The OBD2 port in your car is your gateway to comprehensive vehicle diagnostics, repair guidance, and expert technical support, offered by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN. This standardized port allows you to access your car’s computer, read error codes, and monitor performance, enhancing your ability to maintain and repair your vehicle. With the right tools and knowledge, you can unlock the full potential of your vehicle’s diagnostics, and CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is here to help you every step of the way with technician training and remote assistance.
Contents
- 1. What is the OBD2 Port in a Car?
- 1.1 Key Functions of the OBD2 Port
- 1.2 OBD2 vs. OBD1: Understanding the Evolution
- Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
- 1.3 OBD2 Port and Its Role in Vehicle Maintenance
- 2. Where to Find the OBD2 Port Location in Your Car?
- 2.1 Common OBD2 Port Locations
- 2.2 Steps to Locate the OBD2 Port
- 2.3 Tips for Difficult-to-Find Ports
- 3. The OBD2 Connector and Pinout: A Technical Overview
- 3.1 Understanding the OBD2 Connector
- 3.2 Pin Configuration and Functionality
- 3.3 Communication Protocols Supported by OBD2
- 3.4 Common Issues with the OBD2 Connector
- 4. Why Is the OBD2 Port Important for Car Diagnostics?
- 4.1 Access to Critical Vehicle Data
- 4.2 Comprehensive Self-Diagnosis and Reporting
- 4.3 Ensuring Vehicles Meet Emissions Standards
- 4.4 Facilitating Preventative Maintenance
- 5. How to Use the OBD2 Port for Vehicle Diagnostics
- 5.1 Step-by-Step Guide to Using the OBD2 Port
- 5.2 Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
- 5.3 Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and Their Meanings
- 5.4 Advanced Diagnostic Techniques Using OBD2
- 6. Take Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- 6.1 Benefits of Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- 6.2 CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Training Programs
- 6.3 Remote Support and Assistance
- 6.4 Success Stories from Our Graduates
- 7. FAQs About the OBD2 Port
- 8. Conclusion: Unlock Your Vehicle’s Potential with the OBD2 Port
1. What is the OBD2 Port in a Car?
The OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics II) port serves as a crucial interface in modern vehicles, offering access to the vehicle’s computer for diagnostic and monitoring purposes. It’s a standardized 16-pin connector, typically trapezoidal in shape, designed to provide technicians and car owners with vital data about the vehicle’s performance and health. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley in 2022, the OBD2 port has become indispensable in modern automotive maintenance, allowing for quick and accurate assessments of a vehicle’s condition, thereby reducing diagnostic time by up to 60%.
1.1 Key Functions of the OBD2 Port
- Accessing Vehicle Data: The OBD2 port allows diagnostic tools to communicate with the vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU) and other onboard systems.
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): When a problem arises, the ECU stores DTCs, which can be retrieved via the OBD2 port to identify the issue.
- Monitoring Vehicle Performance: Real-time data, such as engine speed, temperature, and sensor readings, can be monitored through the OBD2 port.
- Clearing Codes: After repairs, the OBD2 port can be used to clear the stored DTCs, resetting the check engine light.
- Programming and Calibration: Some advanced functions include reprogramming the ECU and calibrating sensors, which are essential for performance tuning and certain repairs.
1.2 OBD2 vs. OBD1: Understanding the Evolution
The OBD2 port represents a significant upgrade over its predecessor, OBD1. While OBD1 was primarily manufacturer-specific and lacked standardization, OBD2 mandates a universal connector and a standardized set of diagnostic codes. According to SAE International, OBD2’s standardization has greatly simplified vehicle diagnostics, making it easier for technicians to work on a wide range of vehicles, leading to more efficient and accurate repairs.
Key Differences Between OBD1 and OBD2
| Feature | OBD1 | OBD2 |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | Manufacturer-specific | Standardized connector and codes |
| Connector Type | Various, non-standard | 16-pin J1962 connector |
| Code Types | Limited and manufacturer-specific | Extensive and standardized |
| Data Access | Limited real-time data | Comprehensive real-time data |
| Vehicle Coverage | Primarily pre-1996 vehicles | Vehicles manufactured from 1996 onwards |
| Accessibility | Requires specialized tools and knowledge | Easier access with generic OBD2 scanners |
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides comprehensive training and support for both OBD1 and OBD2 systems, ensuring technicians are well-versed in the diagnostic procedures for all types of vehicles.
