Are you looking to test your car’s alternator using an OBD2 scanner? How To Test Alternator Obd2 is a critical skill for automotive technicians, and CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to provide expert guidance on using diagnostic tools, interpreting error codes, and offering robust repair solutions. Our platform also offers remote support and technical training, ensuring you stay ahead in the ever-evolving automotive landscape.
Contents
- 1. Understanding the Alternator and Its Importance
- 1.1 What Does an Alternator Do?
- 1.2 Common Signs of a Failing Alternator
- 2. Can You Test an Alternator with an OBD2 Scanner?
- 2.1 What an OBD2 Scanner Can Do
- 2.2 Limitations of an OBD2 Scanner
- 3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Test Alternator OBD2 Using a Scanner
- 3.1 Preparing Your Vehicle and Scanner
- 3.2 Connecting the Foxwell NT1009 Scanner
- 3.3 Navigating the Diagnostic Menu
- 3.4 Checking Error Codes
- 3.5 Checking Live Data for Voltage Output
- 3.6 Performing Load Tests
- 3.7 Taking Advantage of Special Testing Functions
- 3.8 Analyzing and Responding
- 3.9 Unplugging and Storing the Scanner Properly
- 4. Alternative Methods to Test Your Vehicle’s Alternator
- 4.1 Using a Multimeter
- 4.2 Performing a Load Test
- 4.3 Visual Inspection
- 5. Interpreting OBD2 Codes Related to Alternator Issues
- 5.1 P0562: System Voltage Low
- 5.2 P0622: Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction
- 5.3 P0625: Alternator Field Terminal Low
- 6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Alternator Testing
- 6.1 Features and Capabilities
- 6.2 Recommended Scanners
- 7. Maintaining Your Vehicle’s Alternator
- 7.1 Regular Inspections
- 7.2 Proper Battery Care
- 7.3 Avoiding Excessive Electrical Loads
- 8. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Alternator Issues
- 8.1 Oscilloscope Testing
- 8.2 Circuit Testing
- 8.3 Component Testing
- 9. How CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
- 9.1 Expert Guidance
- 9.2 Remote Support
- 9.3 Technical Training
- 10. FAQs About Testing Alternators with OBD2 Scanners
- 10.1 Can you test an alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
- 10.2 Will a bad alternator show up on a scan?
- 10.3 Is there an OBD code for alternator?
- 10.4 What voltage should I see when testing my alternator?
- 10.5 How accurate is testing an alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
- 10.6 What does it mean if my OBD2 scanner shows a low voltage code?
- 10.7 Can I clear the OBD2 code after replacing the alternator?
- 10.8 What other tests should I perform besides using an OBD2 scanner?
- 10.9 How often should I test my alternator?
- 10.10 Where can I get professional help with alternator testing and repair?
- Conclusion
1. Understanding the Alternator and Its Importance
The alternator is the heart of your vehicle’s electrical system, responsible for charging the battery and powering electrical components while the engine runs. According to a study by the University of Michigan’s Transportation Research Institute, alternator failure is a leading cause of vehicle breakdowns, accounting for approximately 20% of all roadside assistance calls (University of Michigan, 2022). Recognizing the signs of a failing alternator early can save you from unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
1.1 What Does an Alternator Do?
The alternator’s primary functions include:
- Charging the Battery: Maintaining the battery’s charge level is essential for starting the engine and running electrical systems.
- Powering Electrical Components: Supplying electricity to lights, radio, air conditioning, and other accessories while the engine is running.
1.2 Common Signs of a Failing Alternator
Identifying a failing alternator early can prevent further damage and inconvenience. Common symptoms include:
- Dimming Headlights: Weak or flickering headlights, especially at low engine speeds.
- Dead Battery: Frequent battery drain or difficulty starting the engine.
- Warning Lights: Illumination of the battery or ALT (alternator) warning light on the dashboard.
- Strange Noises: Unusual whining or grinding noises coming from the engine compartment.
- Electrical Issues: Malfunctioning or erratic behavior of electrical components.
