provides comprehensive training to help you use them effectively. Our expert technicians can guide you through the diagnostic process, helping you leverage these advanced features to identify and address complex issues.
6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner depends on your specific needs and budget. Here are some factors to consider:
6.1 Budget
OBD2 scanners range in price from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools. Determine how much you’re willing to spend before you start shopping.
6.2 Features
Consider the features you need. If you only need to read and clear codes, a basic code reader may suffice. If you need more advanced capabilities, such as real-time data streaming and ABS diagnostics, you’ll need a more advanced scanner.
6.3 Compatibility
Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle. Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all OBD2-compliant vehicles, but it’s always a good idea to check.
6.4 Ease of Use
Choose a scanner that is easy to use. Look for scanners with intuitive menus and clear instructions.
6.5 Brand Reputation
Consider the brand reputation of the scanner. Choose a scanner from a reputable brand known for producing high-quality diagnostic tools.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a wide selection of OBD2 scanners from leading brands. Our knowledgeable staff can help you choose the right scanner for your needs and budget.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using an OBD2 Scanner
To ensure accurate diagnostics and prevent damage to your vehicle, avoid these common mistakes when using an OBD2 scanner:
7.1 Ignoring the Manual
Always read the scanner’s manual before using it. The manual contains important information about the scanner’s features and how to use them properly.
7.2 Clearing Codes Without Diagnosing the Problem
Never clear codes without diagnosing the underlying problem. Clearing codes without fixing the issue will only turn off the check engine light temporarily.
7.3 Misinterpreting the Codes
Be sure to interpret the codes correctly. Consult a reliable DTC lookup resource to understand the meaning of each code.
7.4 Neglecting Real-Time Data
Don’t neglect real-time data. Monitoring real-time data can provide valuable clues about the cause of the problem.
7.5 Using an Incompatible Scanner
Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle. Using an incompatible scanner can damage your vehicle’s ECU.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive training and support to help you avoid these common mistakes and use your OBD2 scanner effectively. Our expert technicians can guide you through the diagnostic process, helping you interpret codes and monitor real-time data accurately.
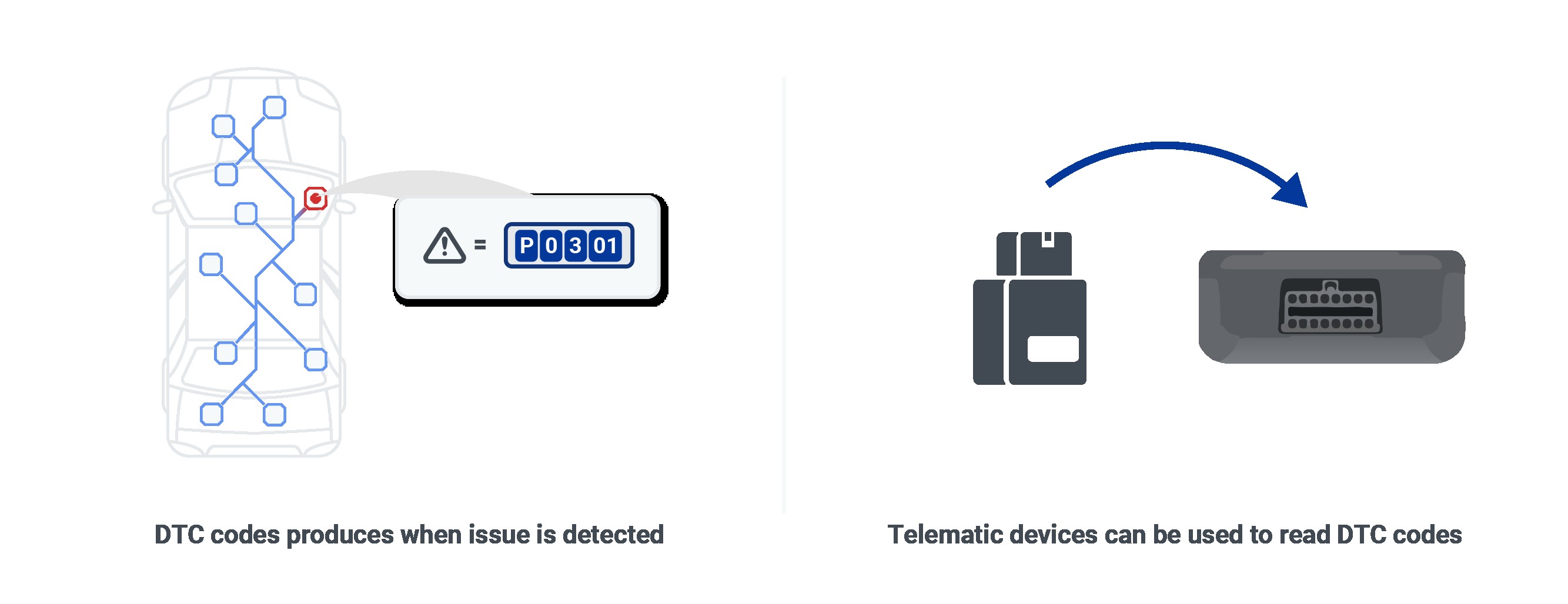 DTC codes in OBD-II systems
DTC codes in OBD-II systems
8. The Future of OBD2 Technology
OBD2 technology continues to evolve, with new features and capabilities being developed all the time. Here are some of the trends shaping the future of OBD2 technology:
8.1 Enhanced Connectivity
Future OBD2 scanners will offer enhanced connectivity, with seamless integration with smartphones, tablets, and cloud-based diagnostic platforms.