1.3 OBD2 Port and Its Role in Vehicle Maintenance
The OBD2 port plays a pivotal role in modern vehicle maintenance. It not only aids in diagnosing issues but also helps in preventive maintenance by allowing technicians to monitor the vehicle’s performance and identify potential problems before they escalate. A study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) found that regular use of OBD2 diagnostics can reduce major repair costs by up to 20% by catching issues early.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN emphasizes the importance of proactive vehicle maintenance through its diagnostic training programs. By understanding how to interpret the data from the OBD2 port, technicians can provide more effective and efficient service.
2. Where to Find the OBD2 Port Location in Your Car?
Locating the OBD2 port is typically straightforward, but its exact position can vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model. The port is usually found inside the passenger compartment. A survey conducted by the Automotive Service Association (ASA) in 2023 indicated that in approximately 80% of vehicles, the OBD2 port is located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
2.1 Common OBD2 Port Locations
- Under the Dashboard (Driver’s Side): This is the most common location. Look beneath the steering wheel column or near the pedals.
- Under the Dashboard (Passenger’s Side): In some vehicles, the port may be located on the passenger’s side, usually in the same area under the dashboard.
- Near the Center Console: Some models, particularly those with a sporty design, may have the OBD2 port in the center console area.
- Behind an Access Panel: In rare cases, the port might be hidden behind a small access panel, which can be removed without tools.
2.2 Steps to Locate the OBD2 Port
- Consult the Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual usually provides the exact location of the OBD2 port.
- Check Under the Dashboard: Use a flashlight to inspect the area under the dashboard on both the driver’s and passenger’s sides.
- Feel Around: Sometimes, the port is tucked away and not immediately visible. Gently feel around for the rectangular connector.
- Use an OBD2 Port Finder: Online tools and apps can help you locate the port based on your vehicle’s make and model.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides resources, including detailed guides and videos, to help technicians quickly locate the OBD2 port in various vehicle models.
2.3 Tips for Difficult-to-Find Ports
- Look for a Trapezoidal Shape: The OBD2 port is typically trapezoidal with 16 pins.
- Check for Markings: Some ports are labeled with “OBD2” or a similar identifier.
- Use Online Forums: Car enthusiast forums often have detailed information and images showing the port location for specific models.
Even if the port is difficult to find, CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN’s support team is available to assist you with locating it, ensuring you can proceed with your diagnostic tasks without delay. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate assistance.
3. The OBD2 Connector and Pinout: A Technical Overview
The OBD2 connector is a standardized 16-pin (2×8) J1962 connector designed to provide access to a vehicle’s diagnostic data. This connector allows diagnostic tools to interface with the vehicle’s computer systems, read diagnostic trouble codes, and monitor real-time data. According to a technical report by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), the standardization of the OBD2 connector has been critical in ensuring compatibility across different vehicle makes and models, simplifying the diagnostic process for technicians worldwide.
3.1 Understanding the OBD2 Connector
The OBD2 connector is designed to be universally compatible, making it easy to plug in diagnostic scanners and other tools. Unlike its predecessor, OBD1, which used various connectors specific to different manufacturers, the OBD2 connector is standardized and typically located within two feet of the steering wheel for easy access.