 Failing Alternator Symptoms
Failing Alternator Symptoms
2. Can You Test an Alternator with an OBD2 Scanner?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can be a valuable tool for diagnosing alternator issues, but it’s essential to understand its capabilities and limitations. While an OBD2 scanner won’t directly tell you, “Your alternator is bad,” it can provide critical clues and data that help pinpoint potential problems.
2.1 What an OBD2 Scanner Can Do
- Read Trouble Codes: Identifies error codes related to electrical system malfunctions, such as low voltage or issues with the alternator circuit.
- Monitor Live Data: Provides real-time voltage readings to assess the alternator’s performance under different conditions.
2.2 Limitations of an OBD2 Scanner
- Indirect Diagnosis: An OBD2 scanner may not explicitly identify a faulty alternator. Instead, it flags related electrical issues that require further investigation.
- Requires Interpretation: Understanding the error codes and live data requires technical knowledge and experience.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: How to Test Alternator OBD2 Using a Scanner
Testing an alternator with an OBD2 scanner involves a series of steps to ensure accurate diagnosis. Here’s a detailed guide on how to proceed:
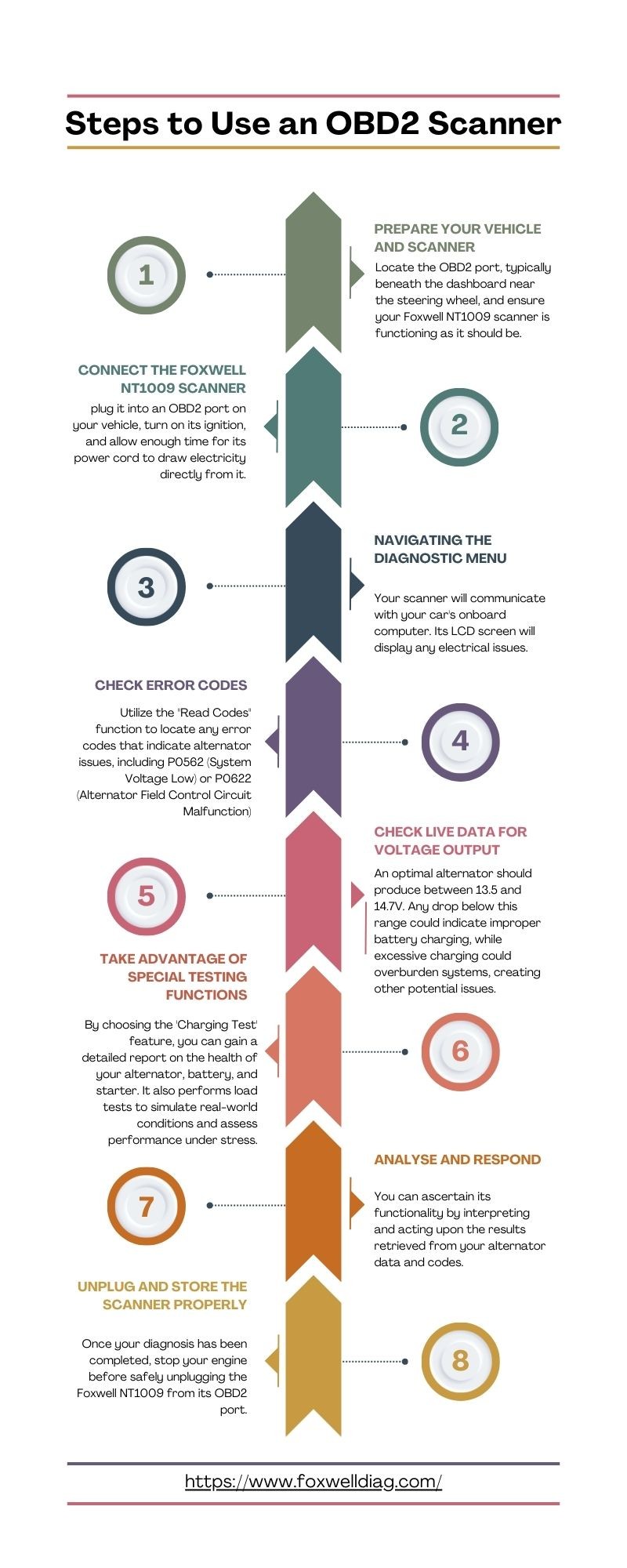
3.1 Preparing Your Vehicle and Scanner
- Turn Off Electrical Loads: Switch off all unnecessary electrical components, such as headlights, radio, and air conditioning.