8.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI will play an increasing role in OBD2 technology, with AI-powered diagnostic tools that can automatically diagnose complex issues and provide repair recommendations.
8.3 Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
Future OBD2 scanners will receive over-the-air updates, ensuring that they always have the latest features and capabilities.
8.4 Integration with Electric Vehicles (EVs)
OBD2 technology will be increasingly integrated with electric vehicles, providing diagnostics and monitoring for EV-specific systems such as battery management and electric motors.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to staying at the forefront of OBD2 technology. We continuously update our training programs and diagnostic tools to reflect the latest advancements in the field.
9. OBD2 Scanner and CAN Bus Connection
The OBD2 diagnostic system functions as a high-level protocol, while the CAN bus serves as its communication method. The OBD2 standard defines a distinct connector, encompassing five main protocols. Since 1996, the CAN bus has been an essential OBD2 protocol for all vehicles in the U.S. By 2001, Europe mandated all cars to be OBD2 compliant, and this became a requirement in Australia and New Zealand starting 2006.
10. Maximize Your Vehicle Performance with OBD2 Scanners
Understanding and utilizing OBD2 technology is crucial for maintaining vehicle health, whether you are a developer, fleet manager, or vehicle owner. OBD2 systems provide comprehensive diagnostics, monitoring a wide range of vehicle functions and offering early detection of potential issues. By leveraging OBD2, you can enhance fuel efficiency, ensure compliance with emission standards, and maintain overall vehicle safety. With tools like OBD2 scanners and vehicle telematics devices, diagnosing and addressing vehicle performance issues becomes more efficient and effective, ultimately leading to significant cost savings and extended vehicle lifespan. Embrace OBD2 technology to keep your vehicles running smoothly and reliably.
FAQ: Your Questions About OBD2 Scanners Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about OBD2 scanners:
1. What is an OBD2 scanner?
An OBD2 scanner is a diagnostic tool used to read data from a vehicle’s On-Board Diagnostics system, helping to identify and troubleshoot potential issues.
2. How does an OBD2 scanner work?
It connects to the car’s OBD2 port, reads diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), and provides real-time data about various vehicle systems.
3. What are the benefits of using an OBD2 scanner?
Early problem detection, cost savings, improved fuel efficiency, emission control compliance, and enhanced vehicle performance.
4. Where is the OBD2 port located in my car?
Typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
5. Can I clear codes with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, most OBD2 scanners allow you to clear codes after you’ve diagnosed and fixed the underlying problem.
6. What is real-time data monitoring?
It is a feature that displays live data from various sensors in the vehicle, such as engine speed, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
7. What is freeze frame data?
It captures data from the moment a DTC was triggered, providing a snapshot of the conditions at the time of the fault.
8. Are all OBD2 scanners compatible with all cars?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all OBD2-compliant vehicles (1996 and newer in the US), but it’s always a good idea to check.
9. What are some common OBD2 codes?
P0171 (System Too Lean), P0300 (Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire), P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold).
10. Where can I get training on how to use an OBD2 scanner?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training programs and expert technical support to help you use OBD2 scanners effectively.
At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the tools and knowledge you need to maintain your vehicle in top condition. Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a vehicle owner, our comprehensive solutions can help you diagnose and address issues quickly and efficiently.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s health? Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert advice and support.
Don’t let vehicle issues slow you down. Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN now!
Address: 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
Website: CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN stands ready to equip you with the best tools and knowledge in the automotive industry. Contact us now to explore how our remote support and training programs can revolutionize your approach to vehicle diagnostics and repair. Let us help you drive your skills and your business forward.