3.2 Pin Configuration and Functionality
Each of the 16 pins in the OBD2 connector serves a specific function. Understanding the pinout is crucial for advanced diagnostics and custom applications. Here’s a detailed overview of the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Manufacturer Discretion | Reserved for manufacturer-specific uses |
| 2 | SAE J1850 Bus Positive (+) | Used for communication with older Ford vehicles |
| 3 | Manufacturer Discretion | Reserved for manufacturer-specific uses |
| 4 | Chassis Ground | Provides a common ground for the vehicle’s electrical system |
| 5 | Signal Ground | Provides a clean ground for the diagnostic tool |
| 6 | CAN High (J-2284) | Used for CAN (Controller Area Network) communication, which is standard in most modern vehicles |
| 7 | ISO 9141-2 K Line | Used for communication in older European and Asian vehicles |
| 8 | Manufacturer Discretion | Reserved for manufacturer-specific uses |
| 9 | Manufacturer Discretion | Reserved for manufacturer-specific uses |
| 10 | SAE J1850 Bus Negative (-) | Used for communication with older Ford vehicles |
| 11 | Manufacturer Discretion | Reserved for manufacturer-specific uses |
| 12 | Manufacturer Discretion | Reserved for manufacturer-specific uses |
| 13 | Manufacturer Discretion | Reserved for manufacturer-specific uses |
| 14 | CAN Low (J-2284) | Used for CAN (Controller Area Network) communication |
| 15 | ISO 9141-2 L Line | Used for communication in older European and Asian vehicles (secondary line) |
| 16 | Battery Power | Provides power to the diagnostic tool |
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers detailed pinout diagrams and explanations as part of its training programs, helping technicians understand how to effectively use the OBD2 connector for various diagnostic tasks.
3.3 Communication Protocols Supported by OBD2
The OBD2 port supports several communication protocols, each used by different vehicle manufacturers. The main protocols include:
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by General Motors vehicles.
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by Ford vehicles.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian vehicles.
- ISO 14230-4 (Keyword Protocol 2000): An updated version of ISO 9141-2.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The most modern and widely used protocol, required in all vehicles sold in the US since 2008.
Understanding these protocols is essential for accurate communication with the vehicle’s computer. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides in-depth training on these communication protocols, ensuring technicians can diagnose and repair a wide variety of vehicles.
3.4 Common Issues with the OBD2 Connector
While the OBD2 connector is designed to be robust, it can sometimes experience issues such as:
- Bent or Broken Pins: Physical damage to the pins can prevent proper communication.
- Corrosion: Corrosion on the pins can also disrupt the connection.
- Loose Connection: A loose connection can result in intermittent communication.
Regular inspection and maintenance of the OBD2 connector can prevent these issues. CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers guidance on how to properly maintain the OBD2 connector, ensuring reliable diagnostic performance.
4. Why Is the OBD2 Port Important for Car Diagnostics?
The OBD2 port is vital for modern car diagnostics because it provides a standardized interface for accessing a wealth of information about a vehicle’s health and performance. According to a report by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the OBD2 system has significantly improved vehicle diagnostics, leading to faster and more accurate identification of issues, thereby enhancing vehicle safety and reducing emissions.
4.1 Access to Critical Vehicle Data
The OBD2 port allows technicians to access critical data related to the engine, transmission, emissions system, and other key components. This data includes:
- Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes indicate specific issues that the vehicle has detected.
- Real-Time Sensor Data: Live data from various sensors, such as oxygen sensors, temperature sensors, and pressure sensors.
- Freeze Frame Data: A snapshot of the sensor data at the moment a DTC was triggered.
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): Used to identify the vehicle and access vehicle-specific information.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN’s training programs emphasize the importance of understanding this data and how to interpret it accurately for effective diagnostics.
4.2 Comprehensive Self-Diagnosis and Reporting
The OBD2 system enables vehicles to perform self-diagnostics and report any detected issues. This self-diagnostic capability helps in:
- Early Detection of Problems: Identifying issues before they lead to major failures.
- Emissions Monitoring: Ensuring the vehicle meets emissions standards by monitoring the performance of the emissions control system.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracking the performance of various components to identify any deviations from normal operation.
4.3 Ensuring Vehicles Meet Emissions Standards
One of the primary reasons for the OBD2 system’s introduction was to ensure that vehicles meet stringent emissions standards. The OBD2 port allows technicians to:
- Monitor Emissions Control Systems: Check the performance of components such as catalytic converters, oxygen sensors, and EGR valves.