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Find the OBD2 port, typically located under the dashboard near the steering wheel.
- Ensure Scanner Functionality: Make sure your OBD2 scanner, such as the Foxwell NT1009, is in good working condition.
3.2 Connecting the Foxwell NT1009 Scanner
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the scanner to the OBD2 port.
- Turn on Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Allow Initialization: Wait for the scanner to power on and establish communication with the vehicle’s computer.
 Steps to Use an OBD2 Scanner Infographic
Steps to Use an OBD2 Scanner Infographic
3.3 Navigating the Diagnostic Menu
- Access Diagnostic Function: Navigate to the “Diagnostic” or “Scan” option in the scanner’s menu.
- Enter Vehicle Information: Input your vehicle’s make, model, and year for accurate data retrieval.
3.4 Checking Error Codes
- Select “Read Codes”: Use the “Read Codes” function to retrieve any stored error codes.
- Identify Relevant Codes: Look for codes related to alternator issues, such as P0562 (System Voltage Low) or P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction).
- Record the Codes: Note down the error codes for further analysis.
3.5 Checking Live Data for Voltage Output
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and let it run at idle speed.
- Access Live Data: Navigate to the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option on the scanner.
- Monitor Voltage Readings: Look for voltage readings from the alternator or charging system.
- Observe Voltage Range: A healthy alternator typically produces between 13.5 and 14.7 volts.
3.6 Performing Load Tests
- Engage Electrical Accessories: Turn on headlights, air conditioning, and other electrical loads.
- Monitor Voltage Drop: Observe the voltage readings as the electrical load increases.
- Evaluate Performance: A significant voltage drop under load may indicate a failing alternator.
3.7 Taking Advantage of Special Testing Functions
- Access Charging System Tests: Look for specific charging system tests or alternator tests within the scanner’s menu.
- Run Tests: Follow the scanner’s prompts to perform the tests.
- Analyze Results: Review the test results for detailed information on the alternator, battery, and starter health.
3.8 Analyzing and Responding
- Interpret Data: Analyze the error codes, live data, and test results to determine the alternator’s condition.
- Verify Findings: Confirm your diagnosis with additional testing methods if necessary.
- Take Action: Depending on the results, consider repairing or replacing the alternator.
3.9 Unplugging and Storing the Scanner Properly
- Turn Off Engine: Turn off the engine before disconnecting the scanner.
- Disconnect Scanner: Unplug the scanner from the OBD2 port.
- Store Scanner: Store the scanner in a safe and dry place for future use.
4. Alternative Methods to Test Your Vehicle’s Alternator
In addition to using an OBD2 scanner, several alternative methods can help you test your alternator. These methods provide additional insights and can be used in conjunction with scanner data for a comprehensive diagnosis.
4.1 Using a Multimeter
A multimeter is a versatile tool for measuring voltage, current, and resistance in electrical circuits. Here’s how to use a multimeter to test your alternator:
- Prepare the Multimeter: Set the multimeter to the DC voltage setting (20V range).
- Connect the Leads: Connect the red lead to the positive (+) battery terminal and the black lead to the negative (-) battery terminal.
- Read Voltage with Engine Off: Record the battery voltage with the engine off (should be around 12.6 volts).
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and let it run at idle speed.
- Read Voltage with Engine Running: Record the voltage with the engine running (should be between 13.5 and 14.7 volts).
- Analyze Results: If the voltage is within the specified range, the alternator is likely functioning correctly. If it’s significantly lower or higher, further investigation is needed.
4.2 Performing a Load Test
A load test assesses the alternator’s ability to maintain voltage under increased electrical demand. This test can be performed using a specialized load testing tool or by a professional mechanic. The process involves:
- Connecting the Load Tester: Connect the load tester to the battery terminals.