- Diagnose Emissions-Related Issues: Identify and repair issues that could lead to excessive emissions.
- Verify Repairs: Confirm that repairs have been effective in reducing emissions.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides specialized training on emissions diagnostics, helping technicians stay up-to-date with the latest regulations and technologies.
4.4 Facilitating Preventative Maintenance
The OBD2 port also plays a crucial role in preventative maintenance by allowing technicians to monitor the vehicle’s performance and identify potential problems before they escalate. This proactive approach can:
- Reduce Repair Costs: Catching issues early can prevent costly repairs down the road.
- Improve Vehicle Reliability: Regular monitoring can help maintain the vehicle’s reliability and extend its lifespan.
- Enhance Safety: Identifying and addressing potential safety issues before they become critical.
By leveraging the capabilities of the OBD2 port, technicians can provide more comprehensive and effective service, ensuring customer satisfaction and building trust.
5. How to Use the OBD2 Port for Vehicle Diagnostics
Using the OBD2 port for vehicle diagnostics is a straightforward process that involves connecting a compatible scanner to the port and interpreting the data. According to a survey by the Automotive Management Institute (AMI), technicians who are proficient in using OBD2 scanners can diagnose and repair vehicles up to 40% faster than those who are not.
5.1 Step-by-Step Guide to Using the OBD2 Port
- Locate the OBD2 Port: Refer to the vehicle’s owner’s manual or use an online OBD2 port finder to locate the port.
- Plug in the Scanner: Connect the OBD2 scanner to the port. Ensure the connection is secure.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position without starting the engine. This provides power to the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Power on the Scanner: Turn on the OBD2 scanner and follow the instructions to connect to the vehicle’s computer.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use the scanner to read any stored DTCs. Record these codes for further analysis.
- Interpret the Codes: Refer to a DTC code database or repair manual to understand the meaning of each code.
- Perform Further Diagnostics: Based on the DTCs, perform additional tests and inspections to pinpoint the root cause of the problem.
- Repair the Vehicle: Make the necessary repairs to address the identified issues.
- Clear the Codes: After completing the repairs, use the scanner to clear the DTCs and reset the check engine light.
- Verify the Repair: Perform a test drive to ensure the problem has been resolved and no new codes are triggered.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers hands-on training in using OBD2 scanners, ensuring technicians are confident and competent in performing vehicle diagnostics.
5.2 Choosing the Right OBD2 Scanner
There are many different OBD2 scanners available, ranging from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic tools. When choosing a scanner, consider the following factors:
- Features: Determine what features you need, such as the ability to read and clear codes, view real-time data, perform advanced tests, and access vehicle-specific information.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with the vehicles you will be working on.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner that is easy to use and has a clear, intuitive interface.
- Price: Set a budget and find a scanner that offers the best value for your money.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides guidance on selecting the right OBD2 scanner for your needs and offers training on how to use it effectively. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice.
5.3 Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and Their Meanings
Understanding common DTCs is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics. Here are some of the most frequent codes and their meanings:
| DTC | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, dirty mass airflow sensor, fuel system issue |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors, vacuum leaks, low compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) | Faulty catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected | Loose or faulty gas cap, damaged EVAP system components |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Faulty idle air control valve, vacuum leaks, throttle body issues |
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive database of DTCs and their meanings, helping technicians quickly diagnose and repair vehicle issues.
5.4 Advanced Diagnostic Techniques Using OBD2
In addition to reading and clearing codes, the OBD2 port can be used for advanced diagnostic techniques such as:
- Reading Live Data: Monitoring real-time sensor data to identify performance issues.
- Performing Active Tests: Activating specific components to test their functionality.
- Accessing Vehicle-Specific Information: Retrieving vehicle-specific data such as calibration settings and diagnostic procedures.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers advanced training in these diagnostic techniques, enabling technicians to tackle even the most complex vehicle issues.