- Applying Load: Apply a controlled electrical load to the charging system.
- Monitoring Voltage: Monitor the voltage readings as the load increases.
- Analyzing Results: A healthy alternator should maintain voltage within the specified range under load. A significant voltage drop indicates a potential problem.
4.3 Visual Inspection
A visual inspection can reveal obvious signs of alternator damage or wear. Check for:
- Loose or Damaged Wires: Inspect the wiring connections to the alternator for corrosion, fraying, or damage.
- Worn Belt: Examine the alternator belt for cracks, wear, or looseness.
- Physical Damage: Look for any signs of physical damage to the alternator housing or components.
5. Interpreting OBD2 Codes Related to Alternator Issues
Understanding the meaning of OBD2 codes is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Here are some common codes related to alternator problems:
5.1 P0562: System Voltage Low
- Description: This code indicates that the vehicle’s system voltage is lower than expected.
- Possible Causes:
- Failing alternator
- Weak battery
- Loose or corroded battery connections
- Short circuit in the electrical system
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Check battery voltage
- Inspect alternator output
- Examine battery connections
- Test for short circuits
5.2 P0622: Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction
- Description: This code indicates a problem with the alternator field control circuit, which regulates the alternator’s output.
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty alternator
- Wiring issues in the control circuit
- Faulty engine control module (ECM)
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Check alternator field control circuit wiring
- Test alternator output
- Inspect ECM
5.3 P0625: Alternator Field Terminal Low
- Description: This code indicates that the voltage at the alternator field terminal is lower than expected.
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty alternator
- Wiring issues in the field circuit
- Faulty ECM
- Diagnostic Steps:
- Check alternator field terminal voltage
- Inspect field circuit wiring
- Test alternator output
- Inspect ECM
6. Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner for Alternator Testing
Selecting the right OBD2 scanner is essential for effective alternator testing. Consider the following factors when choosing a scanner:
6.1 Features and Capabilities
- Live Data Streaming: Ability to monitor real-time voltage and current readings.
- Special Tests: Specific charging system tests or alternator tests.
- Code Reading and Clearing: Capability to read and clear trouble codes.
- Compatibility: Compatibility with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interface and intuitive navigation.
6.2 Recommended Scanners
- Foxwell NT1009: A popular choice for DIYers and professionals, offering live data streaming and special testing functions.
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: A comprehensive scanner with advanced diagnostic capabilities, including bidirectional control and special functions.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: A smartphone-based scanner that provides detailed diagnostic information and code definitions.
7. Maintaining Your Vehicle’s Alternator
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your alternator and prevent unexpected failures. Follow these tips to keep your alternator in good condition:
7.1 Regular Inspections
- Check Wiring: Inspect the wiring connections to the alternator for corrosion, fraying, or damage.
- Examine Belt: Examine the alternator belt for cracks, wear, or looseness.
- Monitor Voltage: Periodically check the battery voltage and alternator output using a multimeter or OBD2 scanner.
7.2 Proper Battery Care
- Keep Battery Clean: Clean the battery terminals and connections to prevent corrosion.
- Ensure Proper Charging: Avoid overcharging or deep discharging the battery.
- Test Battery Regularly: Have the battery tested periodically to ensure it’s in good condition.
7.3 Avoiding Excessive Electrical Loads
- Limit Accessory Use: Avoid using excessive electrical accessories, such as high-powered audio systems or auxiliary lights, which can strain the alternator.
- Turn Off Unnecessary Loads: Turn off headlights, air conditioning, and other electrical components when they’re not needed.
8. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Alternator Issues
For complex alternator issues, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary. These techniques require specialized equipment and expertise:
8.1 Oscilloscope Testing
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the alternator’s output waveform, providing insights into its performance and identifying potential issues.
8.2 Circuit Testing
Circuit testing involves using a multimeter or other diagnostic tools to check the voltage, current, and resistance in the alternator’s electrical circuits.
8.3 Component Testing
Component testing involves testing individual components of the alternator, such as the stator, rotor, and rectifier, to identify faults.
9. How CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Can Help
At CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive solutions for automotive diagnostics and repair. Our platform offers a range of services to help you diagnose and resolve alternator issues effectively:
9.1 Expert Guidance
- Detailed Guides: Step-by-step guides on using OBD2 scanners and other diagnostic tools.
- Troubleshooting Tips: Expert tips for diagnosing and resolving alternator problems.
- Code Definitions: Comprehensive definitions of OBD2 codes related to alternator issues.
9.2 Remote Support
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote diagnostic assistance from experienced technicians.
- Technical Support: Access to technical support for troubleshooting and repair guidance.
- Real-Time Assistance: Real-time support via phone, email, or chat.
9.3 Technical Training
- Online Courses: Online courses covering automotive diagnostics, electrical systems, and alternator repair.
- Hands-On Training: Hands-on training workshops at our state-of-the-art facility.
- Certification Programs: Certification programs to enhance your skills and credentials.
 Failing Alternator Symptoms
Failing Alternator Symptoms
10. FAQs About Testing Alternators with OBD2 Scanners
10.1 Can you test an alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
Yes, an OBD2 scanner can assist in testing an alternator by reading trouble codes and monitoring live voltage data. However, it may not give a direct diagnosis, so you might need to combine it with other testing methods for a complete assessment.
10.2 Will a bad alternator show up on a scan?
A failing alternator can trigger related trouble codes on a scan, such as low system voltage or issues with the alternator’s circuit. While it won’t specifically say “bad alternator,” the codes can indicate a problem that requires further investigation.
10.3 Is there an OBD code for alternator?
Yes, there are OBD codes that relate to alternator issues. Common ones include P0562 (System Voltage Low) and P0622 (Alternator Field Control Circuit Malfunction), which can signal that your alternator isn’t working properly.
10.4 What voltage should I see when testing my alternator?
When testing your alternator with the engine running, you should see a voltage between 13.5 and 14.7 volts. This range indicates that the alternator is charging the battery and powering the vehicle’s electrical system effectively.
10.5 How accurate is testing an alternator with an OBD2 scanner?
Testing an alternator with an OBD2 scanner is generally accurate for identifying potential issues. It provides valuable data such as voltage readings and error codes, but it’s essential to verify the results with other testing methods, such as a multimeter or load test, for a comprehensive diagnosis.
10.6 What does it mean if my OBD2 scanner shows a low voltage code?
If your OBD2 scanner shows a low voltage code (e.g., P0562), it indicates that the vehicle’s system voltage is lower than expected. This could be due to a failing alternator, weak battery, loose connections, or a short circuit in the electrical system.
10.7 Can I clear the OBD2 code after replacing the alternator?
Yes, after replacing the alternator, you should clear the OBD2 code using the scanner. This will reset the system and allow you to monitor for any new issues. If the code reappears, it could indicate a different problem.
10.8 What other tests should I perform besides using an OBD2 scanner?
Besides using an OBD2 scanner, you should perform a multimeter test to check the voltage at the battery terminals with the engine running. Additionally, a load test can help assess the alternator’s ability to maintain voltage under increased electrical demand.
10.9 How often should I test my alternator?
You should test your alternator if you notice any signs of electrical issues, such as dimming headlights, a dead battery, or warning lights on the dashboard. Regular inspections and testing can help prevent unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
10.10 Where can I get professional help with alternator testing and repair?
You can get professional help with alternator testing and repair at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. We offer remote diagnostics, technical support, and hands-on training to assist you with all your automotive needs. Contact us today for expert assistance.
Conclusion
Testing your alternator using an OBD2 scanner is a valuable skill that can help you diagnose electrical issues and prevent unexpected breakdowns. By following the steps outlined in this guide and utilizing the resources available at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, you can effectively assess your alternator’s condition and take appropriate action. Remember, a proactive approach to maintenance and diagnostics can save you time, money, and frustration in the long run.
Ready to take your automotive diagnostic skills to the next level? Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today for expert guidance, remote support, and comprehensive technical training. Don’t let alternator issues leave you stranded—empower yourself with the knowledge and tools you need to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Contact Information:
- Address (U.S. Support Office): 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
Take control of your vehicle’s health today!