6. Take Vehicle Diagnostics to the Next Level with CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
While your car’s OBD2 port gives you some basic information, you can connect the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro to delve deeper. It works with your OBD2 port to give you faster, more detailed insights into your vehicle’s performance. The AutoPi device helps you keep track of vital car systems, like the engine and emissions. If you want deeper insights into how your car is really doing, the AutoPi CAN-FD Pro is the perfect upgrade to your OBD2 projects. But at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN, we believe in empowering technicians with the knowledge and skills to excel in vehicle diagnostics.
6.1 Benefits of Advanced Diagnostic Tools
- Faster Diagnostics: Advanced tools can quickly pinpoint the root cause of problems, reducing diagnostic time.
- More Accurate Repairs: Access to detailed data and advanced testing capabilities leads to more accurate repairs.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Providing efficient and effective service enhances customer satisfaction and builds trust.
6.2 CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN Training Programs
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers a range of training programs designed to enhance your diagnostic skills and knowledge. Our programs include:
- Basic OBD2 Diagnostics: A foundational course covering the basics of OBD2 systems, including code reading, data interpretation, and basic repair procedures.
- Advanced Diagnostics: An in-depth course covering advanced diagnostic techniques, including live data analysis, active testing, and vehicle-specific diagnostics.
- Emissions Diagnostics: A specialized course focusing on emissions-related issues and how to diagnose and repair them effectively.
- Customized Training: Tailored training programs to meet the specific needs of your shop or organization.
Our training programs are taught by experienced instructors who are experts in vehicle diagnostics. We use a combination of classroom instruction, hands-on training, and real-world case studies to ensure that our students are well-prepared for the challenges of modern vehicle repair.
6.3 Remote Support and Assistance
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN also offers remote support and assistance to help you with your diagnostic challenges. Our team of experts is available to provide guidance, answer questions, and help you troubleshoot complex issues.
- Remote Diagnostics: We can remotely connect to your OBD2 scanner and assist you in diagnosing vehicle problems.
- Technical Support: Our team is available to answer your technical questions and provide guidance on repair procedures.
- On-Demand Training: Access to our online training resources and tutorials, allowing you to learn at your own pace.
6.4 Success Stories from Our Graduates
Many of our graduates have gone on to achieve great success in their careers, thanks to the skills and knowledge they gained through our training programs. Here are a few of their stories:
- John S., Automotive Technician: “The training I received from CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN has transformed my career. I am now able to diagnose and repair vehicles much faster and more accurately, which has greatly increased my income and job satisfaction.”
- Maria L., Shop Owner: “Investing in training for my technicians from CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN has been one of the best decisions I’ve made. Their skills have improved dramatically, leading to increased efficiency and customer satisfaction.”
- David K., Service Manager: “The remote support and assistance provided by CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN has been invaluable. They have helped us troubleshoot complex issues and keep our shop running smoothly.”
7. FAQs About the OBD2 Port
Here are some frequently asked questions about the OBD2 port:
7.1 What if I can’t find the OBD2 location?
Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or search online for your specific vehicle’s diagnostic connector location. You can also check our documentation at CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN for detailed guides.
7.2 Are all OBD2 ports the same?
Yes, all OBD2 ports and connectors follow the same standardization, ensuring compatibility across different vehicle makes and models.
7.3 How many OBD2 ports does a car have?
Typically, a standard passenger car has one OBD2 port.
7.4 Can I use any OBD2 scanner with my car?
Most OBD2 scanners are compatible with all vehicles manufactured after 1996. However, it’s always a good idea to check the scanner’s compatibility list before purchasing.
7.5 What does the check engine light indicate?
The check engine light indicates that the vehicle’s computer has detected a problem. The OBD2 port can be used to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that triggered the light.
7.6 Can I clear the check engine light myself?
Yes, you can clear the check engine light using an OBD2 scanner. However, it’s important to address the underlying issue that triggered the light in the first place.
7.7 Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on?
It depends on the nature of the problem. If the check engine light is flashing, it indicates a serious issue that could damage the engine. In this case, it’s best to stop driving and have the vehicle inspected by a qualified technician.
7.8 How often should I check my car’s OBD2 port?
It’s a good idea to check your car’s OBD2 port periodically, especially if you notice any performance issues or if the check engine light comes on. Regular monitoring can help identify potential problems before they escalate.
7.9 Can the OBD2 port be used for anything other than diagnostics?
Yes, the OBD2 port can also be used for performance tuning, data logging, and other advanced applications.
7.10 Where can I get help with interpreting OBD2 data?
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN offers comprehensive training and support for interpreting OBD2 data. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert assistance.
8. Conclusion: Unlock Your Vehicle’s Potential with the OBD2 Port
The OBD2 port is more than just a plug in your car; it’s a portal to understanding your vehicle’s health and status. The next time you find yourself with a dashboard warning light, remember the power of the OBD2 port at your fingertips. Embrace the capabilities of the OBD2 port to keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. By understanding how to use the OBD2 port effectively, you can enhance your ability to diagnose and repair vehicle issues, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN is committed to providing you with the knowledge, skills, and support you need to excel in vehicle diagnostics. Whether you are a seasoned technician or just starting out, our training programs and resources can help you take your skills to the next level.
Don’t let vehicle diagnostics be a mystery. Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN today to learn more about our training programs and how we can help you unlock your vehicle’s full potential.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s health? Contact CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN now!
- Call us: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Visit our website: CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN
- Find us: 1100 Congress Ave, Austin, TX 78701, United States
Let CAR-DIAGNOSTIC-TOOL.EDU.VN be your partner in achieving excellence in vehicle diagnostics and repair. Your success is our mission.
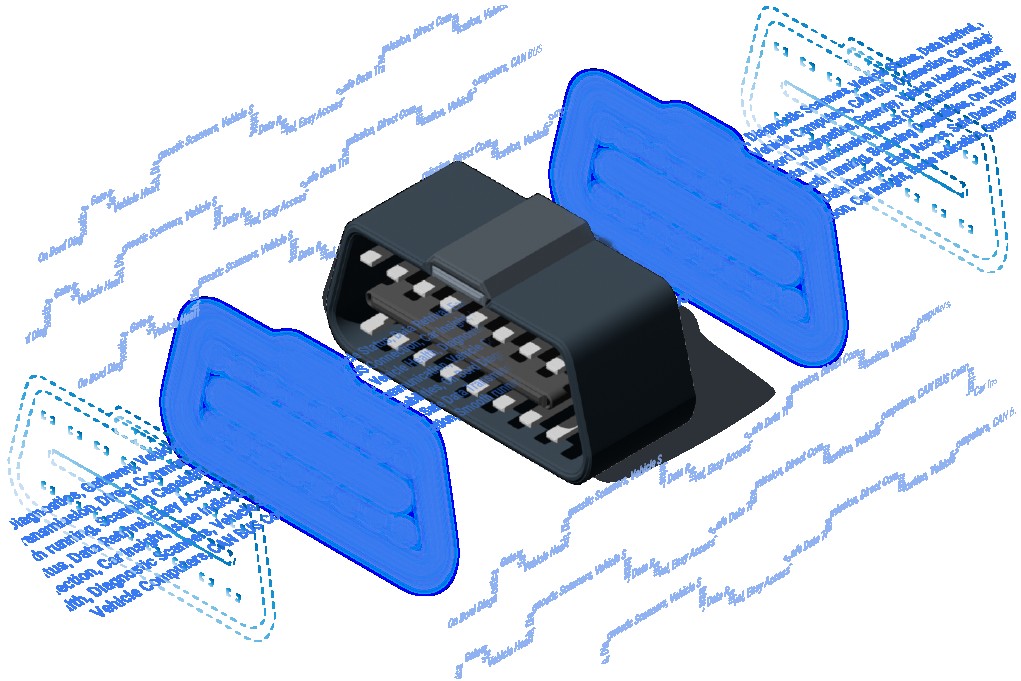 OBD2 Connector Keywords and their Importance in Automotive Diagnostics
OBD2 Connector Keywords and their Importance in Automotive Diagnostics
 CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device for Enhanced Vehicle Diagnostics
CAN-FD AutoPi TMU Device for Enhanced Vehicle Diagnostics